Most broadband routers and other wireless access points contain an optional capability known as MAC address filtering, sometimes known as hardware address filtering. It increases security by limiting the devices that can connect to a network. MAC address filtering adds an additional layer of security by comparing the device’s MAC address to a list of approved addresses. The client joins the network only if its IP address matches one on the router’s list and access is allowed; otherwise, its access is denied. A MAC address is similar to a government ID or Social Security number issued to citizens. MAC is a permanent address for a device in a network that does not change under normal circumstances.
Introduction to MAC Filtering
MAC filtering is an access-control-based security approach. Each address is given a 48-bit address, and it is used to determine whether we can access a network or not. It assists in listing a collection of allowed devices you require on your Wi-Fi and a list of disallowed devices you do not want on your Wi-Fi. It aids in the prevention of unauthorized network access. In other words, we can prohibit or allow particular computers based on their MAC address. We can configure the filter to allow connections only to devices on the safelist. Safelists are more secure than banned lists since the router only allows access to specific devices.
The router’s web interface allows you to configure a list of approved MAC addresses, enabling you to determine which devices can join your network. The router offers several capabilities intended to increase network security, but not all are practical. Although media access management appears to be useful, it has several limitations.
The addition of MAC address filtering adds an additional layer of security by comparing the device’s MAC address to a list of approved addresses. The client joins the network only if the MAC address of the client’s device matches one on the router’s permitted list, and then access is allowed; otherwise, its access is denied.
Note:- On a wireless network, a device with the correct user credentials, such as an SSID and password, can join the network and receive an IP address as well as access to the internet and any shared resources.
Working of MAC Address Filtering
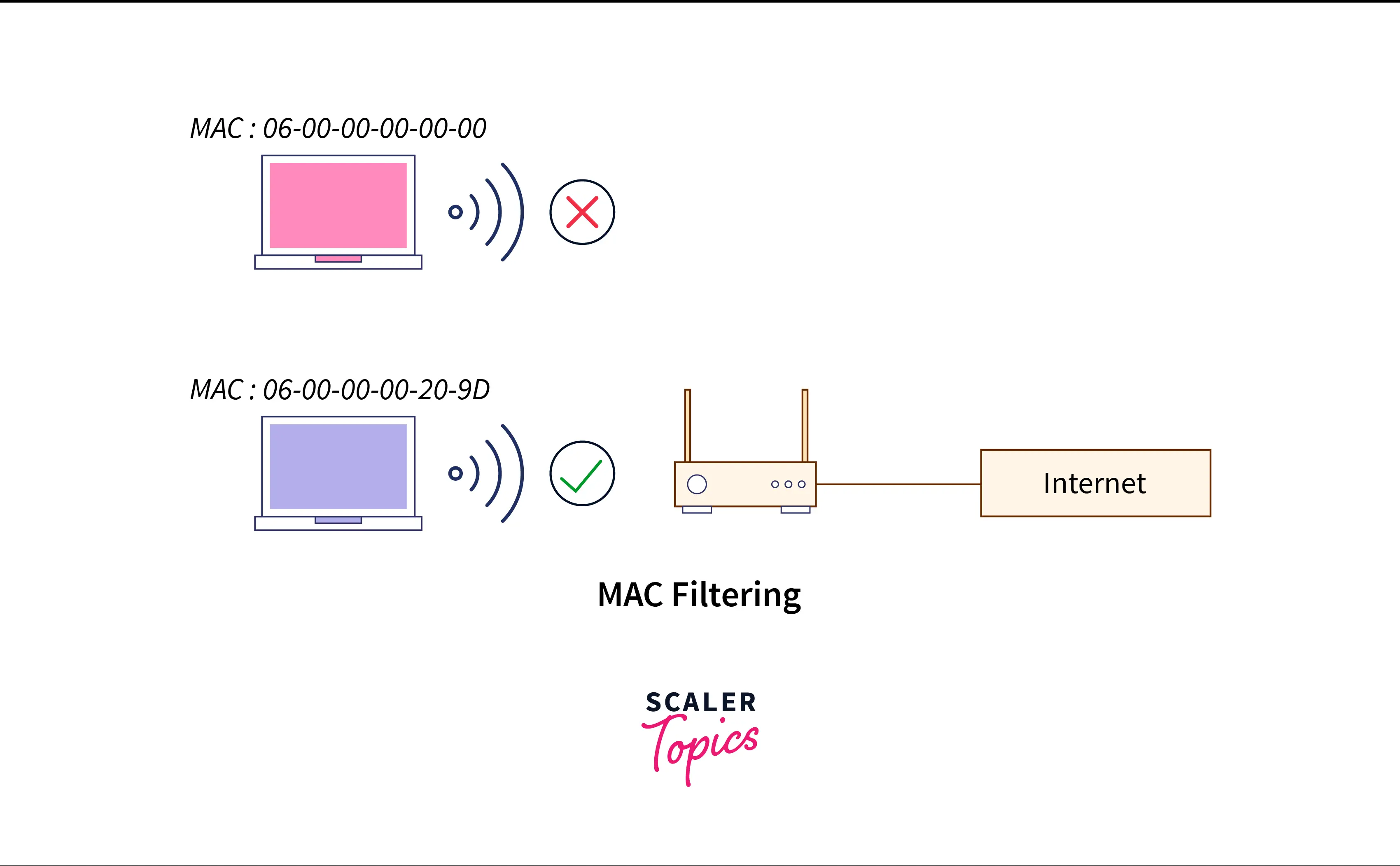
Let’s look at the various steps for MAC Address Filtering:
- Specify a permitted device list. The DHCP will only offer services to the MAC addresses that are on the list.
- Create a list of denied devices. MAC addresses in this list won’t receive server access from DHCP.
- The service will be refused if the MAC address appears on both the permitted and denied list.
Follow the instructions below to enable a list of authorized devices, denied, or both.
- Right-click the IPv4 node in the DHCP console and select Properties.
- Use an allow list by selecting enable allow list, and use a denied list by selecting enable deny list while using the current filter configuration settings on the filter tab.
- Save the changes.
How to Configure MAC Filtering?
An administrator must configure a list of devices that are allowed to join in order to set up MAC filtering on a router. It is necessary to identify the physical addresses of each authorized device, enter those addresses into the router, and enable the MAC address filtering feature.
In the admin console of most routers, you can see the MAC addresses of connected devices. If not, use your operating system to complete the task. Once you have the list of MAC addresses, enter the router’s settings and place each one where it belongs.
For instance, go to the Wireless > Wireless MAC Filter page on a Linksys Wireless-N router to enable the MAC filter. The same can be done on some D-Link routers under Advanced > Network Filter and on some NETGEAR routers under Advanced > Security > Access Control.
Updating MAC Filtering
The wireless device connected to the router won’t be able to connect if MAC Filtering is activated on the wireless router and the MAC address is not specified. If MAC Filtering is already disabled for troubleshooting, there is no need to enable it. Manufacturers of routers possess more significant expertise in this area.
Let’s look at the steps to update the MAC Filtering settings:
- Go to the router’s settings. Find the “MAC Filtering” tab or setting in the router’s settings. This can be found in a router’s “Wireless” or “Wireless Security” options. In certain routers, MAC filtering is also known as “MAC Address Control,” “Address Reservation,” or “Wireless MAC Authentication.”
- If MAC Filtering is on or enabled, one must add the MAC Address of the Nintendo system to the list of permitted devices and save or apply this adjustment. Turn off or disable MAC filtering if you don’t want it active on your network.
Does MAC Address Filtering Improve Network Security?
Theoretically, the likelihood of stopping malicious network activity increases when a router checks this connection before admitting devices. But by analyzing the packet using Wireshark, hackers using a toolset such as Kali Linux can gain access to the network since they can obtain the MAC addresses of approved devices, then the attacker can modify the device’s MAC address to the allowed MAC address and connect by masquerading as that device. They can employ the “deauth” or “deassoc” attacks, which forcefully detach a device from a Wi-Fi network, or they can utilize aireplay-ng, which sends disassociation packets to clients and then connects in the device’s place.
On the other hand, the MAC addresses of wireless clients cannot be modified because they are encoded in the hardware. However, some critics have pointed out that MAC addresses can be forged. An attacker only has to know one of the legitimate addresses. They do not need to break the encryption or crack your WPA2 encrypted password to gain access to your network. The attackers need to pose as a trusted computer.
A common question arises in your mind how these hackers obtain our MAC address if they were unable to connect to the network? Even if there is a WPA2 encrypted network, the MAC addresses on those packets are not encrypted. This means that anyone having network sniffing software and a wireless card within range of your network can easily capture all of the MAC addresses talking with your router.
Finding the MAC Addresses on a Windows 10 PC
The command prompt is the quickest way to look up MAC addresses on a Windows PC. Start an instance by pressing the Start button and entering “CMD”. When you run it, a command prompt window will emerge. Enter the command “ipconfig/all” and press Enter to run it.
By glancing at the entry next to “Physical Address” in the following list, you can determine the MAC addresses of certain cards. It will be a 12-digit hexadecimal number. Go to the Settings menu if you want a strict GUI-based method. Navigate to Network & Internet and choose the name of any active connection. The “Physical Address (MAC)” is located at the bottom of “Properties.”
Managing MAC Filtering in Windows 10
You must access your network router to enable or disable MAC filtering in Windows 10. In most cases, it is your home wireless router. Every router has an IP address you may use in your browser to access its controls. This IP address is normally provided in the router’s documentation. If you don’t have it, you can check it on the command prompt by typing ipconfig. Locate your active connection among the listed networks and note its default gateway. Now enter this address in the web browser’s search bar and log in with valid credentials.
MAC filtering is normally available in Advanced Settings, Security, Access Control, or something similar settings. The precise location will differ depending on the router brand. Inside, you have the choice of selecting your filtering method from two options:
- Allowed Devices:- This list contains the MAC address of the devices allowed to join the network.
- Denied Devices:- This list contains the MAC address of the devices whose entry is prohibited.
Choose your preferred method and add/remove MAC addresses from devices in your network. To make these changes permanent, save and quit your router settings.
How MAC Filtering is Useful?
A MAC address is similar to a government ID or Social Security number issued to citizens. MAC is a permanent address for a device in a network that does not change under normal circumstances. On the other hand, network devices’ IP addresses are constantly changing unless configured as “static” by the system administrator. Thus, a MAC address provides network administrators with a dependable address to keep track of known devices within the system. They are an effective access control method, similar to the duties of a bouncer in front of a nightclub. If your name is on his list, you’re in; if not, you’re out!
MAC filtering is less useful in personal and home networks unless numerous networks and many users/devices are involved or if you are a parent who wants to limit your children’s access to the internet at certain times of the day. Otherwise, an enterprise or institutional context is frequently the most significant use case for MAC filtering.
MAC filtering prevents unwanted connections by allowing you to add a list of denied devices to control that device’s access. This feature provides flexibility to network admins to improve their security. It is also a lightweight security feature as it does not require installation in the router or computer. It is a pre-installed feature of a broadband router. Apart from this, it is a less complex security solution because it is just a set of rules that block or allow any device based on its MAC address.
Administrators can use MAC filtering to limit user access to particular networks in large, complicated networks with numerous gateways and access points. The majority of its functions are organizational or administrative.
Disadvantages
- It is time-consuming and tiresome, especially if you have a large number of Wi-Fi-enabled devices because it is a must to obtain the MAC address for each device. When we buy a new computer or mobile device or provide authorization for a new device, we should update the list of approved devices.
- It will not defend against knowledgeable hackers. However, you can utilize it to prevent access for kids who don’t have sufficient expertise.
- For the PC, two MAC addresses should be added, one for the cable adapter and one for the wireless adapter.
- It may make the network less secure because the hacker no longer has to crack your WPA2 encrypted password.
How to Turn Off MAC Filtering?
MAC addresses (Multimedia Access Control) are unique sets of codes for electronic devices that allow them to be identified on a network. Only specified MAC addresses are permitted or denied by MAC filters. MAC filters are excellent security protection; nevertheless, if your network must be available to the public or guests, or if you often add and remove devices, you should consider disabling MAC filtering.
Method 1: For Windows
- Open Command Prompt. You can access the command prompt by pressing the windows + R key and typing cmd. You can also find the command prompt in the start menu.
- Enter the ipconfig command and hit enter.

- Find your active network. There may be numerous connections shown in the readout, and you may need to scroll up to identify your active connection.
- Look for the Default Gateway entry. This is your router’s address. Take note of it.
- Open any web browser. In the browser’s address bar, type the Default Gateway address.
- Login with your admin account. Routers are secured via an administrator login and password. To retrieve the default login details, consult your router’s instructions or seek up the model online.
- Look for “MAC Filtering,” “Access Control,” or something similar in the “Advanced” section. The actual placement of the “MAC Filtering” section is challenging to define because the location and labeling differ from router to router. The “MAC Filtering” or “Access Control” settings are usually found in the “Advanced” section, although they can also be found in the “Security” or “Wireless Settings” sections.
- Now disable MAC filtering. Again, the wording and position will vary depending on the router, but you should be able to turn off MAC filtering by selecting a “Disable” option.
- Save your changes. Click the “Apply” or “Save” button to save your changes to the router settings. The modifications will be applied by your router, which may take a few moments.
Method 2: For macOS
- Open the Utilities folder. You may get to it via the Go menu or your Applications folder.
- Now open AirPort Utility. This program can easily configure your AirPort router without using a web browser interface.
- Choose your AirPort base station. If you have numerous AirPort routers on your network, choose the one you wish to modify and click Edit.
- Open the “Access Control” tab.
- Select “Not Enabled” from the “MAC Address Access Control” drop-down option.
- Click the Update button. This will save the changes made to your AirPort router, which will disable MAC filtering.
Conclusion
- MAC is a permanent address for a device in a network that does not change under normal circumstances.
- You can use the ipconfig command in CMD to find the MAC address of any network device.
- MAC filtering is an access-control-based security approach. Each address is given a 48-bit address, and it is used to determine whether we can access a network or not.
- The router’s web interface allows you to configure a list of approved MAC addresses, enabling you to determine which devices can join your network.
- MAC filtering is less useful in personal and home networks unless numerous networks and many users/devices are involved or if you are a parent who wants to limit your children’s access to the internet at certain times of the day.
- Administrators can use MAC filtering to limit user access to particular networks in large, complicated networks with numerous gateways and access points.
- A Hackers using a toolset such as Kali Linux can gain access to the network since they can obtain the MAC addresses of approved devices, then the attacker can modify the device’s MAC address to the allowed MAC address and connect by masquerading as that device.
