Computers or devices require IP addresses to communicate on the network. In today’s world, there are numerous network types available, including the internet, intranet, local area network, wide area network, storage area network, and so on. To communicate on those networks, each device requires an IP address. We can manually or automatically assign an IP address to the device (using DHCP). The IP address will be assigned to the required computer automatically by the DHCP server. A DHCP relay agent is used by a DHCP server and a DHCP client to assign an IP address between two or more networks.
What is a DHCP Relay Agent?
Before learning about DHCP Relay agents, we should know about the protocols and processes involved in the DHCP Relay agent life cycle. They are –
| ATTRIBUTES | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
| Process | DORA | Discover Offer Request Acknowledge |
| Protocol | BROADCAST | From one source to many destinations |
| Protocol | UNICAST | From one source to one destination |
| End Device | DHCP CLIENT | The device where the DHCP client is installed |
| End Device | DHCP SERVER | The server which is responsible for allocating the IP address to the devices dynamically within the same network or a different network |
Computers and devices use the DHCP protocol to obtain an IP address from the DHCP server using the DORA process.
In the DORA process, the DHCP Client Discover message is the broadcast address. If the address is broadcast, it will reside in the local subnet only.
A DHCP relay agent is used to forward the DHCP messages of the DHCP client to the DHCP server if the DHCP client and DHCP server reside in different subnets.
Example:
Consider that we have one DHCP client on network 192.168.10.0/24 and a DHCP server on network 192.168.20.0/24.
| Device | Network |
|---|---|
| Computer | 192.168.10.5/32 |
| DHCP Server | 192.168.20.5/32 |
| Router | 192.168.10.0/24 and 192.168.20.0/24 |
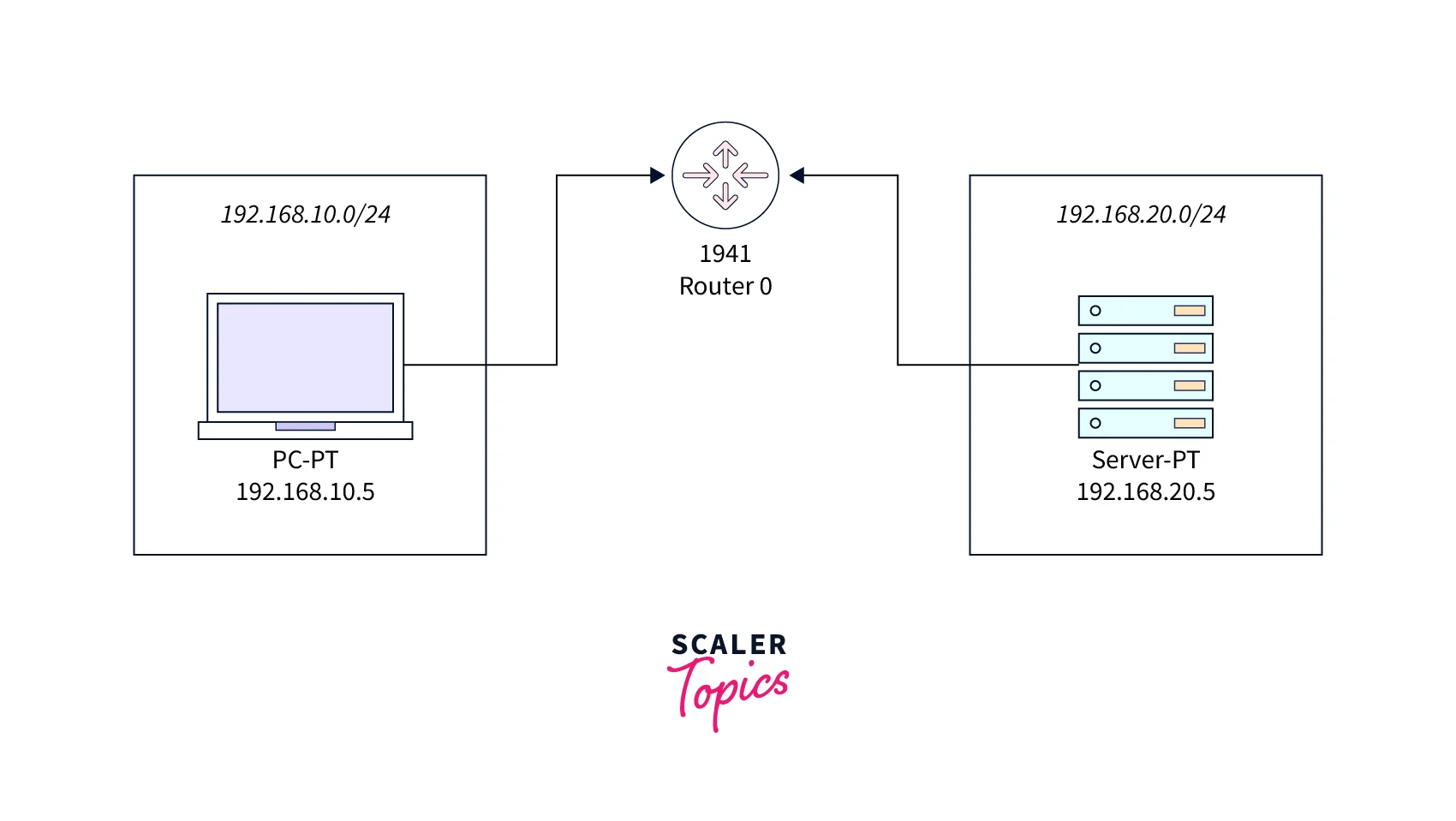
As we said earlier, we need a DHCP relay agent if the two devices are in different subnets. The above diagram depicts a DHCP client device (192.168.10.5/32), and a DHCP server device (192.168.20.5/32), on different networks (192.168.20.0/24 and 192.168.10.0/24), connected via the router. The DHCP relay agent is essentially installed on the router.
DHCP Relay Agent Configuration
The DHCP Relay Agent can be configured on routers by adding the below command
R1 (config-if) # ip helper-address <any available IP address of DHCP Server network>By adding the above command to the router, it will act as a DHCP relay agent, sending the unicast request to the DHCP server.
A unicast message is returned by the DHCP server in response to a DHCP relay agent request.
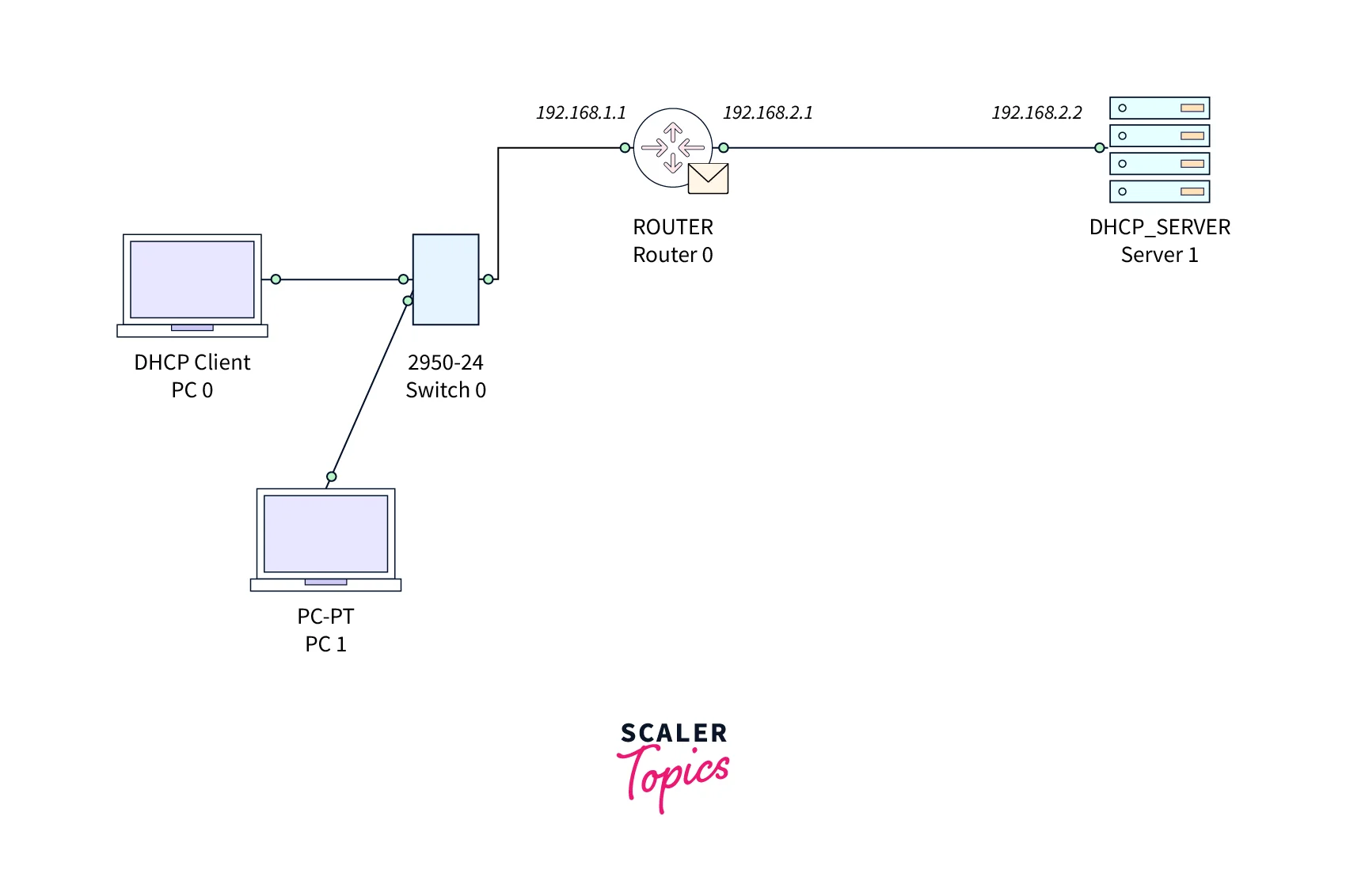
Here, we can see that by configuring the DHCP relay agent, the router will be able to send a request to the network of the DHCP server. i.e., the DHCP client is on one network and the DHCP server is on another network.
How Does DHCP Relay Agent Work?
Scenario 1:
In the below image, we can see that the DHCP client and DHCP server are on different subnets.
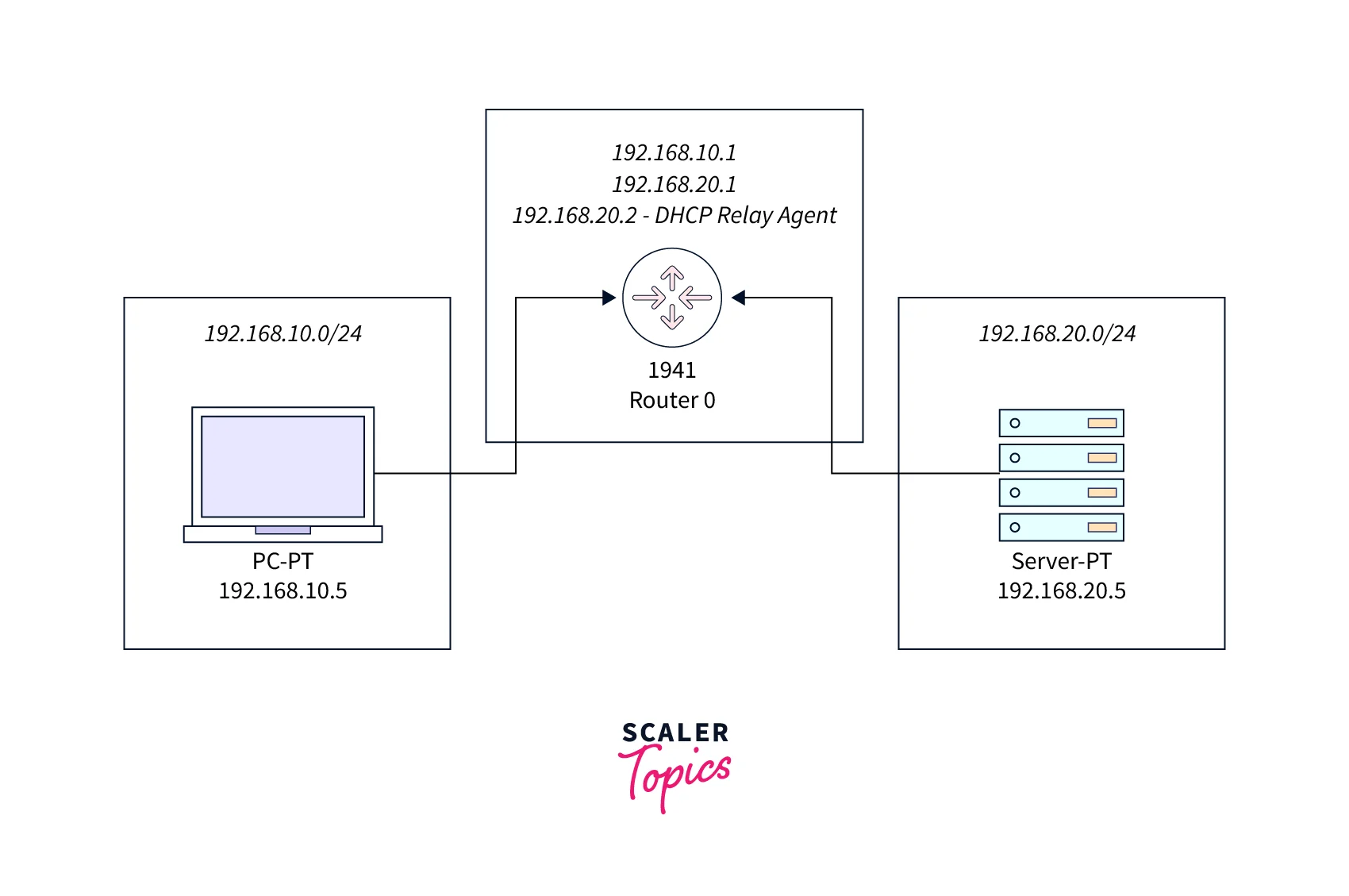
- The DHCP client will send the broadcast message to the router where we installed the DHCP relay agent.
- The router configures or installs the DHCP relay agent, which then forwards that DHCP client IP address as a unicast message to the DHCP server.
- The DHCP server provides the IP address to the DHCP relay agent.
- The DHCP relay agent forwards that message to the DHCP client.
Scenario 2:
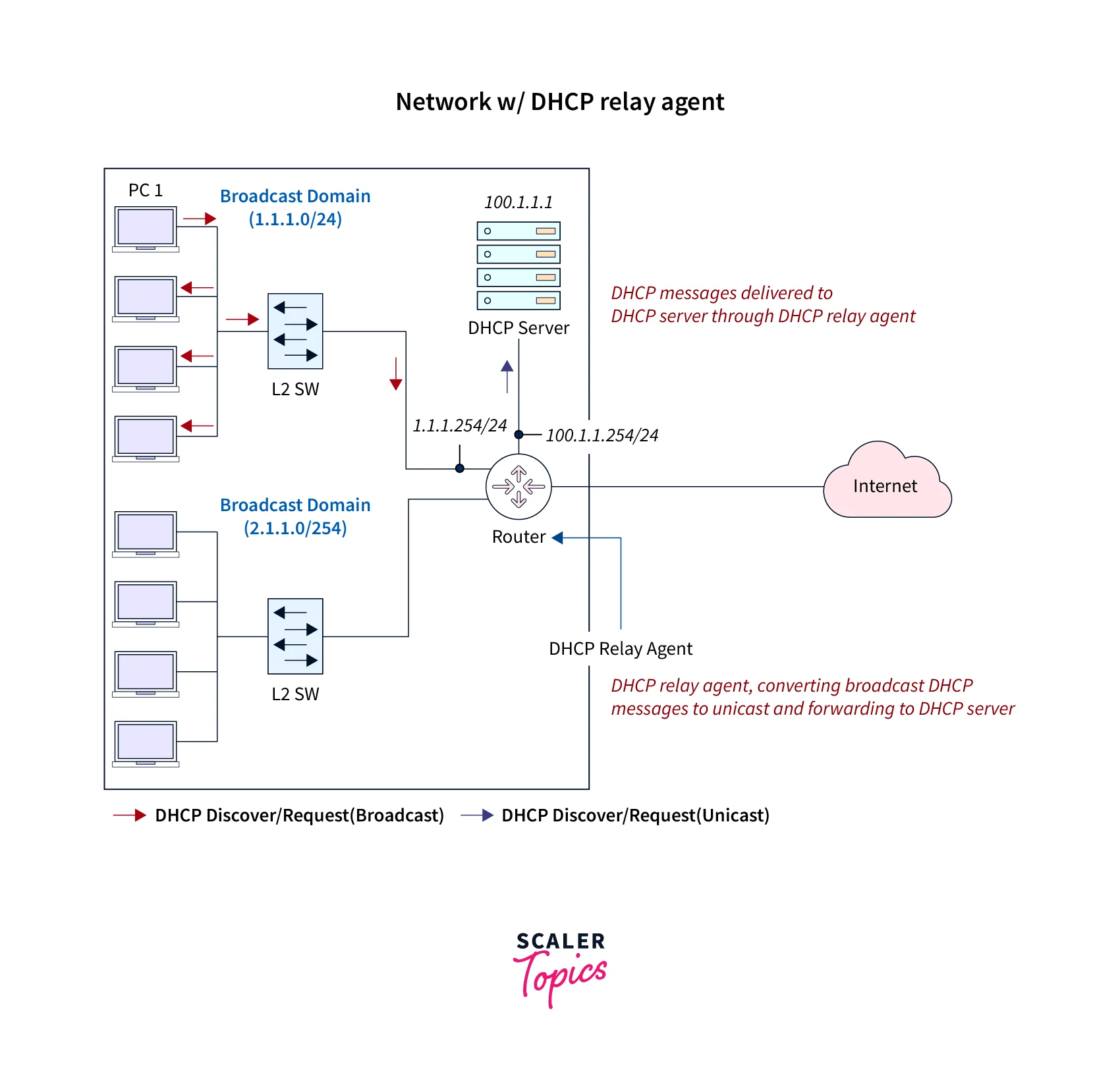
In the above image, we can see that there are multiple end devices available between the two networks. In this case, the router connected to the switches where the end devices are connected is configured with a DHCP relay agent to forward the message to the DHCP server and vice versa.
Basic Operations of DHCP Relay Agents
The DHCP client will send the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message. The message payload looks like the below format.
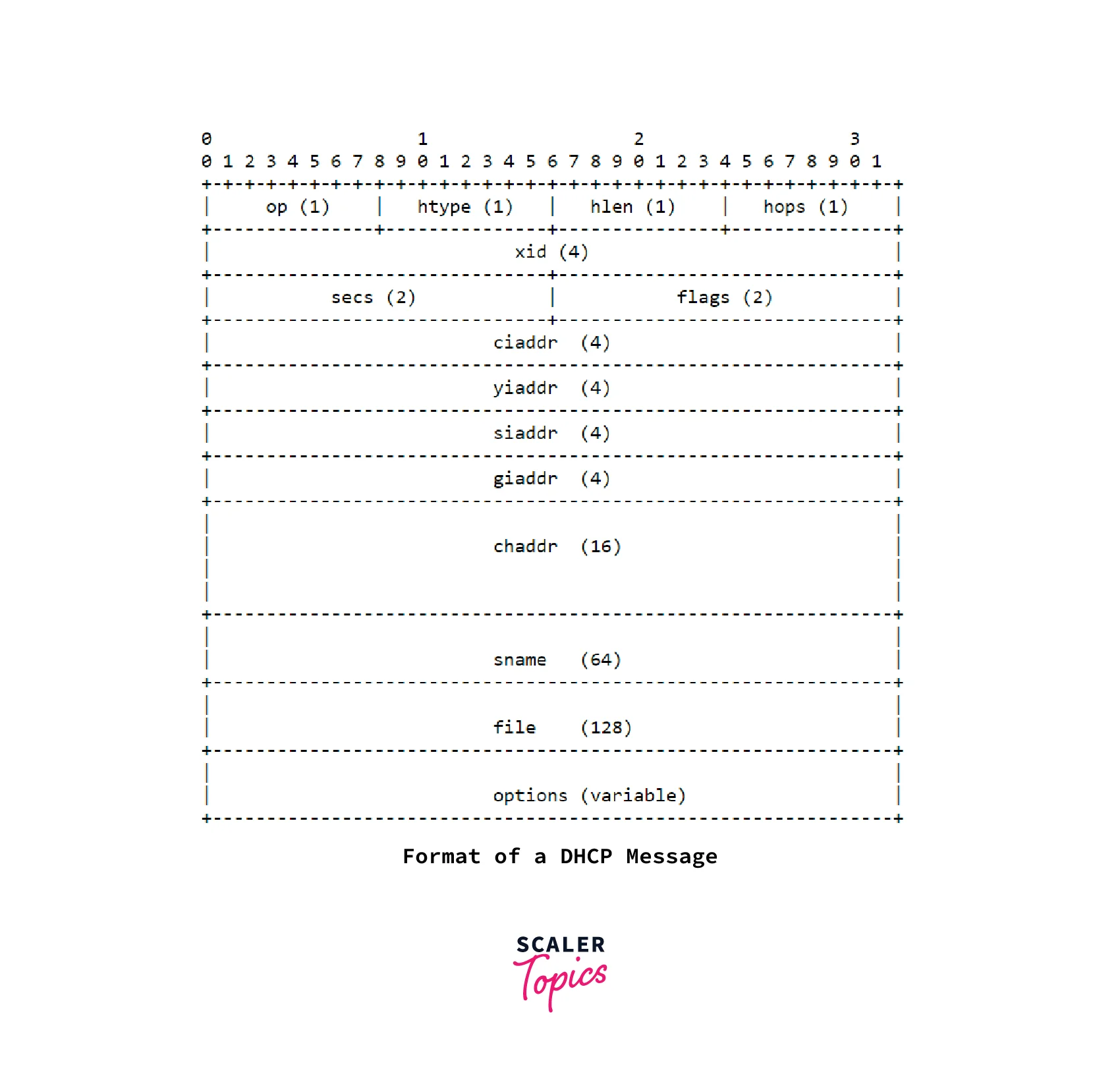
- If the giaddr header value is
0x0or0xffffff, the DHCP relay agent configured in the router or switch will append its relay agent option information to the giaddr header and forward DHCP messages to the DHCP server.
Steps Involves in Adding Giaddr Header:
- Once the router or switch receives the DHCP client messages, it will forward those messages to the DHCP server by adding the header giaddr in the DHCP message payload.
- In the giaddr header, the DHCP relay agent will add the next hop IP address, i.e., the DHCP server IP address.
- Once the DHCP server receives the DHCP messages with DHCP relay agent option information, the DHCP server will do any one of the below-mentioned responses.
Unaware of the DHCP Relay Agent:
- If the DHCP server is unaware of the DHCP relay agent information upon receiving the DHCP message, it will ignore the request.
Aware of the DHCP Relay Agent:
- If the DHCP server is aware of the DHCP relay agent information, the DHCP server will respond with the DHCP relay option information response by adding it to the OPTIONS header in all packets.
The below table describes each field in the DHCP message format:
| Field | Octet | Description |
|---|---|---|
| op | 1 | Message op code / message type. 1 = BOOTREQUEST, 2 = BOOTREPLY |
| htype | 1 | Hardware address type. e.g., ‘1’ = 10mb ethernet. |
| hlen | 1 | Hardware address length, e.g. ‘6’ for 10mb ethernet |
| hops | 1 | DHCP Client sets this field to 0. It will optionally be used by the DHCP relay agent |
| xid | 4 | Transaction ID |
| secs | 2 | Filled in by client |
| flags | 2 | Broadcast flag |
| ciaddr | 4 | Client IP address; only filled in if the client is in BOUND, RENEW, or REBINDING state and can respond to ARP requests. |
| yiaddr | 4 | client IP address |
| siaddr | 4 | IP address of next server |
| giaddr | 4 | Relay Agent IP address |
| chaddr | 16 | Hardware address of the client |
| sname | 64 | Optional server hostname |
| file | 128 | Boot file name |
| options | var | Optional parameters field |
Note: The DHCP Client sends the minimum size of a DHCP message up to 576 octets/bytes. However, the DHCP server message size differs by the size of the variable added in the option field.
Why are DHCP Relay Agents Needed in DHCP Operations?
DHCP clients and servers use the DORA process to assign the IP address to devices dynamically. The DHCP Relay Agent is needed to achieve two things in the DORA process. They are:
- Allocation of IP Address
- Renewal of IP Address
Allocation of IP Addresses:
- If the DHCP relay agent receives the broadcast DHCP messages, then the DHCP relay agent stores the information in a table and sends the unicast messages to the DHCP server.
- The DHCP Client messages will use the DHCP relay agent until the allocation of an IP address.
Renewal of IP Address:
- Once the IP address has expired, the DHCP client will directly send the unicast message to the DHCP server, since the DHCPREQUEST message from the renewing state in the DORA process is a unicast address, the DHCP relay agent does not necessarily convert the address.
Conclusion
- A DHCP relay agent is used to forward the messages from the DHCP client to the DHCP server when the DHCP server and client are on different subnets or networks.
- The number of hops from the DHCP server to the DHCP client and vice versa will be reduced via DHCP relay agents.
- DHCP relay agents assist in resolving Layer
3device-related network problems for the DHCP server and client.