Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a network protocol. EIGRP protocol allows the routers for transmitting information in a more efficient way than earlier network protocols. EIGRP protocol is the enhancement of the IGRP protocol and it uses the same distance vector algorithm and distance information as used by the IGRP protocol.
Introduction to Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a network protocol that enables routers to exchange information more efficiently than earlier network protocols, such as Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). The distance vector algorithm and distance information used by the EIGRP protocol is similar to the IGRP protocol. The name of this protocol suggests that this protocol is the enhancement in operating efficiency and convergence properties over the IGRP protocol. EIGRP is considered dynamic writing used to select the best path for transmitting the packet between any two devices working on layer 3. It operates on the network layer of the OSI model and this protocol uses 88 port numbers.
EIGRP Fundamentals
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol abbreviated as EIGRP is a dynamic protocol. This protocol is used for the decision and configuration of the routers. EIGRP transmits incremental updates only. Transmitting incremental updates only decreases the router’s workload and also reduces the amount of information exchanged. EIGRP is considered a classic hybrid protocol and supports the classless routing type. EIGRP protocol is considered one of the classic hybrid protocols and classless routing is supported by this protocol. It also enables automatic manual summarization on an EIGRP-enabled interface. For managing the un-equal cost and equal-cost path it performs load balancing. Hybrid protocols combine reactive and proactive protocols capabilities for better results. In classless routing, if no specific routes are founded then the default route is used by the router for forwarding the traffic. For performing all the functioning of EIGRP 3 types of tables are created:
- Neighbor Table
- Topology Table
- Routing Table
Ideas and concepts used behind the above 3 tables are given below:
Neighbor Table
- The neighbor table is a table that consists of router information and the information of neighborship relations with which the relationship is established.
- For listing router information command is: show ip eigrp neighbors
- The neighbor table consists of fields such as Address, Hold Time, Smooth Round Trip Time, Interface, Retransmission Timeout, Handle, Uptime, Queue Count, and Sequence Number.
Topology Table
- The topology table is a table that contains the information related to all the paths to the network that are understood by the EIGRP.
- For listing router information command is: show ip eigrp topology .
- The topology table consists of fields such as Feasible distance, passive, Advertised distance, and Feasible Distance.
Routing Table
- The routing table contains the information on routes currently participating in transmitting the packets to the network.
- The routing table stores the routes which are currently active in sending packets to the network. It stores the optimal route for the destination from the sender.
- For listing router information command is: show ipv6 route .
- The routing table consists of fields such as GigabitEthernet0/1, D, 90/ 5632. Via 11.0.0.2.
EIGRP Configuration Modes
There are two methods of EIGRP protocol configuration modes which are given below:
Classic Configuration Mode
When we use the classic mode of EIGRP configuration then most configurations will be done in the process of EIGRP but some of the settings are required to be configured in the interface configuration submodel. Because users are required to scroll back and forth between the individual network interfaces and the EIGRP process so this may result in an increment of troubleshooting and deployment complexity. Split-horizon, authentication, hello advertisement interval, and summary route advertisements are some of the settings that are required to be set individually.
EIGRP Named Mode
EIGRP Named Mode is developed to overcome the difficulties faced by network engineers in the classic mode of EIGRP configurations. Scattered configurations and unclear scope of commands are some of the difficulties of classic configuration mode which are overcome by this mode.
Path Metric Calculation
For Any type of Routing protocol calculating metrics is considered a critical component. Multiple factors are used by the EIGRP protocol for calculating the path metric. By default bandwidth and delay are used for calculating the metric but interface load and reliability can also be involved. Below is the formula given for EIGRP classic metric.
EIGRP Classic metric formula:
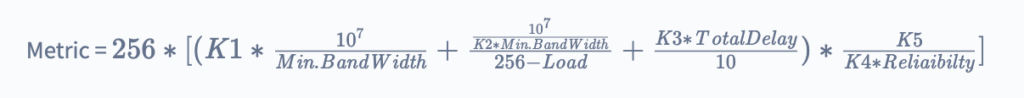
The value of k is used by EIGRP for defining the factors used by the formula and to define the impact of the factor at the time of matric calculation. And there is a misconception related to the k value that the key value can directly be applied to load, delay, bandwidth, or reliability but this is not an accurate thing.
The lowest link of the path is represented by bandwidth and its scale up to 10 GPS. The collection of link speed is done from the configured interface band on an interface. Delay is calculated as the total delay measurement in the path and delay is measured in terms of microseconds which is represented by μs.
The formula of EIGRP is formed based on the metric formula of IGRP except for the multiplication of output by 256 for a change in metric from 24 to 32 bits. By considering all the above definitions the EIGRP protocol formula derived is given below.
EIGRP Classic metric formula with definitions:
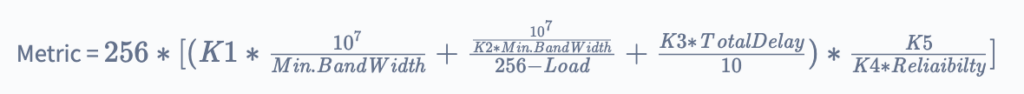
The value of K1 and K3 is one by default, and the value of K2 K4, and K5 is said to be zero. After placing the default value of k we get a formula-streamlined version. And that streamlined version is given below.
EIGRP Classic metric formula by putting default values of K:
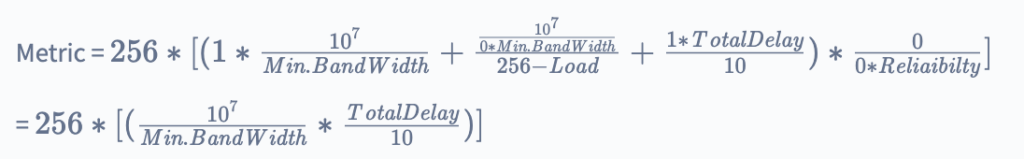
Path attributes established with every prefix are included in the update packet of EIGRP. The path attributes of EIGRP may consist of minimum bandwidth link speed, hop count, RD, and cumulative delay. Every hop on the way updates the path attributes, which enables us to find the shortest path by every router independently.
Below is the table given which represents the commonly used network types, delay, link speeds, and EIGRP metric, using the streamlined formula.
| Type of interface | Speed of Link(kbps) | Delay | Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serial | 64 | 20,000 μs | 40,512,000 |
| T1 | 1544 | 20,000 μs | 2,170,031 |
| Ethernet | 10,000 | 1000 μs | 281,600 |
| FastEthernet | 100,000 | 100 μs | 28,160 |
| GigabitEthernet | 1,000,000 | 10 μs | 2816 |
| TenGigabitEthernet | 10,000,000 | 10 μs | 512 |
Define Key Terms
- Autonomous System: An autonomous system is a system that consists of a group of networks or a single network that is all supervised and managed by An autonomous system (AS) is a network or a collection of networks that are managed and supervised by one organization or an entity.
- Successor route: The route which is the best metric for reaching the destination is the successor route. And routing table is used to store the successor route.
- Feasible successor: The backup path used immediately for reaching the destination if the successor path fails is considered the feasible successor and the topology table is used to store the feasible successor.
- Topology table: The topology table is a table that contains information related to all the paths to the network that are understood by the EIGRP.
- EIGRP classic configuration: In the classic mode of EIGRP configuration, most configurations will be done in the process of EIGRP protocol but some of the settings are required to be configured in the interface configuration submodel.
EIGRP named mode configuration:EIGRP Named Mode is developed to overcome the difficulties faced by network engineers in the classic mode of EIGRP configurations.
Use the Command Reference to Check Your Memory
| Task | Command Syntax |
|---|---|
| EIGRP Initialization in classic configuration mode | router eigrp as-number |
| network network mask | |
| router eigrp process-name | |
| EIGRP Initialization in named configuration | address-family {ipv4 / ipv6} {unicast vrf vrf-name} autonomous-system as-number |
| network network mask | |
| Defining the router ID of the EIGRP | eigrp router-id router-id |
| Classic: (EIGRP Process) | |
| For preventing neighbor adjacencies, configuring an EIGRP-enabled interface | passive-interface interface-id |
| Named Mode: af-interface {default / interface-id} | |
| passive-interface | |
| Configuring a keychain for MD5 authentication of EIGRP | key key-number key-chain-name |
| key key-number | |
| key-string password | |
| Classic: (EIGRP Process) | |
| Configuring MD5 authentication for an interface of the EIGRP | ip authentication key-chain eigrp as-number key-chain-name |
| ip authentication mode eigrp as-number md5 | |
| Named Mode: af-interface {default / interface- id} | |
| authentication key-chain eigrp key-chain-name | |
| authentication mode md5 | |
| For EIGRP named mode interfaces, Configuration of SHA authentication | Named Mode: af-interface {default / interface-id} |
| authentication mode hmac-sha-256 password | |
| Modification of the interface delay for an interface | delay tens-of-microseconds |
| Modification of the K values of EIGRP | metric weights TOS K 1 K 2 K 3 K 4 K 5 [K 6 ] |
| Modification of EIGRP maximum-paths default number that can be installed | maximum-paths maximum-paths |
| Modification of variance multiplier of EIGRP for load balancing of unequal-cost | variance multiplier |
| Show EIGRP-enabled interfaces | show ip eigrp interface [{interface-id [detail] / detail}] |
| Show EIGRP topology table | show ip eigrp topology [all-links] |
| Displaying the Configured EIGRP passwords and keychains | show key chain |
| Displaying the information of IP routing protocol that is configured on the router | show ip protocols |
Conclusion
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a network protocol that enables routers to exchange information more efficiently than earlier network protocols.
- EIGRP protocol is an enhancement over the IGRP protocol.
- The EIGRP protocol creates Neighbor Table, Topology Table, and Routing Table for performing its functioning.
- Classic Configuration Mode and EIGRP named mode are two configuration modes of the EIGRP protocol.