An active directory is used for the management of computers and other devices on a network. Active Directory is a directory service that runs on Microsoft Windows Server. It is used for identification and also provides access management. Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is the most important component of Active Directory. The hierarchal structure of the active Directory includes domain, trees, forest, organizational unit, and container.
Introduction to Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft technology and is used for managing computers and other devices on a network. Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is the most important component of Active Directory and provides the core service for authenticating users and helps in determining which service they can access or not. Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) also manages computers and users and provides services to sysadmins to organize the data into logical hierarchies.
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) plays the role of a crucial server within Microsoft’s Active Directory (AD) platform.
- AD DS is one of the core services in
AD. - AD DS enables the storing and management of users’ information, services, and devices connected within the network into a tiered structure.
- AD DS are hosted by the servers that are called Domain controllers (DCS).
- An organization may also have some DCs, and every DC in an organization stores a copy of the AD DS for their whole domain.
- AD DS is used by almost every organization for managing on-premises
IAM(Identity and access management) in a Windows environment.
History of Active Directory Domain Services
- The lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) is kicked off largely by modern
IAM(Identity and access management) space. IAM space contains many directories including internet white pages, domain name systems (DNS), and email systems. However, these directories are not able to define the standards for a true directory service such as LDAP. - LDAP acted as a basis for two of the major directory services solutions:
- * Microsoft AD: Active directory is a Microsoft technology used for the management of computers and other devices on a network.
- * Open source LDAP (OpenLDAP): OpenLDAP is considered an open-source, free implementation of the LDAP protocol, and LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol that defines the protocol for communication of the user with the directory server.
- However, the main aim of
ADis to become a leader in the commercial market on the other side the open source market is led by OpenLDAP. - Both these solutions are widely considered as the underlying protocols for identity providers (IdPs) worldwide. The major idea used by an IDP was the creation of central user and data storage for an organization. Then after it, user accounts would be stored within the specific IDP along with the information of IT resources.
- These two object sets then interrelated with each other to connect to the IT resources they require. Some of these resources such as systems, networks, applications, and more, would each be tied directly to the user identities that needed them, as well as limited by the privileges of that specific user’s role.
- If we see in the case of Active Directory Domain Services, then this was done largely for Windows networks and resources. Because in the present time, an average network of IT is virtually based on Windows. Whenever the user logs in to their machine with their details, AD DS allows them to access all resources according to the requirements of the user.
How are Active Directory Domain Services Used?
Active Directory is a directory service that runs on Microsoft Windows Server. It provides the service of identity and access management. AD DS generally stores and organizes information about the users, devices, and services connected to a specific network. AD DS is also used in on-premises Windows environments, and for cloud-based Windows environments, Microsoft Azure AD DS is used. They can also be used together in hybrid cloud environments.
Working on Active Directory Domain Services
AD DS is the most important component of Active Directory which allows users to authenticate and also access resources on the network. Active Directory organizes objects into a hierarchy, that allows various Domain Services to connect with them and users to access or manage them. The hierarchical structure of AD DS is given below:
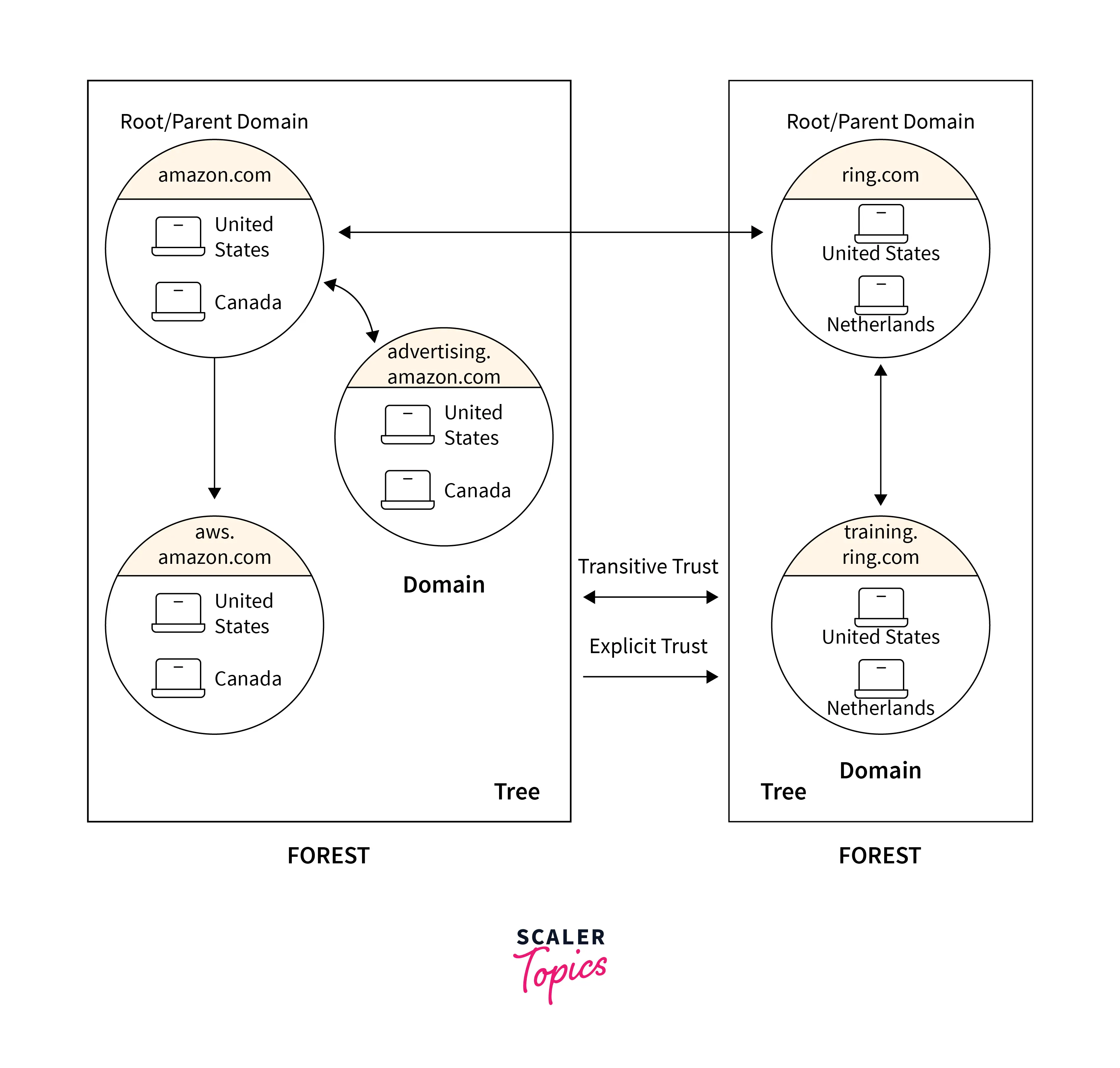
Domains: A domain is a collection of objects, such as users or groups of devices, and these must share the same AD database. You can also consider a domain as a branch in a tree. The structure of the domain is similar to standard domains and sub-domains. A domain can also consist of multiple other sub-domains and those subdomains also have their sub-domains.
Organizational units: Within a domain, the organization of objects is done by Organizational units. It is considered the smallest unit and the IT team can assign group policy settings. or account permissions to this smallest unit.
Active Directory trees: An AD tree is a collection of multiple domains in a logical hierarchy. And there is a bond between these domains in a tree known as trust. The tree can also be considered as a group of multiple domains within a similar Active Directory Network and they share common namespaces and boundaries.
Active Directory forests: In this AD functional level, multiple trees are grouped. Trees also share trust in an AD forest, just like domains share trust in a tree. Trusts enable constituent parts of a tree or forest to share resources like directory schemas, configuration specifications, and many more.
The Hierarchical Structure of Active Directory Domain Services
Domains
The domain is used for representing groups of objects such as users, groups, and devices having the same AD database. You can imagine a domain as a branch in a tree. The structure of the domain is the same as that of standard domains and sub-domains. In the domain, transitive trust relationships are used for the authentication of users.
Trees
A tree is a group of two or more domains arranged in a logical hierarchy. Since domains in a tree are related to each other that’s why they are said to “trust” each other. The group of domains that are connected in a tree shares a common namespace and boundary. Every domain has exactly one root or we can say that each domain has one parent, which allows for forming a hierarchical structure. However, the common namespace is not shared by two different trees.
Forest
The highest level of organization within AD is a forest which is a collection of a group of trees. Like the trees in a forest can also trust each other, the domains also share their directory schemas, catalogs, application information, and domain configurations with each other. Every forest has a global single address list and every forest also shares a database security boundary. IT administrator or user who was in one forest by default is not allowed to access another forest.
Organizational Units(OU)
An OU is the smallest unit used to organize users, groups, computers, and other organizational units. IT team can assign the group setting policy and account permissions to the organizational units. There are multiple OUs in each organizational unit. But in the OU all the attributes do not share AD objects.
Containers
A container is the same as that of an OU, however, unlike an OU, it is not possible to link a Group Policy Object (GPO) to a generic Active Directory container.
Refer to the below image to show the hierarchical structure of ADDS
Services Provided in Active Directory Domain Services
The following are the services provided by the active directory domain services:
Lightweight Directory Services
AD LDS is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory service. It becomes more versatile in terms of where it can be run by providing only a subset of AD DS. For example, it can be run as a stand-alone directory service without proper integration of ActDirectory’s full implementation.
AD LDS is similar to Domain Services, but it allows usage of Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), which may lead to very few restrictions. AD LDS provides cross-platform capabilities, for example, Linux-based computers function on the network.
Certificate Services
Certificate Services provide the facilities to create and manage digital certificates, signatures, and public key cryptography by the domain controller. Also allows the creation, management, and sharing of encryption certificates, through this users can exchange information securely over the Internet.
Active Directory Federation Services:
ADFS is a Single Sign-On (SSO) solution for AD which provides the facility of accessing multiple applications with a single set of credentials, thus simplifying the experience of the user.
A single sign-on authentication service is also provided by AD FS that allows users to sign in once so that they can access multiple applications in the same session.
Rights Management Services
Controlling data access policies and providing access rights is one main service provided by the right management services. For example, Rights Management allows the determination of folders that users can access. AD RMS is a set of tools that allow the management of security technologies that will help organizations to keep their data secure. Some of these techniques are encryption, certificates, and authentication, and cover a range of applications and content types, such as emails and Word documents.
Domain Services
Domain Services allows us to store centralized directory information and lets users and domains communicate with each other. Whenever a user tries to connect to a device or resource in a network, they may go through login authentication, verifying the user’s login credentials and then access permissions.
Advantages of Active Directory Domain Services
- You can organize your data in a customized manner so that you can meet your company’s requirements
- If necessary, AD DS can be managed from any computer on the network.
- Built-in replication and redundancy are also provided by AD DS, due to some reasons if one Domain Controller (DC) fails, then another DC picks up the load.
- It keeps network access rights management centralized as all access to network resources needs to go through AD DS.
- Providing a hierarchical structure for the information stored in Active Directory is also one of the main advantages of Active Directory Domain Services
- The service of flexibility in determining how data is organized on the network is also provided by AD DS. Administrative tasks are simplified by centralizing services like user and rights management and providing some security. Active Directory can be accessed by the user from any computer on the network.
- Single point of access is also one of the advantages of AD DS, which is created by Domain Services. This allows IT teams to collaborate more efficiently and limit access points to sensitive resources.
Role of Domain Controllers in Active Directory Domain Services
The domain controller is a server that runs on AD DS. The main work of domain controllers is to host and replicate the directory service database within the forest. The services for managing and authenticating resources within a forest are also provided by the directory service. Some essential services in AD DS are hosted by these servers. Some of them are given below:
- Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC)
- NetLogon (Netlogon)
- Windows Time (W32time)
- Intersite Messaging (IsmServ)
Conclusion
- Active Directory is a directory service that runs on Microsoft Windows Server
- You can organize your data in a customized manner using AD DS
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is the core function in Active Directory that manages users and computers
- Domain controller is a server that runs on AD DS and its main work is to host and replicate the directory service database within the forest.
- Active Directory Federation Services, Certificate Services, and Lightweight Directory Services are some of the services provided by AD DS.
- Hierarchal model of AD DS includes domain, trees, organizational unit, container
- The modern
IAMspace largely kicked off with the lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP).