Transmission mode, also known as a communication mode, is the transfer of data between two devices via a communication channel that includes an optical fiber, wireless channels, copper wires, and other storage media . Data is transmitted between two devices in the form of electromagnetic waves. There are numerous data transmission methods in which the message is delivered in the form of a sequence of pulses utilizing digital modulation.
The data transmission method was initially used in modems in a computer networking system in the 1940s1940s, then in LANs, WANs, repeaters, and other networking systems. Based on the direction of the exchange of information.
The transmission mode is classified into three types: simplex, half duplex, and full duplex.
What are Transmission Modes in Computer Networks?
The Data Transmission mode specifies the direction of information flow between two communication devices via a communication channel that includes an optical fiber, wireless channels, copper wires, and other storage media . It is also known as Data Communication Mode. The transmission mode is sometimes referred to as a directional mode because each communication channel is coupled with a direction provided by the transmission media.
The Physical Layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Layer Model is dedicated to data transmission in the network. It primarily determines the direction in which the data must travel to reach the receiving system or node. Data is transmitted between the devices via the communication channel that includes an optical fiber, copper wires, wireless channels , and other storage media .
Types of Transmission Mode
The term transmission mode refers to the transmission of information between two communication devices via an interaction channel that indicates the direction of information flow between the devices. There are three primary types of transmission modes based on the direction of the exchange of information. The first is simplex, followed by half duplex, and finally full duplex.

Simplex mode
The Simplex transmission mode is used in computing networks when there is a single or one-way flow of information from sender to receiver. In this mode of transmission, communication occurs only in one direction, i.e., the circuit is configured so that it is either transmit only or receive only. Simplex mode is just like a one-way road in which the traffic travels only in one direction, which means no vehicle from the opposite direction is allowed to drive through.
Simplex transmission mode is not very popular as mainly communications require two-way data exchange . The simplex mode is used in business as in sales that do not require a corresponding reply.
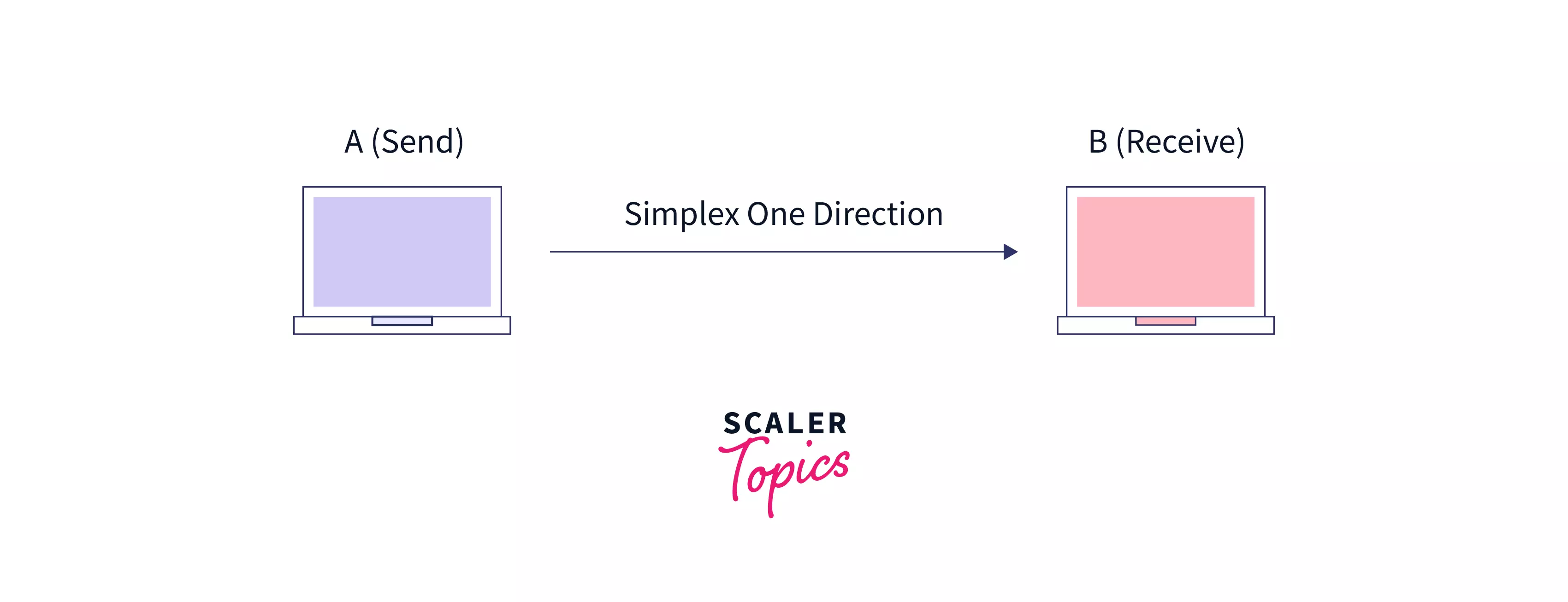
Examples
- A basic example of simplex transmission mode is communication between a computer and a keyboard. The keyboard can only accept data from the user, and the monitor can only display data on the screen.
- The radio station is a simplex channel since it transmits the signal but never permits listeners to transmit it back.
Advantages
- The station can broadcast more data at once when operating in simplex mode since it can use the complete bandwidth of the communication channel.
- In a simplex mode of transmission, radio stations can use the complete bandwidth of the communicating channel to send all data in one shot with no data loss.
Disadvantages
- The simplex transmission mode is primarily utilized in corporate environments where rapid response is not necessary because communications primarily involve two-way data exchange .
- Since device communication is unidirectional in simplex mode, there is no intercommunication between them.
Half duplex mode
The half duplex mode of transmission is used in computer networks when there is a way to flow information from sender to receiver but only one at a time. In this mode, the connected devices can transmit or receive the data but not simultaneously. In half duplex mode, the direction of communication can be reversed as the radio stations can receive as well as transmit the data. The half-duplex mode is used when communication in both directions is not required at the same time .

Examples
- A communication using a Walkie-talkie is an example of a half duplex mode. When using a walkie-talkie, one party speaks while the other listens. After a slight pause, the other party speaks while the first party listens. Speaking at the same time produces a distorted sound that cannot be understood.
Advantages
- In half duplex mode, error detection is available, and if an error occurs, the receiver demands that the sender retransmit the data.
- Since this method of transmission allows for two-way communication, the entire bandwidth of the communication channel is used in only one direction at a time.
Disadvantages
- In half duplex mode, when one of the devices is sending the data, then another one has to wait. This causes a delay in sending the data at the right time.
Full duplex
The Full Duplex mode of transmission is used in computing networks when there is simultaneous information flow in both directions, from sender to receiver. In this mode of transmission, the channel capacity is shared between the two devices, and communication occurs in both directions across a communication link that requires two wires. The Full Duplex mode features two simplex channels. One channel has traffic flowing in one direction, while the other channel has traffic flowing in the other way. The full duplex mode is used when communication in both directions is required.
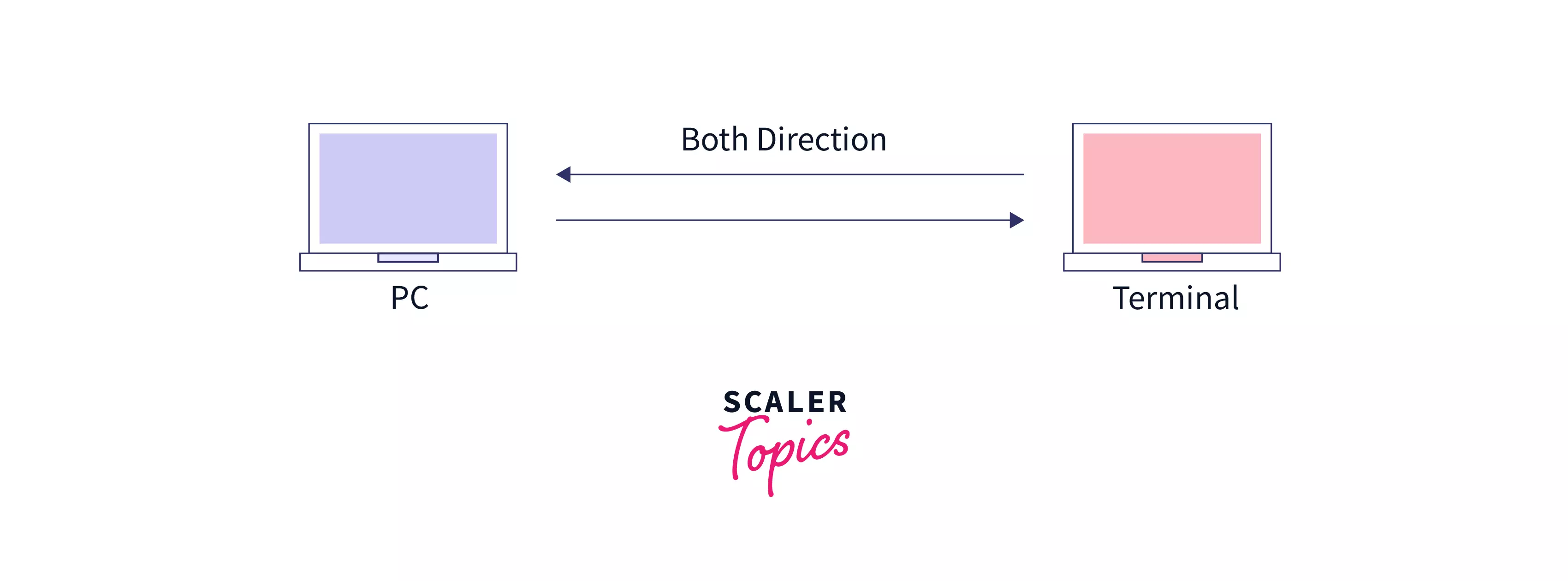
Examples
- A telephone network in which two people communicate over a phone line on which both can talk and listen at the same time.
- In the messaging app, we can send and receive messages simultaneously.
Advantages
- The full duplex transmission mode is the fastest because the transmission happens in both ways.
- Both stations can send and receive data simultaneously.
Disadvantages
- If no dedicated path exists between the devices, the communication channel’s capacity is divided into two parts.
Differences between Simplex, Half-Duplex, and Full-Duplex Mode
| Basis for Comparison | Simplex mode | Half Duplex mode | Full Duplex mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direction of communication | Unidirectional flow of information from the sender to the receiver. | Bidirectional flow of information from sender to receiver but only one at a time. | Bidirectional information flow in both directions, from the sender to the receiver. |
| Transmit/Receive | A device can only send data but cannot receive it, or it can only receive data but cannot send it. | Both devices can send and receive data, but only one can do so at a time. | Both devices can send and receive data simultaneously. |
| Speed | Slow | Relatively faster than simplex mode. | Fastest transmission mode. |
| Utilization of bandwidth | It uses the complete bandwidth of the communicating channel. | The entire bandwidth of the communication channel is used in only one direction at a time. | It either uses two simplex bandwidth communication channel or divide the complete bandwidth channel into two parts for data transmission. |
| Example | Communication between a computer and a keyboard. | Communication using a walkie-talkie. | A telephone network in which two people communicate over a phone line. |
Looking to excel in the world of computer networks? Our Free certification course is tailored for beginners & will guide you towards becoming a confident networking professional.
Conclusion
- Transmission mode, also known as a communication mode, is the transfer of data between two devices via a communication channel that includes an optical fiber, copper wires, wireless channels , and other storage media .
- The Physical Layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Layer Model is dedicated to data transmission in the network.
- There are three primary types of transmission modes based on the direction of exchange of information. The first is simplex, followed by half duplex, and finally full duplex.
- The Simplex transmission mode is used in computing networks when there is a single or one-way flow of information from sender to receiver.
- The half duplex mode of transmission is used in computer networks when there is a way flow of information from sender to receiver but only one at a time .
- The Full-Duplex mode of transmission is used in computing networks when there is simultaneous information flow in both directions, from the sender to the receiver.
