Computer networks rely on various communication methods to transmit data between devices efficiently. Unicast, broadcast, and multicast are the three basic communication methods. Each method serves a specific purpose in distributing information across a network. Unicast allows two devices to communicate privately, broadcast sends data to all devices in a network segment, and multicast efficiently sends data to a selected group of devices.
Difference between Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast
The table below illustrates the key differences between unicast, broadcast, and multicast communication methods in computer networks.
| Feature | Unicast | Broadcast | Multicast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | One sender communicates with one receiver | One sender communicates with all receivers | One sender communicates with a group of receivers |
| Data Transfer | Data sent to a single recipient | Data sent to all recipients in a network | Data sent to a specific group of recipients |
| Addressing | Unique destination address used | Special broadcast address used | Special multicast address used |
| Delivery | Assured delivery of data | Not all devices may need the data | Not all devices may need the data |
| Network Load | Generates minimal network traffic | Generates substantial network traffic | Generates moderate network traffic |
| Security | More secure due to specific recipient targeting | Less secure as data reaches all devices | Moderately secure, intended for a specific group |
| Examples | Email, file transfer | DHCP requests, ARP requests | Video streaming, online gaming |
| Recipients | Single recipient | All devices in the network | Specific group of devices |
| Bandwidth Use | Moderate use of bandwidth | High use of bandwidth | Moderate use of bandwidth |
| Latency | Low latency | High latency | Moderate latency |
What is Unicast?
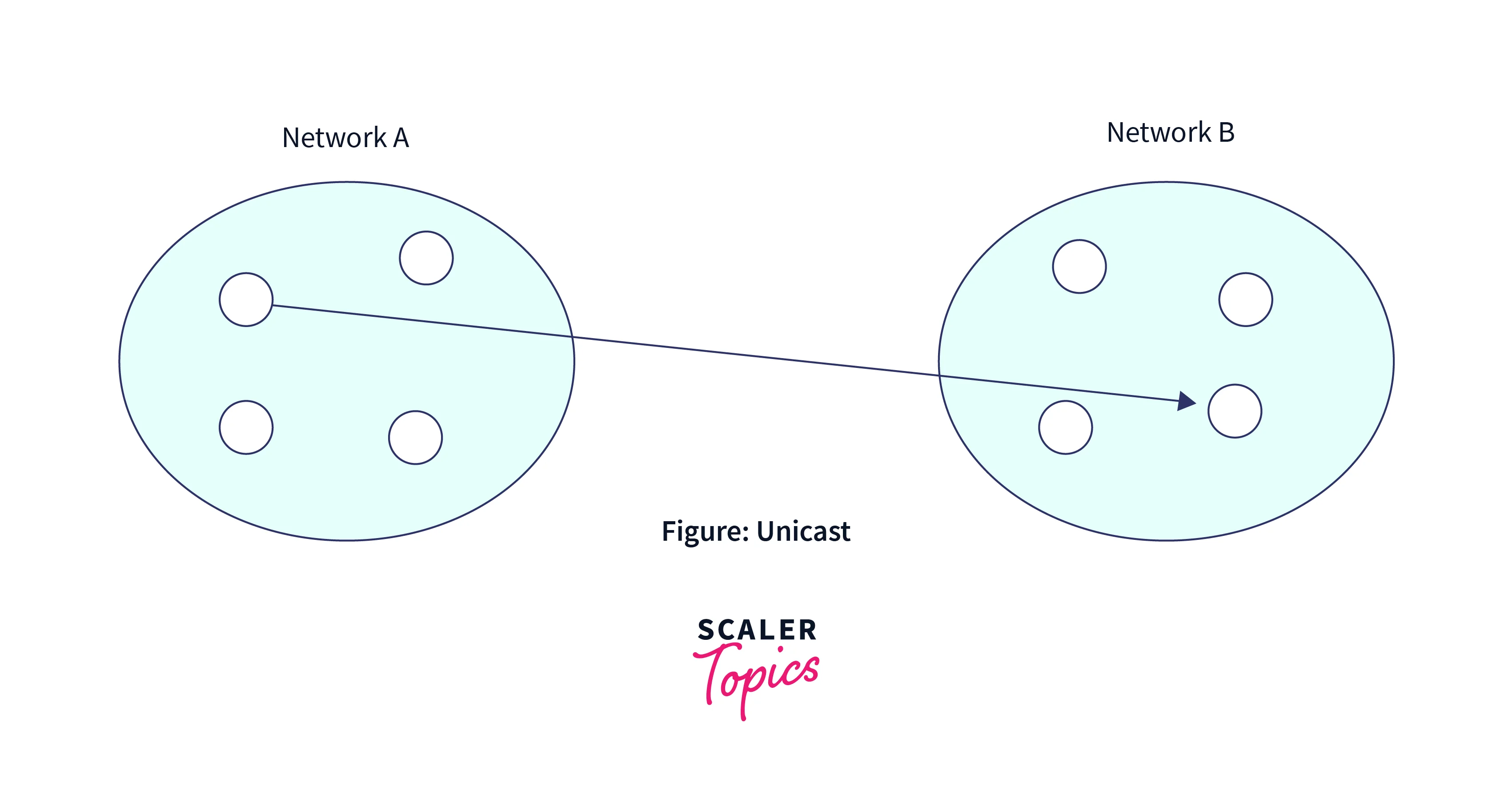
Unicast is beneficial when just one sender and one recipient are involved. In summary, it is a one-to-one transmission. In this method of communication, network switches listen to and recognize the MAC addresses of devices within their connected networks. Following that, they only send packets to networks that contain devices with the corresponding MAC addresses. However, as the number of recipients who need the same data increases, unicast transmission becomes less efficient.
Implementing unicast applications is relatively simple due to their reliance on established IP protocols. However, their efficiency decreases dramatically when conditions require communication among multiple participants. Meanwhile, in many-to-many communication environments, all data stream packets must be transmitted to each host requesting access to the stream. This method is inefficient in terms of network infrastructure and server resources, and it also has obvious scaling issues.
Example
If a device with IP address 10.2.1.0 in one network wants to transmit data packets to a device with IP address 20.11.2.1 in another network, unicast is used. This is the most frequent method of transferring data across networks.
What is Broadcast?
Broadcast transmission involves sending data from one or multiple senders to all receivers within the same network or across different networks. This method is useful for broadcasting network management packets such as ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) and RIP (Routing Information Protocol), where all devices require access to the transmitted data.
There are two types of broadcast transmission:
- Limited Broadcast
- Directed Broadcast
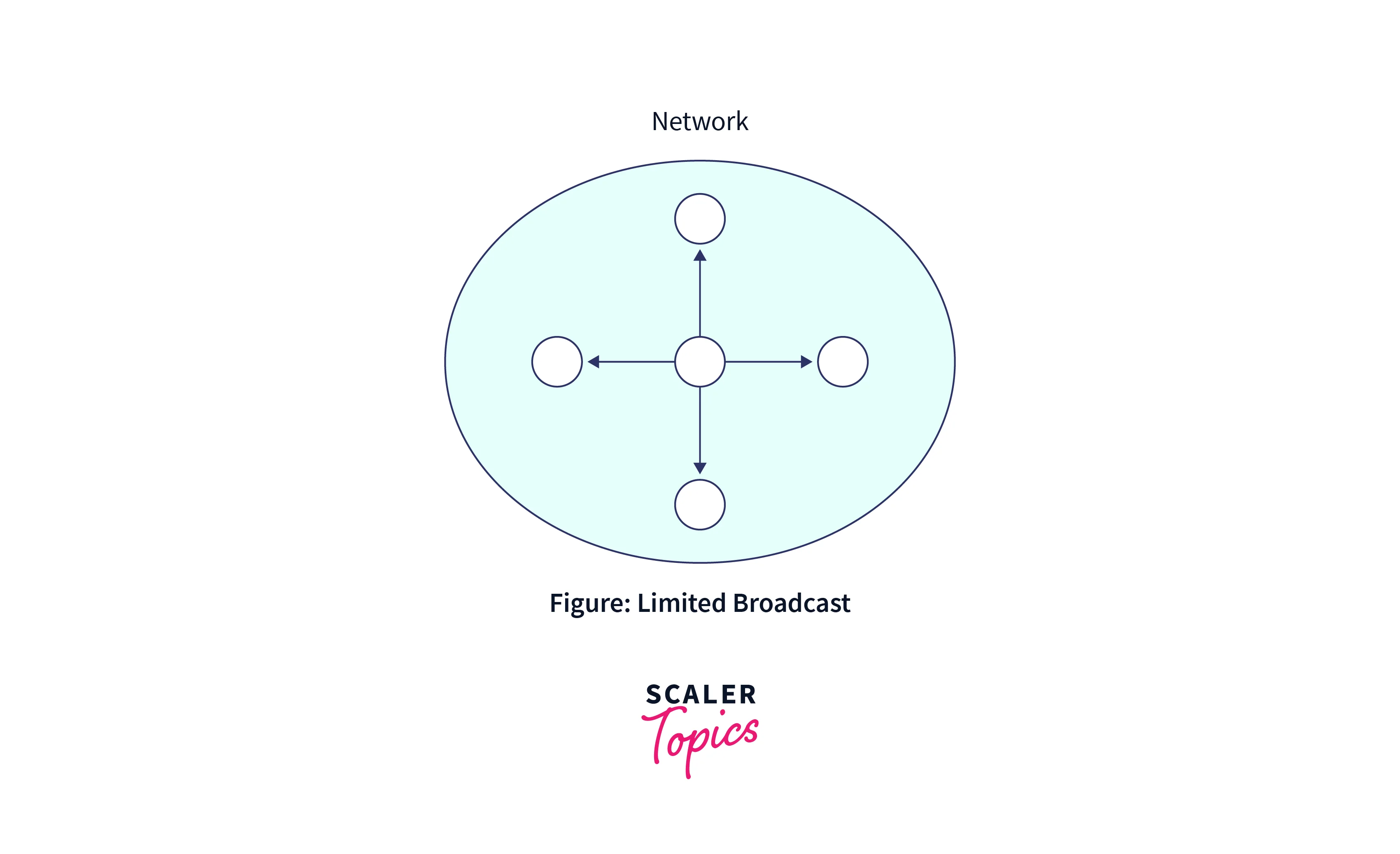
Limited Broadcast
Limited broadcasting is useful when a sender in a network wants to send data to devices on the same network where it is located. This broadcasting provides an appropriate solution if you ever need to send a steady stream of packets to every device connected to your network. To do this, add 255.255.255.255 (where all 32 bits of the IP address are set to 1) to the destination address in each packet’s datagram header. This address is known as the Limited Broadcast Address. It serves the purpose of directing information from a single sender (client) to all recipients across the network.
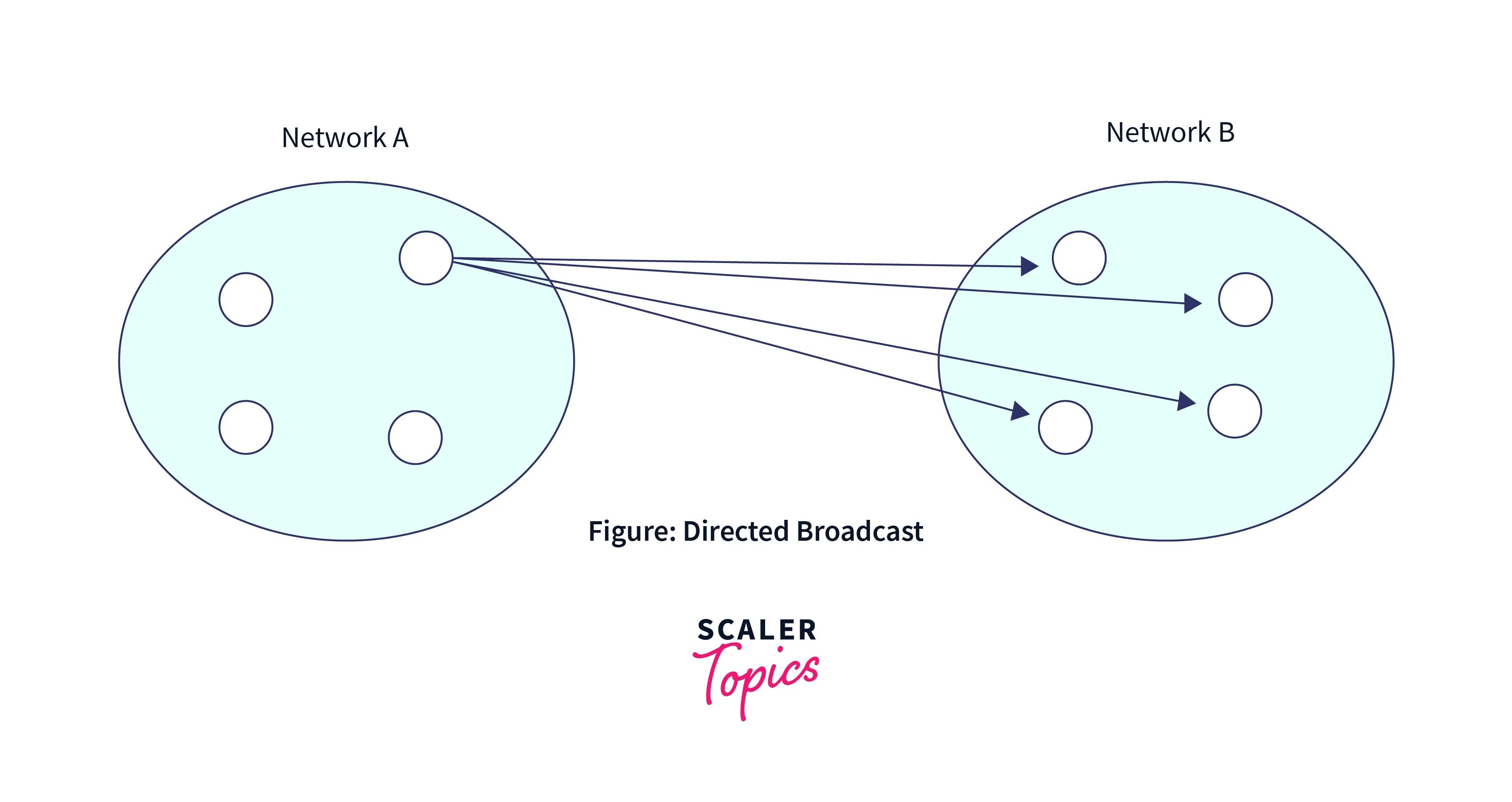
Directed Broadcast
Directed Broadcast transmits data from one source host to all the other hosts that exist in some other network. This is useful when a device in one network wants to transfer packet stream to all the devices over the other network. To achieve this, the Host ID portion of the destination address is converted entirely to 1s, creating what is known as the Direct Broadcast Address. This Direct Broadcast Address is then inserted in the datagram header, allowing information to be sent to multiple recipients. This method is mostly used by television networks for video and audio distribution.
Directed Broadcast is used in two situations:
- When the hosts are responsible for parsing data from broadcast packets.
- When all of the hosts request the same data.
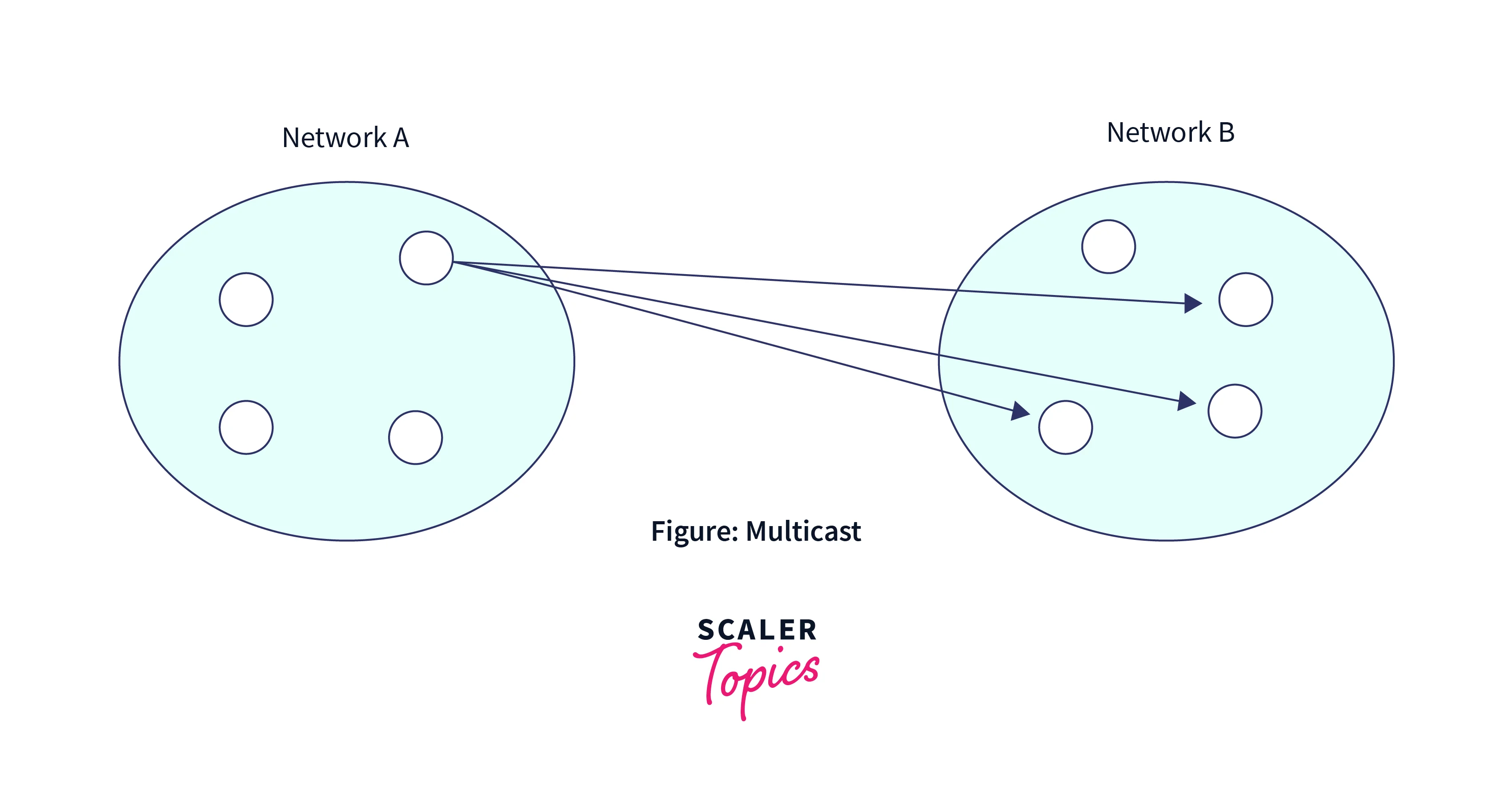
What is Multicast?
Multicasting includes the participation of one or more senders as well as one or more receivers in the data transmission traffic process. This method lies in between the unicast (one-to-one) and broadcast (one-to-all) communication spectrums. Multicast provides the capability for servers to transmit singular copies of data streams, which are then replicated and routed to the hosts that express interest in them. Multicasting requires the assistance of auxiliary protocols such as IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) and multicast routing to operate properly. Class D addresses within Classful IP addresses are specially allocated for multicast groups. This designation allows for efficient organization and management of multicast communication on networks.
Conclusion
- Computer networks rely on various communication methods to transmit data between devices efficiently. Unicast, broadcast, and multicast are the three basic communication methods.
- Unicast is beneficial when just one sender and one recipient are involved. In summary, it is a one-to-one transmission.
- Broadcast transmission involves sending data from one or multiple senders to all receivers within the same network or across different networks.
- Limited broadcasting is useful when a sender in a network wants to send data to devices on the same network where it is located.
- Direct Broadcasting is useful when a device in one network wants to transfer packet stream to all the devices over the other network.
- Multicasting includes the participation of one or more senders as well as one or more receivers in the data transmission traffic process.