DNS (Domain Name Server) translates the domain name into an IP address. DNS attacks target the Domain Name Server and its infrastructure. The most common types of DNS attacks are NXDOMAIN attacks, DNS spoofing, DNS amplification, etc.
Scope
- In this article, we will study the Domain Name Server (DNS) attack and why it is performed.
- We will also cover the types of DNS attacks.
- At last we will discuss how DNS attacks can be prevented.
What Is a Domain Name Server (DNS) Attack?
Domain Name System is abbreviated as DNS and it is the protocol for the translation of domain names like website.com into their respective IP address like 204.23.21.3.
The infrastructure of DNS is targeted by the DNS attack. In a DNS attack, servers that have stored domain names are targeted by hackers. Or in some other cases, attackers try to find out the vulnerabilities inside the system and then use those vulnerabilities for their good.
Why Perform an Attack on the DNS?
If we see the services of the Internet and the IP network then the DNS is one of the primary services of the Internet and the IP network. This indicates that for most of the exchanges, DNS is required. Communication between the web browser and server starts with the resolution of the DNS. If the service of the resolution of the DNS becomes unavailable then many applications will have no use.
Hackers try to deny the services of the DNS, neglecting the function of the protocol standard or with the help of exploits and flaws. All the security holes that have usage or protocol-limited verification are accepted by DNS. And it also provides opportunities for tunneling, data exfiltration, etc.
What are The Major DNS Attack Types?
Types of DNS attacks are explained below:
DNS Tunneling
Refer to the below image for the DNS tunneling
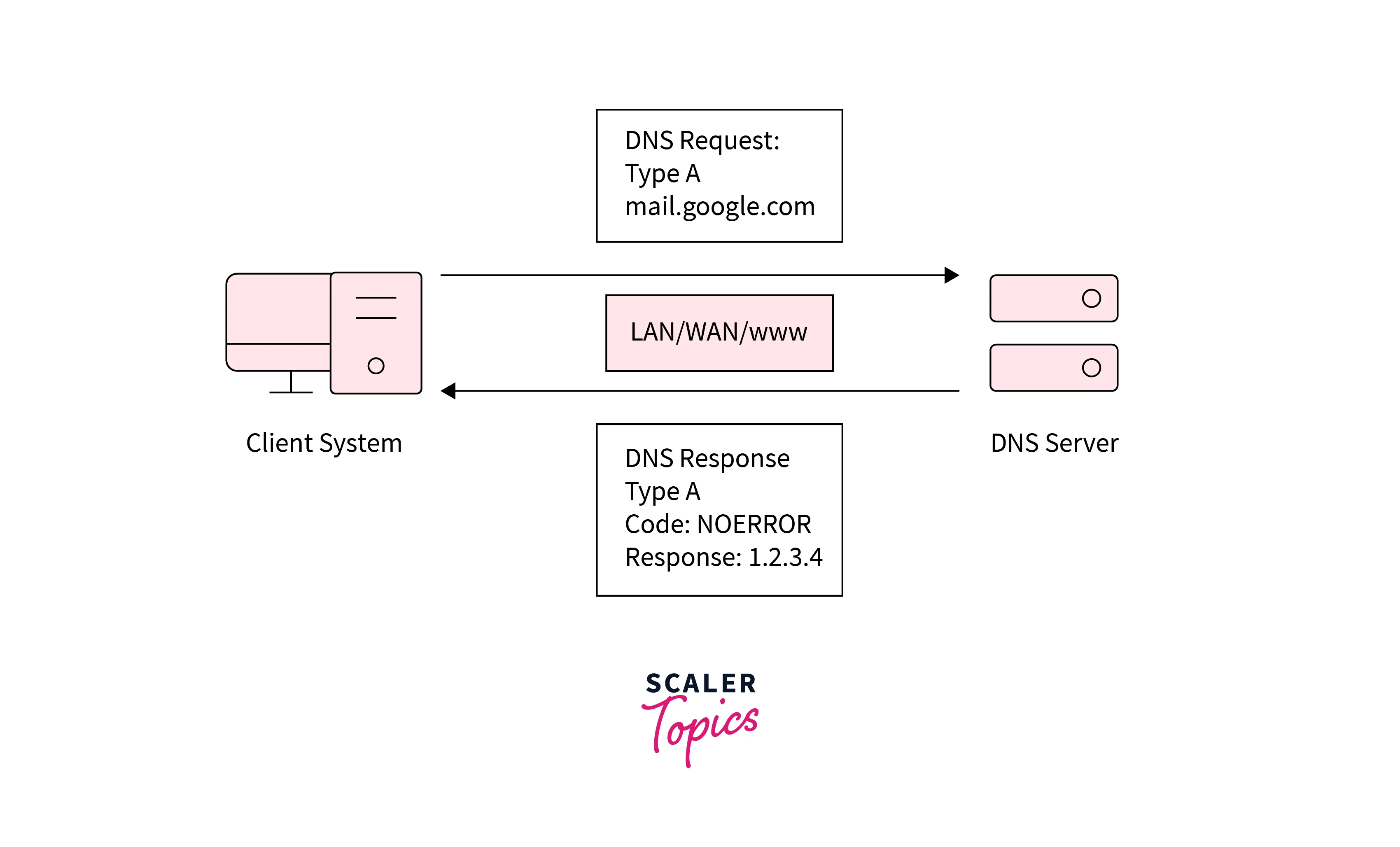
Protocol or program data encoding inside the DNS response and queries is involved in the DNS tunneling. Generally, the DNS server is taken over by the data payloads and also it allows the remote server and application management to the attackers.
Sometimes DNS tunneling relies on the compromised system connectivity of the external network, which way is provided to an internal DNS server with access to the network. Domain and server controlling are also required by it, and this domain and server work like an authoritative server by which executable programs, data payload, and server-side tunneling are carried out.
DNS Amplification
Refer to the below image for the DNS amplification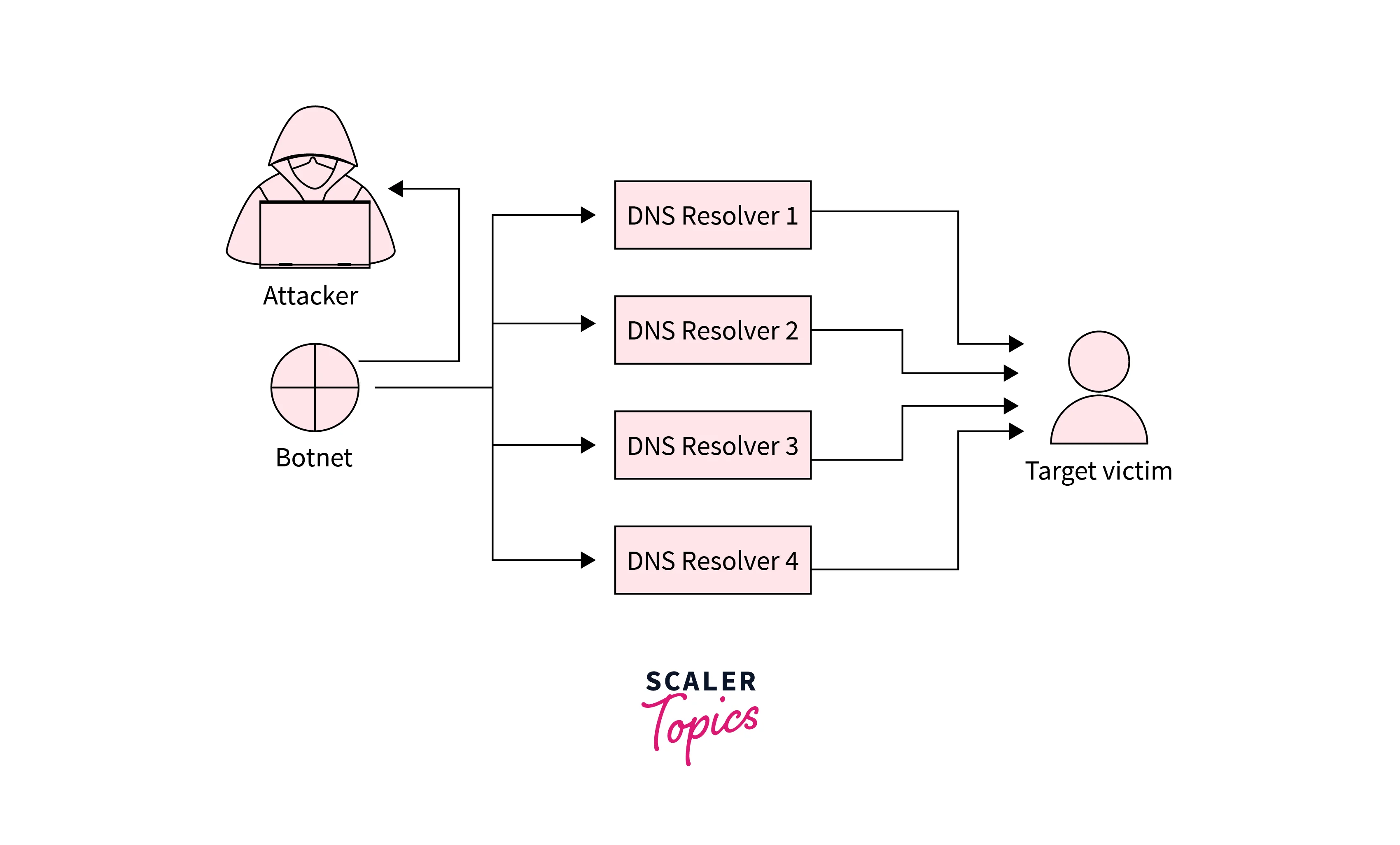
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is performed by the DNS amplification attack on the server. This includes the exploitation of the publicly available DNS server so that the target can be easily submerged with the response traffic of the DNS.
If we see this attack, then it is generally initialized with the threat actor by which a lookup request of the DNS is sent to the open DNS server, source address spoofing for making it the target address. When the DNS record response is returned by the DNS Server then that is sent toward the new target, which is under the control of the attacker.
DNS Flood Attack
Refer to the below image for the DNS flood attack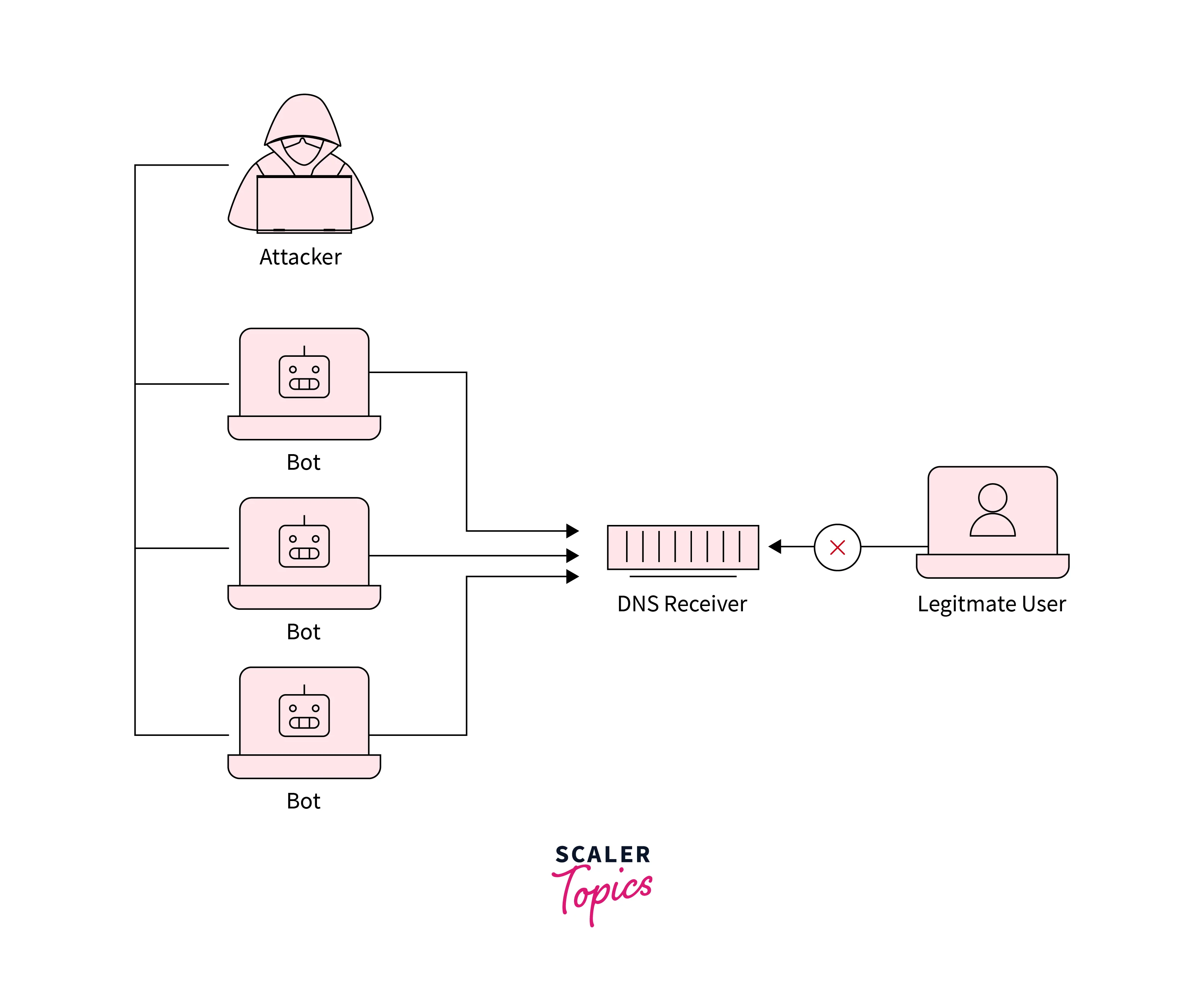
UDP(User Datagram Protocol) flood carried out by the DNS protocol is involved in the DNS flood attacks. Spoofed but valid DNS packets are deployed by the threat actors at a very high packet rate and then the vast group of the IP address of the source is created.
The DNS server responds to all requests as all requests appear to be valid. As there are a vast amount of queries so now the DNS server is overwhelmed. As there is a requirement of huge network resources for the DNS attack, by which the infrastructure of the targeted DNS is tired out till it becomes offline. This results in the slow down of the internet access of the target.
DNS Spoofing
Refer to the below image for the DNS spoofing
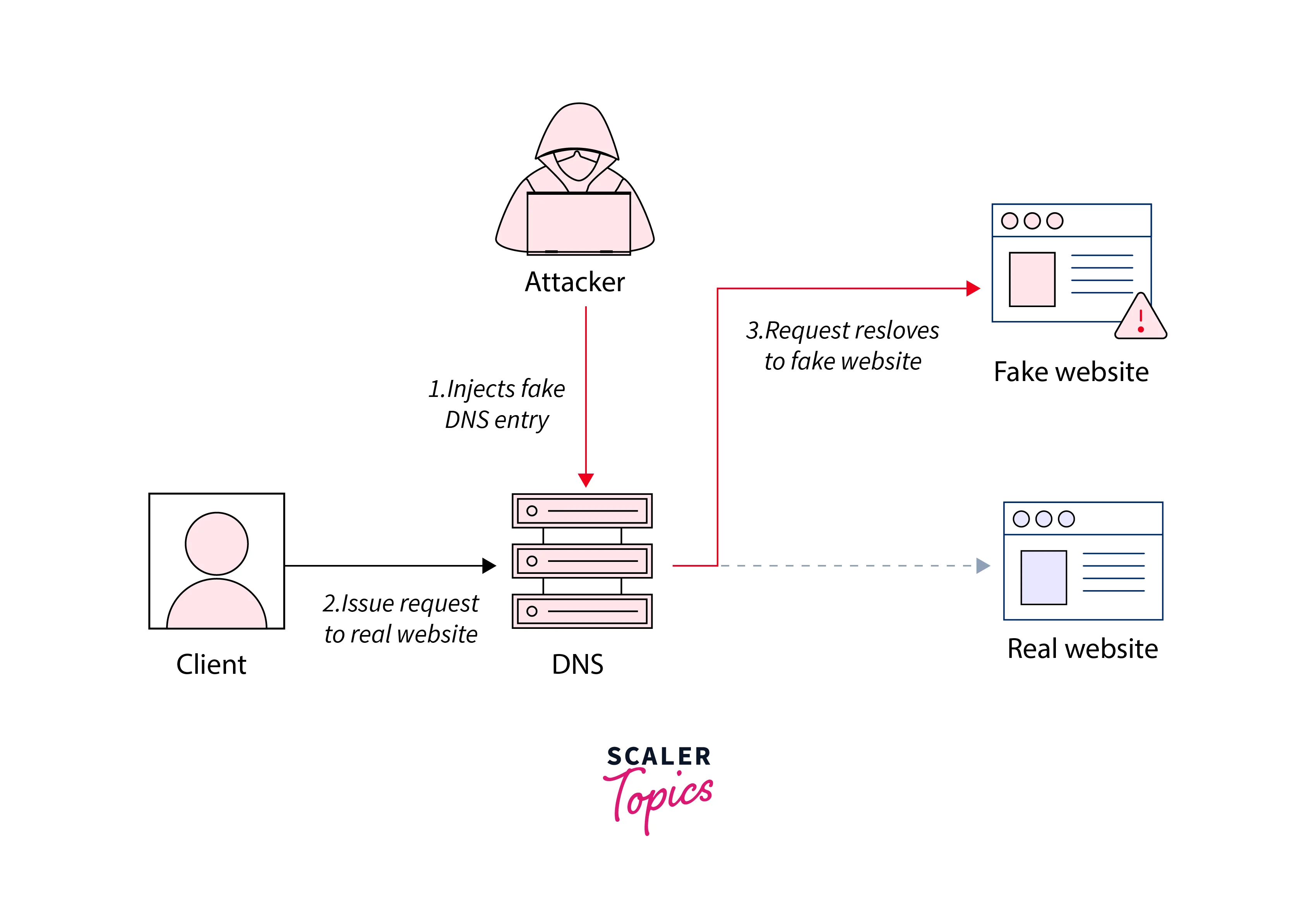
DNS spoofing is also DNS cache poisoning. In this attack, DNS records are manipulated in such a way that the online traffic is redirected to the fraudulent websites by which the intended destination is impersonated. The user gets the prompt for login into their account after reaching the fraudulent destination.
Once the login details are entered by the user on the fraudulent website, the threat actor gets a very big opportunity for stealing the sensitive information and access credentials entered by the user in the login form of the fraudulent website. Attackers use these types of malicious websites to install worms or viruses on the system of the end user, and by installing it the attacker gets long-term access to the system of the user and can also access any of the data stored in the system.
NXDOMAIN Attack
Refer to the below image for the NX DOMAIN
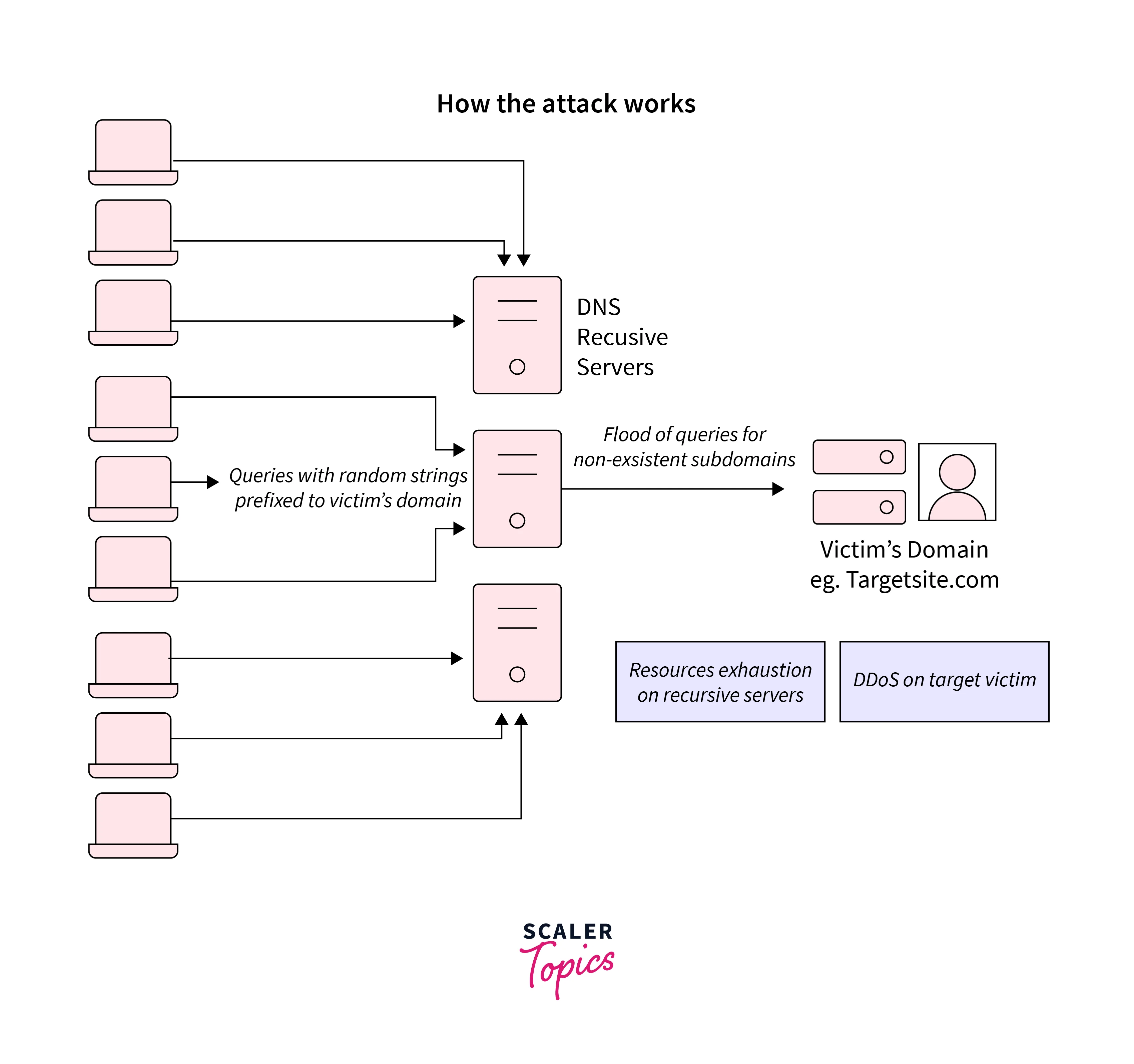
The DDoS attack is flooded by the NXDOMAIN attack by which the DNS server is overwhelmed with a huge number of requests for records that do not exist or are invalid. Sometimes DNS proxy servers handle these attacks by which most of the resources are used for querying the DNS authoritative server. This results in using all the time of the DNS proxy server and the DNS Authoritative server in responding to bad requests and handling them. This causes a slowdown in the response time of the legitimate request until its results stop completely.
DNS Attack Prevention
Following are some of the ways of protecting the organization from DNS attacks:
Keep DNS Resolver Private and Protected
The use of DNS resolver is restricted to the users of the network only, it is never kept open for the external users of the network. By this, we can protect the cache by poisoning it from external actors.
Configure Your DNS Against Cache Poisoning
To protect the organization from cache poisoning, your DNS software security must be configured. Variability can also be added to the request which makes it difficult for the threat actor to slip in a fraudulent request. Try to use randomization for the ID of the query such as in place of UDP port 53 uses the random source port.
Securely Manage Your DNS servers
Through the domain registrar or by the service provider, authoritative nameservers are hosted in-house. You can control it fully if you have the knowledge and skills related to the in-house. You can also take benefit of this if you do not have the required knowledge and skills by outsourcing it.
Test Your Web Applications and APIs for DNS Vulnerabilities
All your APIs and apps are scanned by bright automatically for several vulnerabilities which also include security-related issues. All the findings are validated by the bright before reporting. And for the team, the reports come with very clear guidelines for the remediation. And bright makes it easier for doing rapid repair.
Conclusion
Domain Name Serveris abbreviated as DNS and it is a primary service of the IP and the internet which translates the domain name into the IP address.- DNS attacks the DNS infrastructure and the domain name stored servers.
- DNS Tunneling, DNS Amplification, DNS Flood Attacks, DNS Spoofing, and NXDOMAIN Attacks are the types of DNS attacks.
- Keep DNS Resolver Private and Protected, Configuring Your DNS Against Cache Poisoning, Securely Manage Your DNS servers, and Test Your Web Applications and APIs for DNS Vulnerabilities are the methods that can be used for the protection of the DNS.