FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access), TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access), and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) are three distinct multiple access techniques used in telecommunications and wireless communication systems. These are all data transmission and communication techniques. They are highly effective, but because of their unique features, they are used in various ways. Each technique has advantages and drawbacks that make it suited for different purposes.
Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
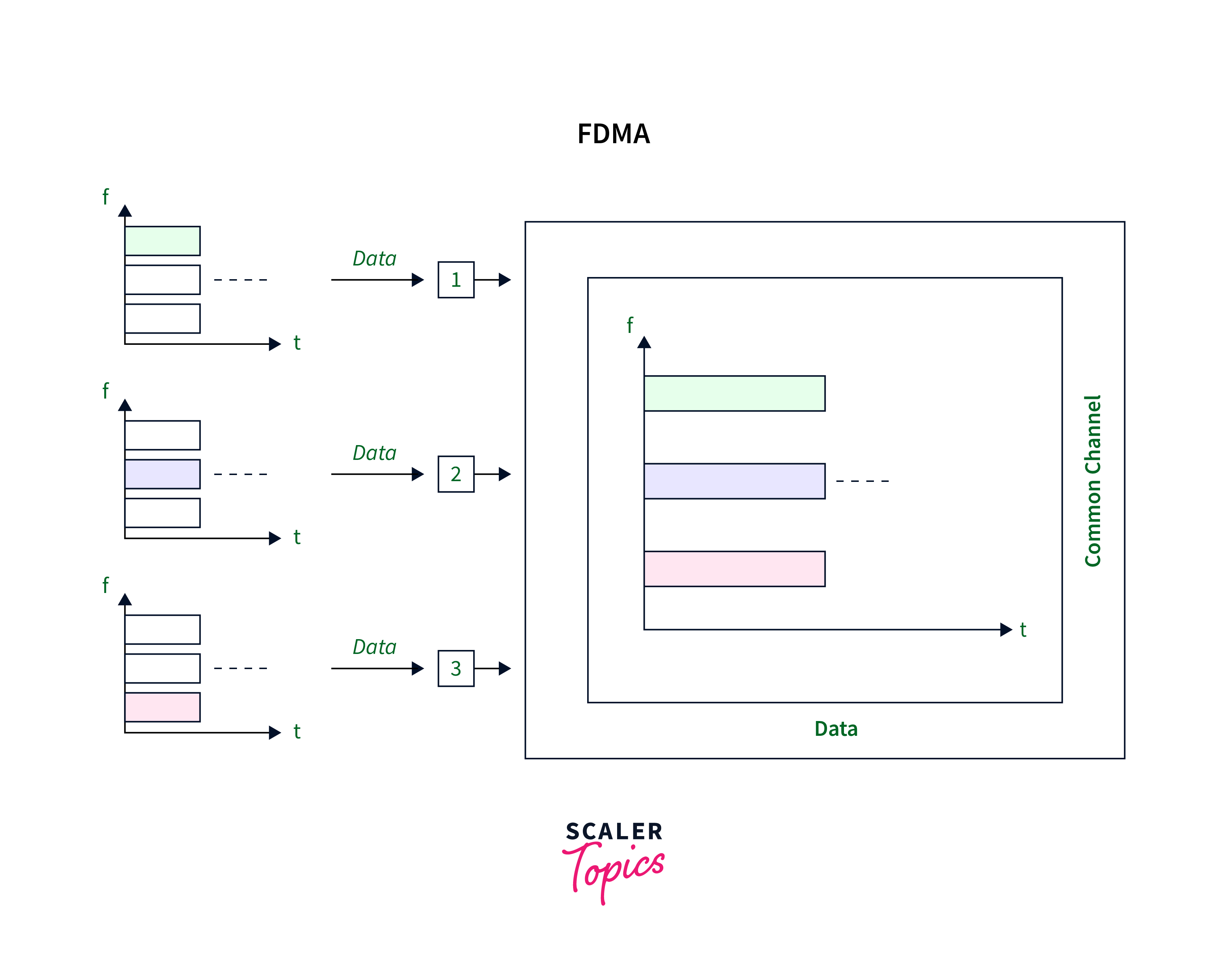
FDMA is an acronym for Frequency Division Multiple Access. It serves as a channelization protocol, where the available bandwidth is partitioned into distinct frequency bands. Each station receives a dedicated band to transmit data, and this specific band remains exclusively reserved for that station continuously. This technique ensures interference-free communication by separating the frequency bands of different stations using guard bands. This process is comparable to data link layer access methods, in which each station’s physical layer transforms data into a bandpass signal inside its allocated frequency band, removing the requirement for a hardware multiplexer at that layer.
Advantages
- It offers simplicity in terms of hardware resources and ease of use.
- FDMA is efficient in handling a smaller user population.
- The system maintains a moderate level of complexity.
- All stations can operate continuously without waiting for their turn.
- It lowers inter-symbol interference.
- The lower information bit rate can positively impact capacity.
Disadvantages
- It exclusively works with analog signals.
- Flexibility is limited, necessitating gradual changes to existing traffic patterns.
- The maximum bit rate per channel is both small and fixed.
- Transponders demand extensive bandwidth.
- RF (Radio Frequency) filters need to meet strict adjacent channel rejection requirements, potentially increasing the system’s cost.
- The carrying capacity of the traffic is not very high.
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
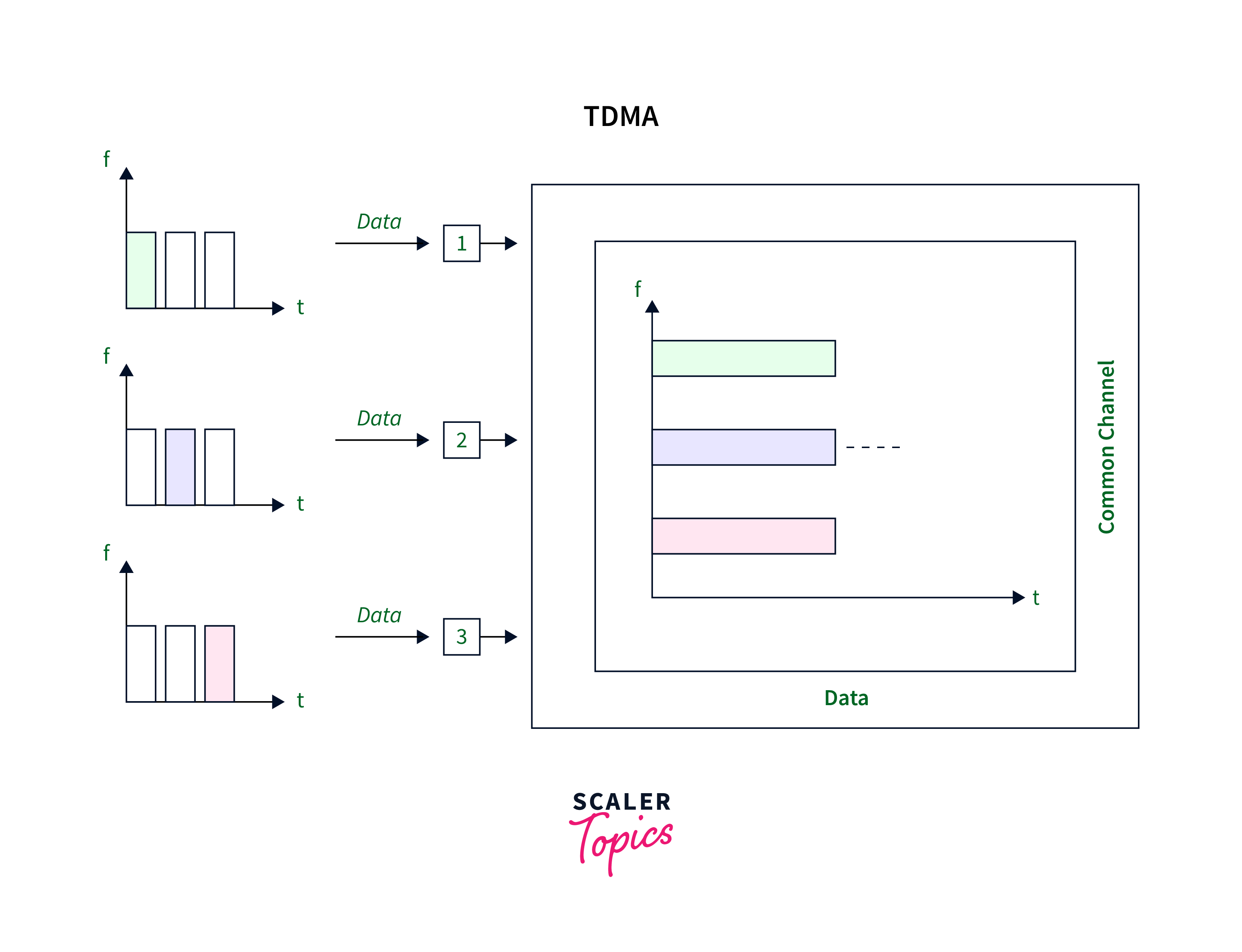
TDMA is an acronym for Time Division Multiple Access. It serves as a channelization protocol where the channel’s bandwidth is distributed among different stations based on time. Each station is provided with a specific time window for transmitting data. It is essential that each station only transmit data within that time slot. The synchronization between stations is critical for successful TDMA implementation. This technique is similar to a data link layer access method, in which the data link layer tells each station to use its given time slot exclusively.
Advantages
- With decreasing cell sizes, TDMA offers notable savings in investment for space, support, and base station hardware.
- It supports data transmission speeds spanning
64kbps to120Mbps. - TDMA’s time-based separation ensures interference-free concurrent transmission.
- Administrative tasks like fax, voiceband data, SMS, and multimedia applications including video conferencing can be efficiently managed using TDMA.
- TDMA easily adjusts to data transmission and voice communication requirements.
- TDMA increases the battery life of the client by communicating alone for part of the time during conversations.
Disadvantages
- If all time slots in the current and target cells are already allocated, users might not be able to connect to a call due to specific slot assignments.
- Frequency and slot allocation can be intricate in the TDMA setup.
- To achieve high data rates in TDMA, equalization is required.
- Network and spectrum planning in TDMA is complex and time-intensive, demanding substantial expertise and resources.
- The emphasis is on organisation and range arrangement.
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
CDMA is an acronym for Code Division Multiple Access, a combination of FDMA and TDMA in which the allocation of resources is affected by both frequency and time. FDMA allocates the frequency band to multiple users during a session, while TDMA offers each user the entire frequency band for a specified session. Conversely, CDMA combines elements from both systems, enabling multiple users to employ the same frequency band simultaneously, differentiated by distinct codes.
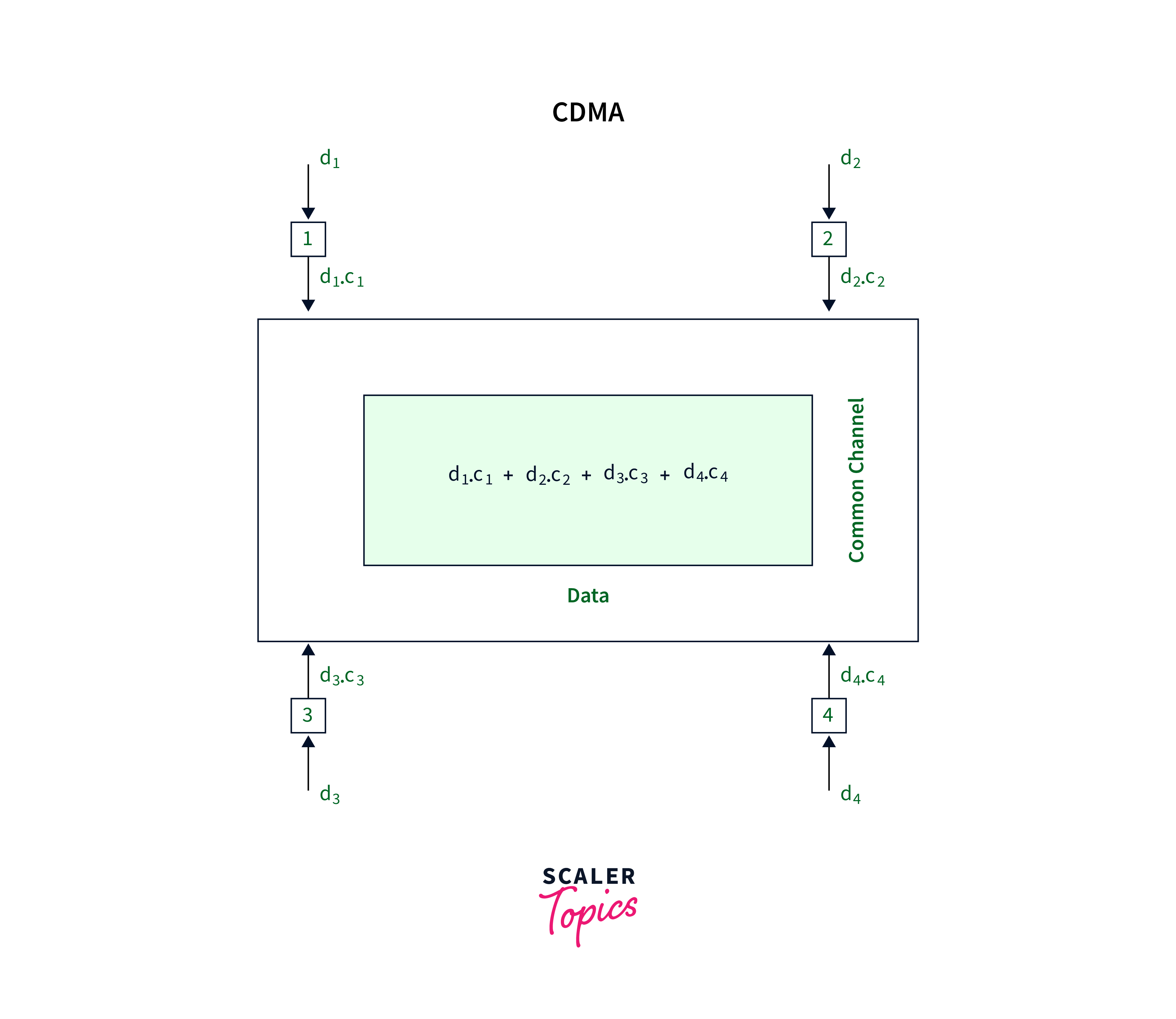
In the above diagram, four stations are labelled 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each station is associated with specific data labelled d1, d2, d3, and d4, respectively. Additionally, corresponding to each station, there is an assigned code denoted as c1, c2, c3, and c4.
Advantages
- CDMA has an extremely high spectral capacity, allowing it to accommodate a large number of users over a wide bandwidth.
- Synchronization is not required in CDMA operation.
- CDMA channels present decoding challenges, enhancing the security of cellular communication.
- It improves transmission security.
- Dropouts occur only when the user is twice the distance from the base station.
Disadvantages
- Channel pollution is a key issue in the CDMA system, which occurs when a user’s phone connects to many cell sites with various intensities, but only one site is powerful.
- CDMA, as a newer technology than GSM, lacks the same level of maturity as an organization.
- Time synchronization is required for CDMA.
- The CDMA system’s performance degrades as the number of users increases.
- The cost is high due to the need for extensive equipment.
Key Differences between FDMA, TDMA and CDMA
| Features | FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) | TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) | CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acronym | FDMA is an acronym for “Frequency Division Multiple Access”. | TDMA is an acronym for “Time Division Multiple Access”. | CDMA is an acronym for “Code Division Multiple Access”. |
| Mode of Operation | It distributes bandwidth among stations by dividing it into sub-channels. | It shares the time of transmission through satellite, not the channel. | It shares time and bandwidth using unique codes for each slot. |
| Codeword | There is no need of any codeword. | There is no need for any codeword. | Codeword is necessary. |
| Flexibility | It is a little flexible. | It is moderately flexible. | It is highly flexible. |
| Rate of Data | It supports a low rate of data. | It supports a medium rate of data. | It supports a high rate of data. |
| Synchronization | It does not require any synchronization. | It requires synchronization. | It also does not require any synchronization. |
| Mode of Data Transfer | It uses continuous signals for data transmission. | It uses signals in bursts for data transmission. | It uses digital signals for data transmission. |
| Terminals | Each terminal has its constant frequency. | Each terminal on the same frequency is active for a short period. | Each terminal can operate simultaneously in the same location without interruption. |
| Cells Capacity | It has limited cell capacity. | It has limited cell capacity. | It has no capacity restriction but is interference-limited. |
| Cost | It has a high installation cost. | It has a low installation cost. | It has a high installation cost, but low operational cost. |
| Guard times and Bands | It requires guard bands. | It requires guard times. | It requires both guard times and guard bands. |
Detailed Comparison between FDMA, TDMA and CDMA
The following are some of the differences between FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA:
- FDMA divides a single bandwidth into sub-channels and distributes it among numerous stations, whereas TDMA just shares the time of transmission through the satellite, not the channel. CDMA, on the other hand, divides time and bandwidth among several stations by assigning a unique code to each slot.
- FDMA requires just guard bands between neighbouring channels, but TDMA requires guard time between adjacent slots. CDMA, on the other hand, requires both guard time and guard bands to ensure optimal operation.
- FDMA operates at a low data rate, while TDMA operates at a medium data rate. In contrast, CDMA operates at a significantly higher data rate.
- FDMA operates without requiring synchronization, while the TDMA system necessitates synchronization. Conversely, CDMA operates without the need for any synchronization.
- FDMA has a significantly low cell capacity, while TDMA likewise has a limited cell capacity. CDMA, on the other hand, has no inherent limitation for a channel, though its performance can be affected by interference.
- In FDMA, a codeword is unnecessary, and the same applies to TDMA. Conversely, CDMA relies on the use of a codeword for its operation.
- FDMA is accomplished by frequency domain filtering, whereas TDMA is accomplished through time domain synchronisation. CDMA, on the other hand, operates through codes and specialised receivers.
- FDMA has less flexibility, but TDMA has considerable flexibility. CDMA, on the other hand, has a high level of flexibility.
Conclusion
- FDMA serves as a channelization protocol, where the available bandwidth is partitioned into distinct frequency bands.
- TDMA serves as a channelization protocol where the channel’s bandwidth is distributed among different stations based on time.
- CDMA is a combination of FDMA and TDMA in which the allocation of resources is affected by both frequency and time.
- FDMA requires just guard bands between neighbouring channels, but TDMA requires guard time between adjacent slots. CDMA, on the other hand, requires both guard time and guard bands to ensure optimal operation.
- FDMA operates at a low data rate, while TDMA operates at a medium data rate. In contrast, CDMA operates at a significantly higher data rate.