The application layer is primarily responsible for setting up a model to identify communication methods to allow users and hosts to interact with the software applications available on the internet.
Several application layer protocols help in the efficient working of our application layer in the network model. The protocols work similarly in different network models that have come into existence. The most common application layer protocols are HTTP, TELNET, DNS, SMTP, and so on. These protocols mechanize a way for users to communicate and interact over the World Wide Web.
What are the Application Layer Protocols?
Protocols in the application layer work similarly in both network models.
We need a model to enable applications to communicate with each other over the Internet. For the same, we have two models.
- OSI model:
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model states the functioning of a networking ecosystem and uses seven layers to do it.
The seven layers are depicted in the image below: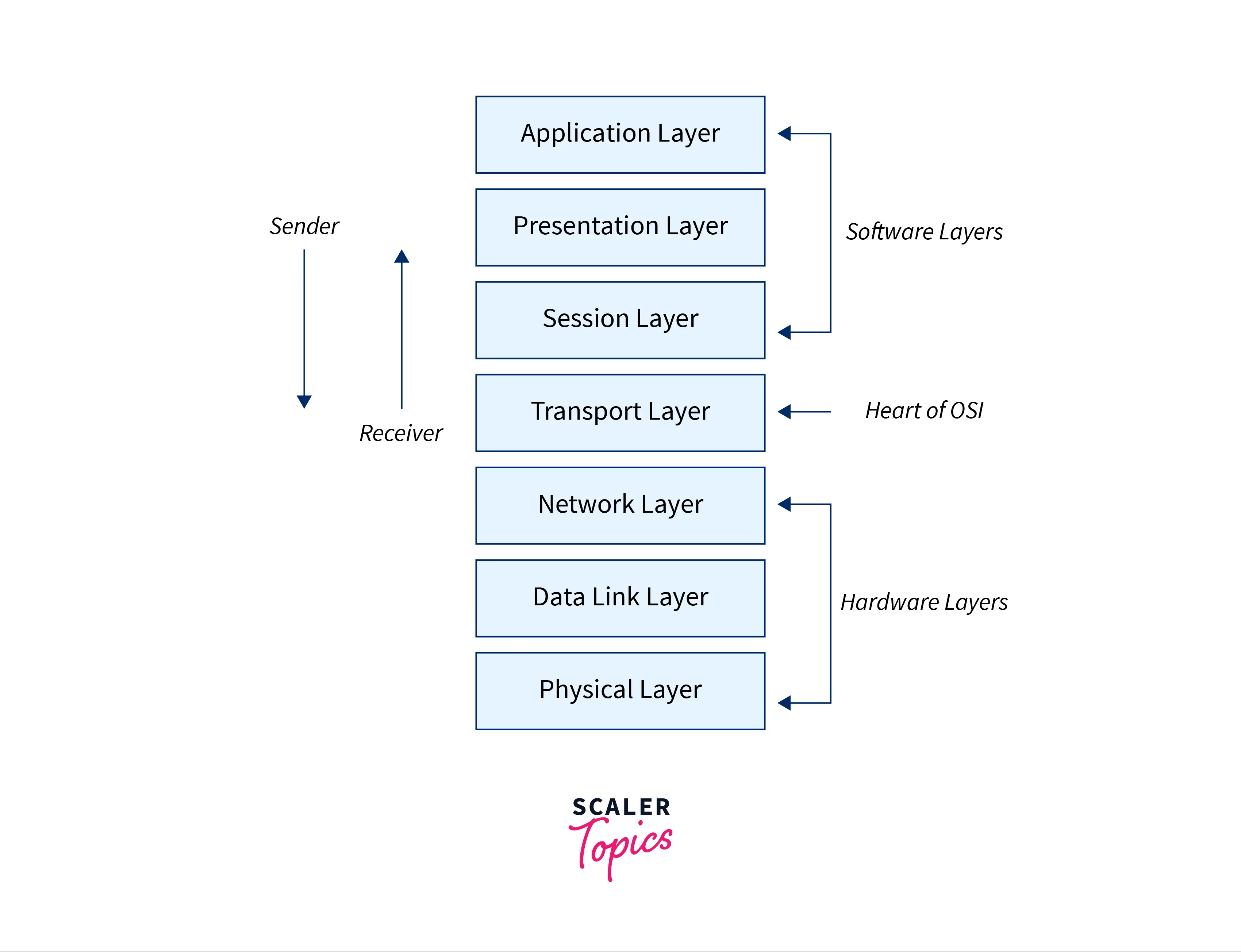
- TCP/IP model:
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol briefs the OSI model into four layers.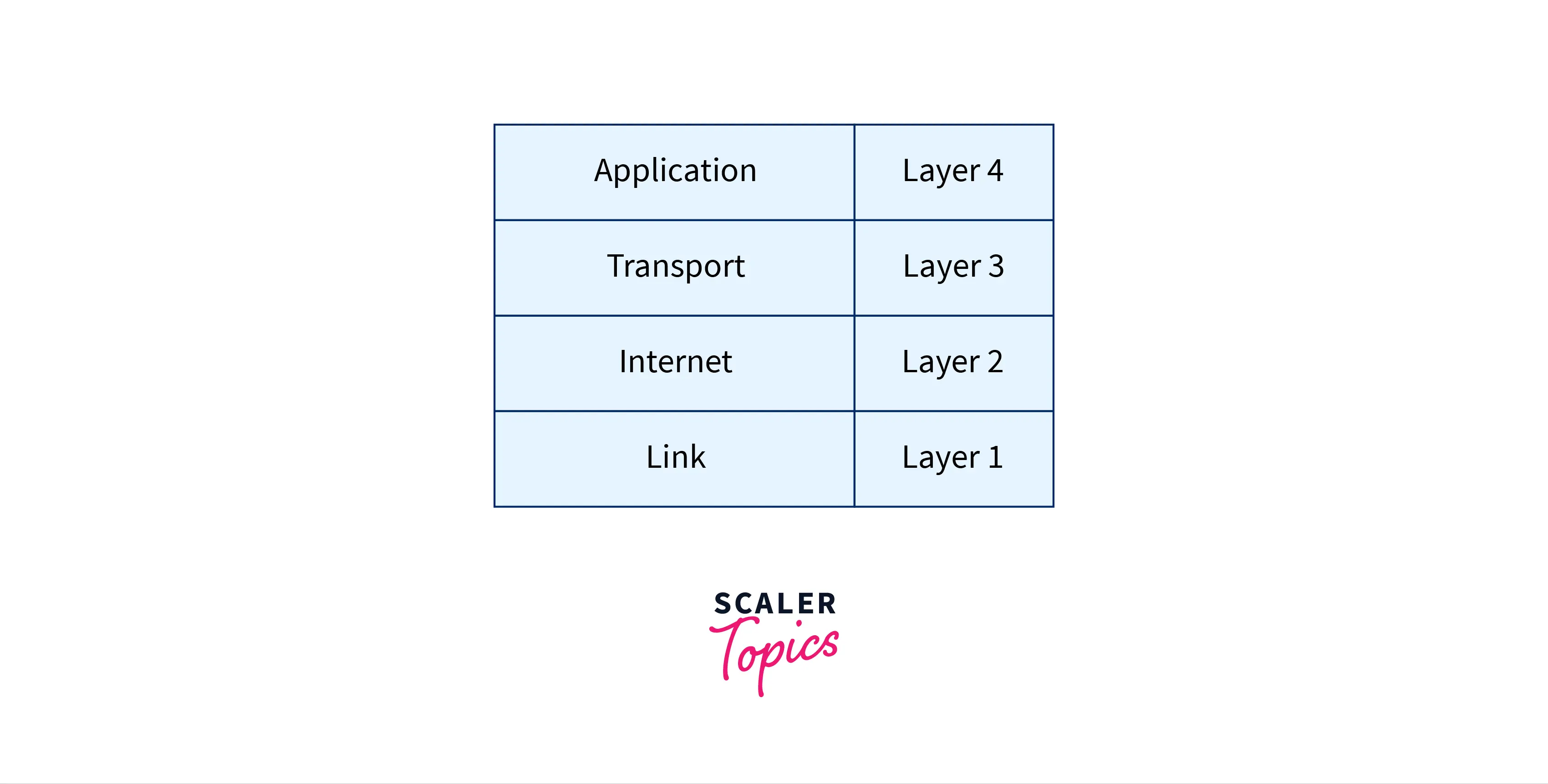
Each layer follows its different protocols for its efficient working. The topmost layer in both the models is known as the application layer & it facilitates users to interact with each other over the internet through different services.
Note:
The application layer and its protocol work similarly in both models.
List of the Application Layer Protocols
Protocols in each layer of the network model provide a mechanism for devices to identify and connect. They also contain formatting rules specifying how data is packaged when the messages are sent and received.
There are several protocols in the application layer used for different services like email services, file transfers, etc. We will look at each one of them one by one.
1. DNS
A service that is used to translate domain names (google.com) to their corresponding IP addresses (8.8.8.8).
DNS stands for “domain name system”. It is used for an effective translation of internet domain names into internet protocol addresses. What does this mean? As humans, we work with a name to identify a particular website. However, that is not how computer networks understand. For viable communication between humans and systems, we need DNS.
For example, the public IP address 1.1.1.1 is used through which the computer locates our desired website i.e. cloudflare.com. An IP address is a 32-bit number similar in structure to 227.82.157.177.
The following are some characteristics of DNS:
- The port number used is number 53.
- The domain name is usually contained in a URL.
- The domain name system follows a hierarchy which is an inverted tree-like structure to manage its distributed database system.
Most activities on the web rely on DNS to quickly make a connection between our computer & remote hosts of our desired location on the internet. The DNS service can be mapped to a phone book service where we receive the phone number using the name of the person we are looking to communicate with.
To understand the simple working of the DNS service, look at the image below:
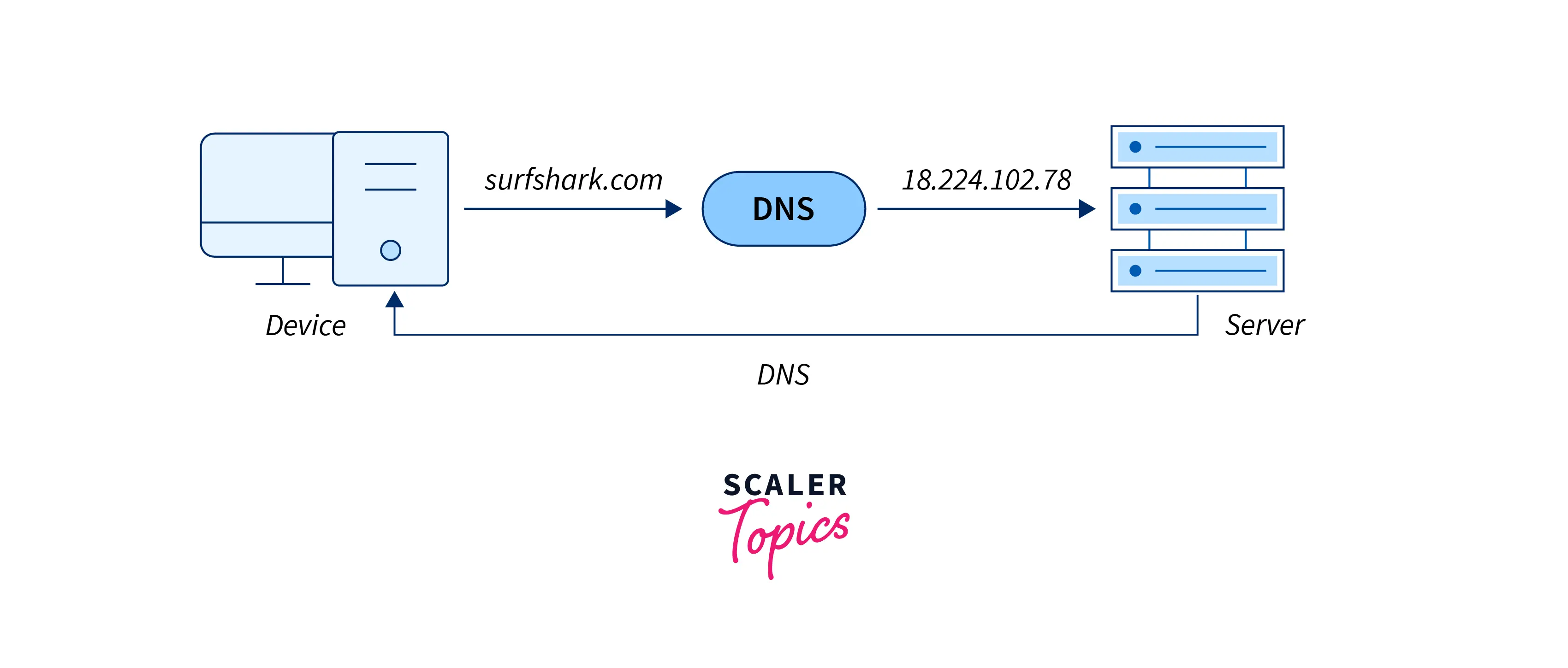
As we can see, if we want to redirect to Google, we will type google.com & DNS will translate it to 216.58.200.206 for connecting our local system to the remote host.
Note:
A domain name can have multiple IP addresses. For example, google.com corresponds to 216.58.200.206, 142.250.193.78, and many more IP addresses. To understand more about the working of DNS, refer to this article
2. TELNET
TELNET provides communication facilities between two hosts using the CLI.
TELNET is used for communication through the command line interface between remote device(s) or server(s). It stands for TELetype NETwork & configures elements of networking hardware.
Some characteristic features of TELNET are:
- It is a client-server type of protocol.
- It is a bidirectional and interactive communication feature for terminals and terminal-oriented processes.
- Information is distributed over an 8-bit byte-oriented data connection.
- On local machines, it is implemented as a program telnet. On remote machines, it works as the daemon in .telnet. A “daemon” is synonymous with a server or agent.
- The port number used is number 23.
The two hosts can communicate over the TELNET user interface through two means:
line-by-line or character-by-character basis.
The below image helps us to understand the working of this protocol:
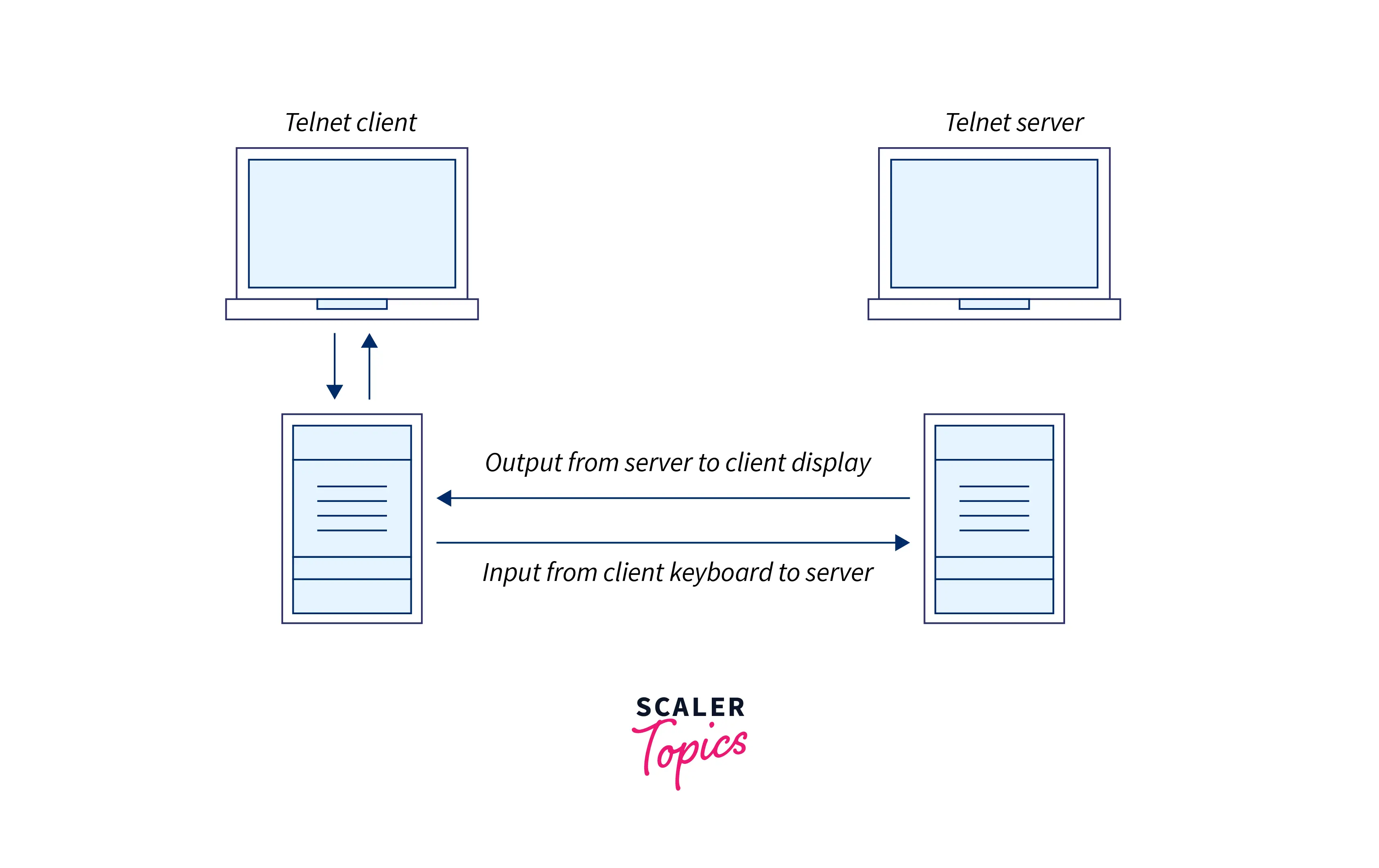
It can be used for testing and diagnosing remote web/mail servers. It is also used by other protocols like FTP to form protocol control channels. Let us look at some advantages and disadvantages of this protocol :
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. It is versatile. | 1. The data exchange is unencrypted, which makes sharing of delicate information like passwords and user IDs unsafe. |
| 2. It can be used cross-platform. | 2. Full access makes it easier for hackers to enter. |
| 3. It provides unlimited access to target resources. | 3. Using TELNET, only a few servers can be reached. |
3. FTP
It models a protocol to download, upload, and transfer files between two devices over the internet.
FTP stands for “File Transfer Protocol” and connects two computer systems to transfer files over a network. Users need to grant access using FTP to receive and send files. Transferring files is a straightforward mechanism, so why do we need FTP? Because it overcomes these problems between two systems :
- Different file conventions.
- Different ways to represent text and data in the files.
- Different directory structures.
But how does it overcome these problems? By establishing two connections between the hosts :
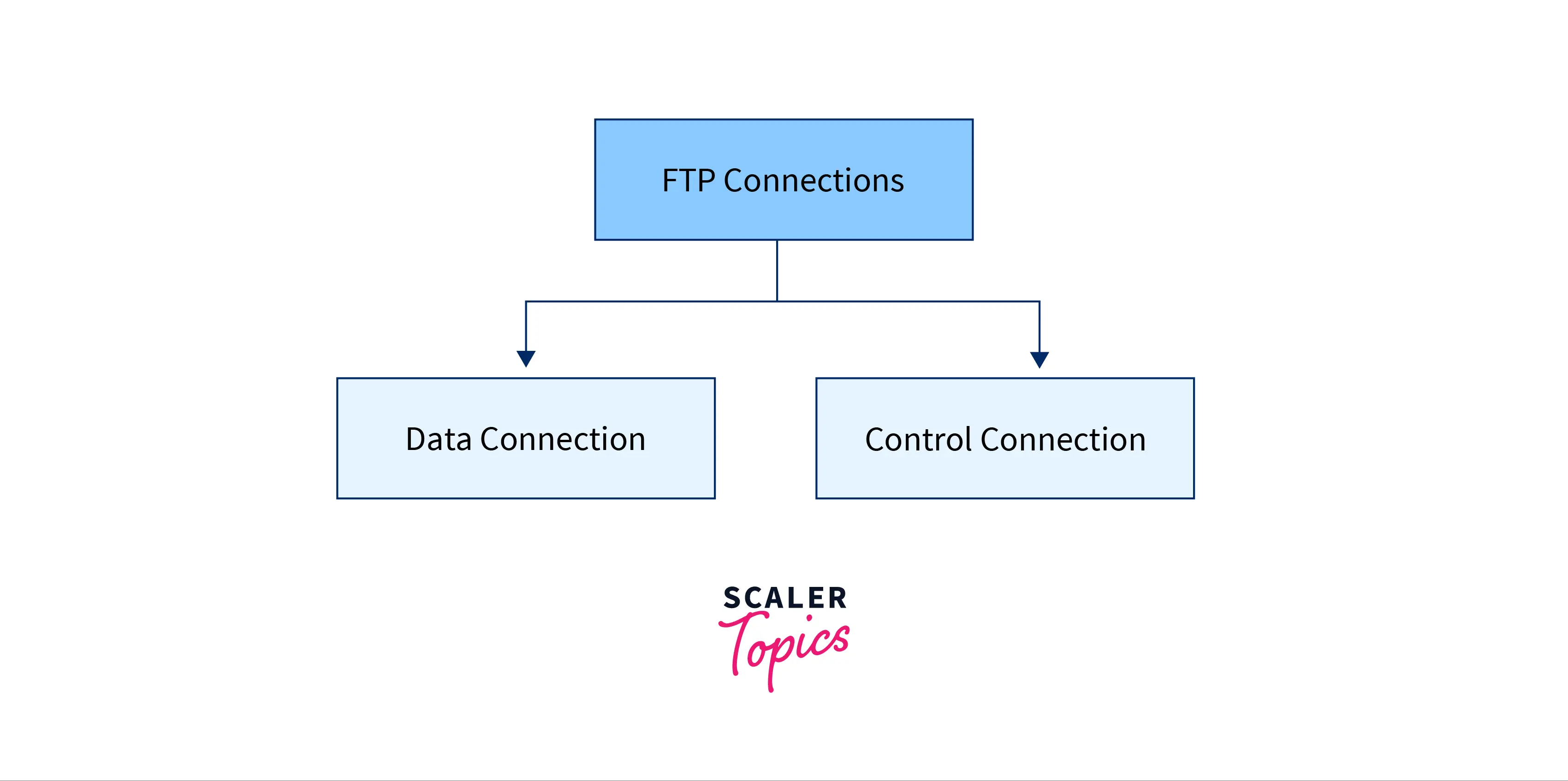
- Data Transfer:
Data connections made during data transfer processes that use complex rules as data types can vary greatly. - Control Connection:
It uses relatively simple rules for communication and is used to transfer a line of command or response at a time.
These are the common characteristics of FTP protocol:
- Users require an internet connection to accomplish FTP transfers.
- It promotes remote transfers.
- The Port number for FTP is 20 for data and 21 for control.
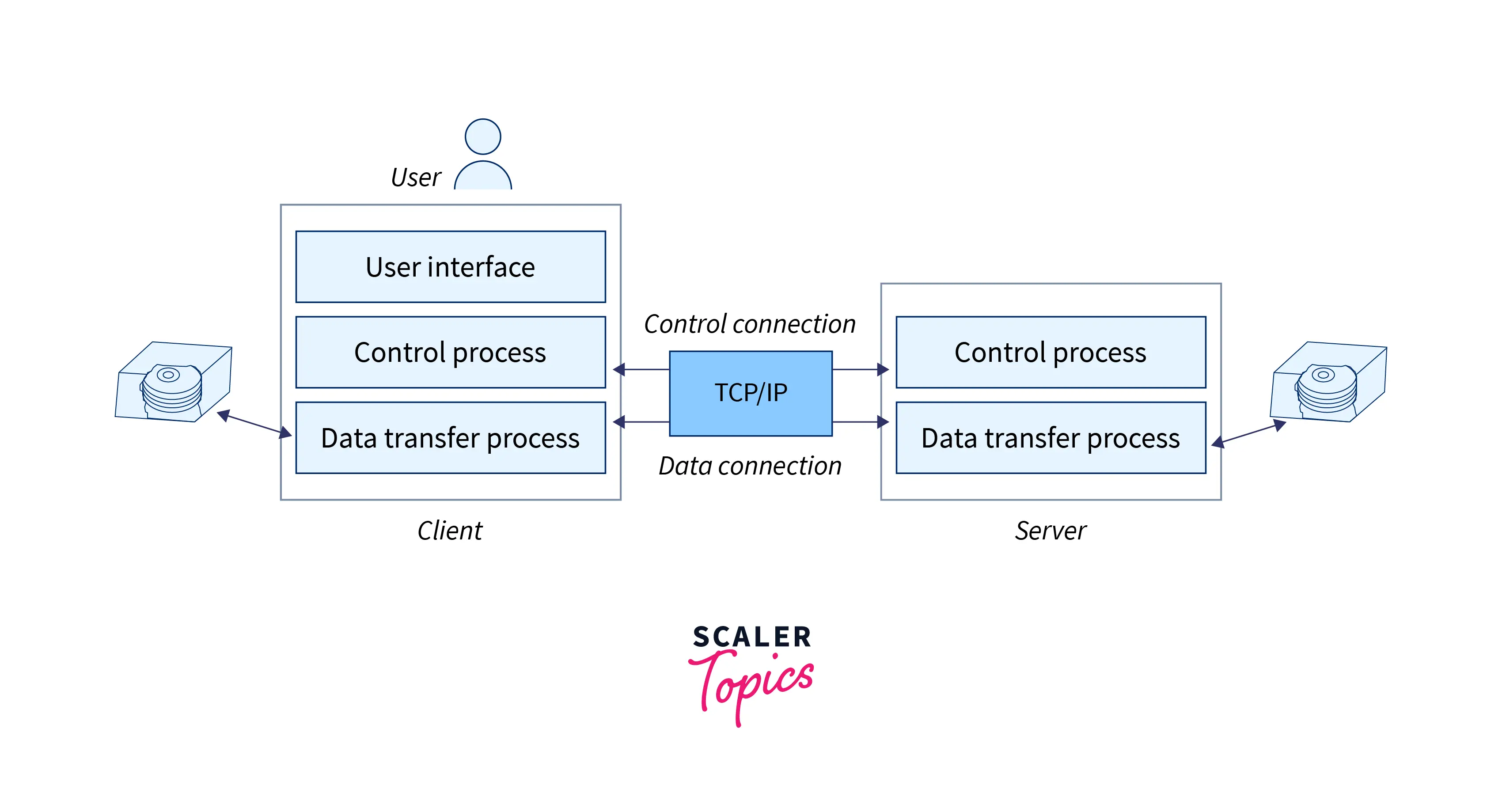
The basic client model of FTP contains three components:
the user interface, control process, and data transfer process whereas the server model contains two units: the server control process and the server data transfer process.
The below image depicts the mechanism of FTP:
FTP is one of the fastest ways to transfer files, is efficient, and needs a username & password to access the server which makes it secure. However, it is not compatible with every system and doesn’t allow running concurrent transfers to multiple receivers.
4. TFTP
A concise version of FTP, it provides a lightweight file transfer mechanism.
A simplified version of FTP, Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is mainly used for reading and writing files to or from a remote server. It also facilitates file transfer, however, with no user authentication. Major characteristics of TFTP are :
- The port number used is number 69.
- It has limited features and provides no security during the transfer of files.
- It is a lightweight file transfer mechanism.
It is often used on private local networks where adapting FTP can be expensive in its implementation or cost. It comes in handy where there are no hard disk drives or storage devices as the implementation is easy using a small amount of memory.
The other common uses can be depicted by the image below: 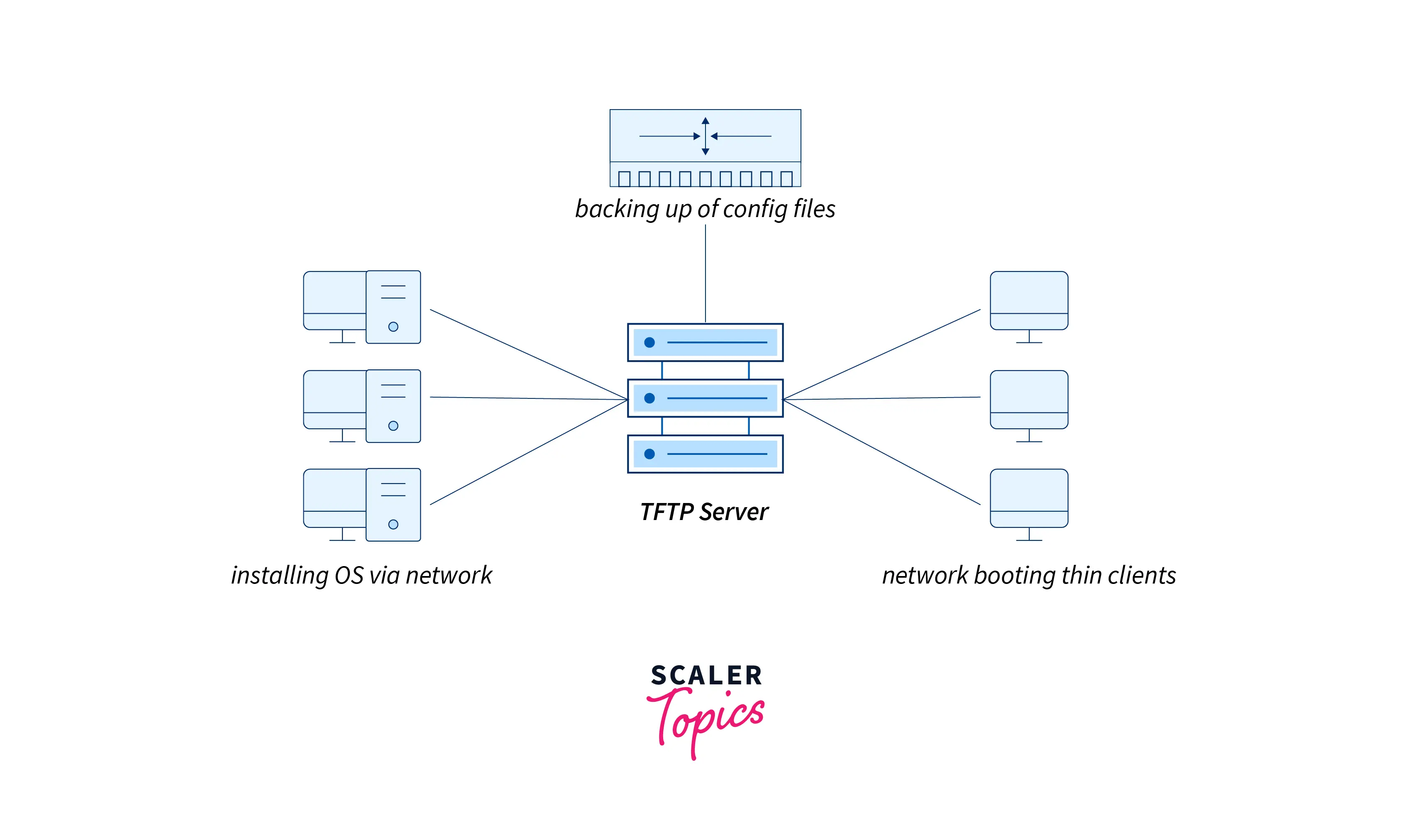
The five types of messages used in the TFTP protocol are:
- RRQ :
Request to read a file - WRQ :
Request to write to a file - DATA :
Contains a block of file data - ACK :
Used by the peer to acknowledge each block of DATA - ERROR :
Used by the peer to indicate erroneous operations
5. NFS
It provides a model to share files remotely between servers over a network.
The Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol that is portable across different machines, operating systems, network architectures, and transport protocols. The distributed file architectures look like this:
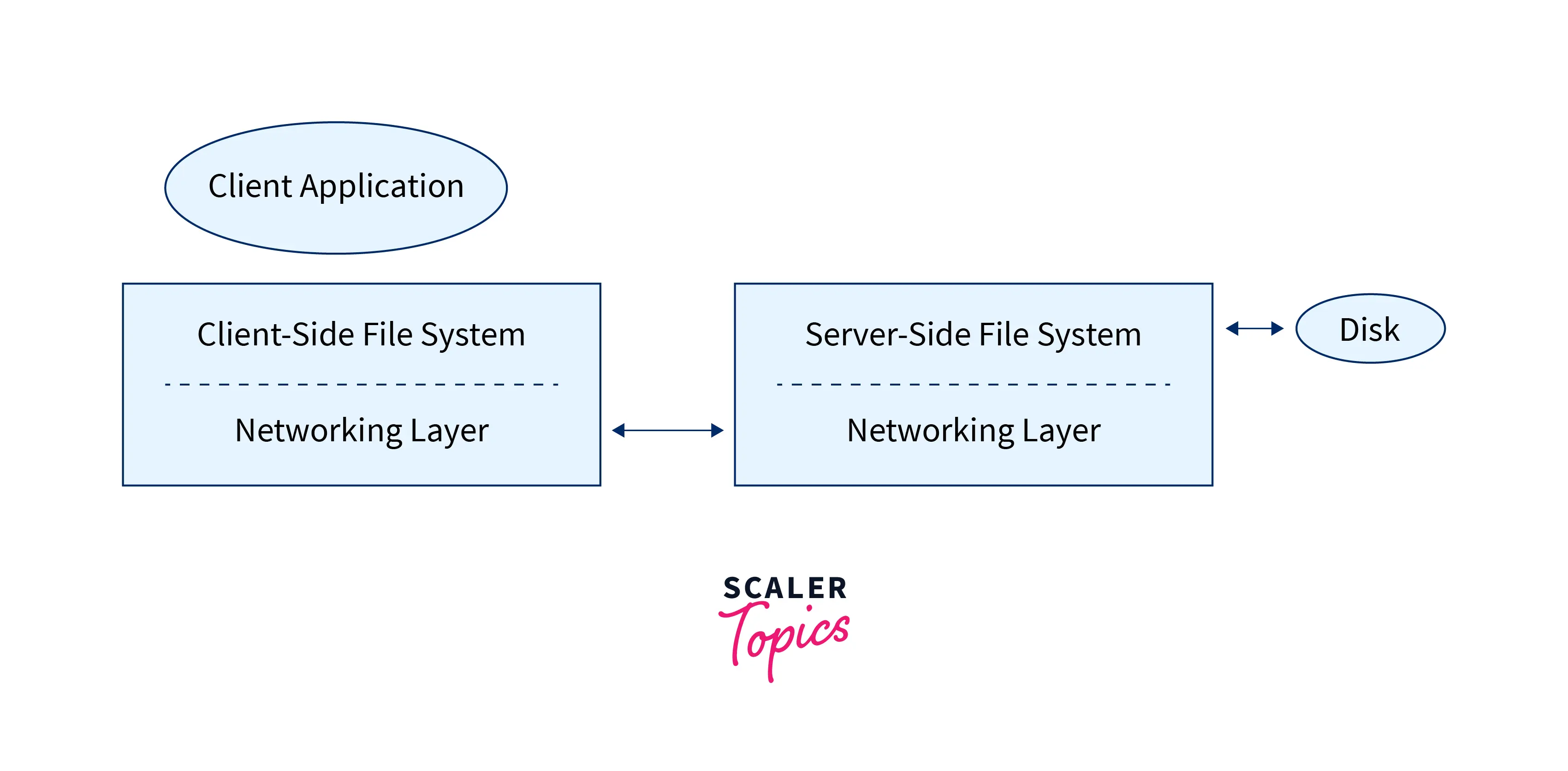
The protocol mounts a file system present in a network & enables interactions with it as though that system is mounted locally. Users can use CLI commands to create, remove, read, write & perform other functions on the remote files accessed using NFS.
Some of the common characteristics to look at are:
- The Port number used is 2049.
- It is an open standard i.e. anyone can implement this protocol.
- It has many versions, the most common of them being NFS v3.
The below table signifies the advantages and disadvantages of NFS:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. Multiple users can access the same file simultaneously. | 1. They are vulnerable to internet threats unless used on a trusted network behind a firewall. |
| 2. Centralization of data reduces system admin overhead. | 2. Parallel file access is not supported by a lot of clients to date. |
6. LPD
It is a protocol defined for print servers between UNIX systems and remote printers.
LPD stands for Line Printer Daemon, and is made for printer sharing. It is used for sending and receiving print jobs on a print server. The LPD print server is either connected to a print device directly or a network print device that supports this protocol.
Let us look at the common characteristics of LPD:
- The port number used is number 515.
- It receives the printing request and processes it forward.
In the old days, it was commonly used between UNIX systems and remote printers. Today’s modern Linux distribution uses CUPS (Common Unix Printing System). In addition to supporting LPD, CUPS also supports IPP (Internet Printing Protocol).
For using it on a Windows system, the LPD needs to be accessed through software to receive requests from any other system (Unix, Linux, Windows, etc.). After that, it is simply printed through the printer associated with the windows system.
Look at the image below:
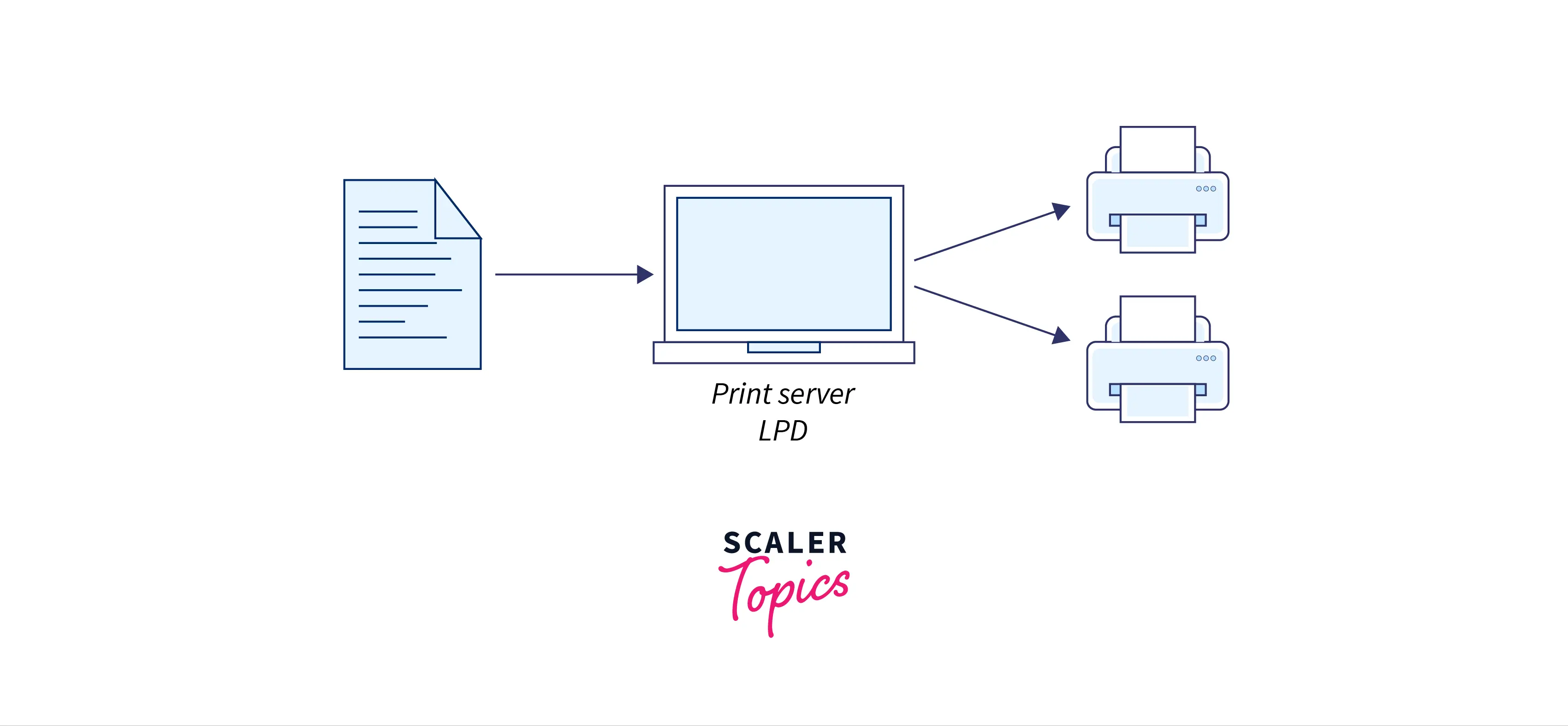
Here, the LPD print server receives the request and sends it forward to one of the host’s print servers.
7. X Window
A computer system software for writing graphical user interface applications.
It is a network protocol providing GUI (Graphical User Interface) for networks in interconnected mainframes. It is used for creating GUI applications based on client & server models.
The picture below shows a basic interaction between X Window applications & various other desktop machines.
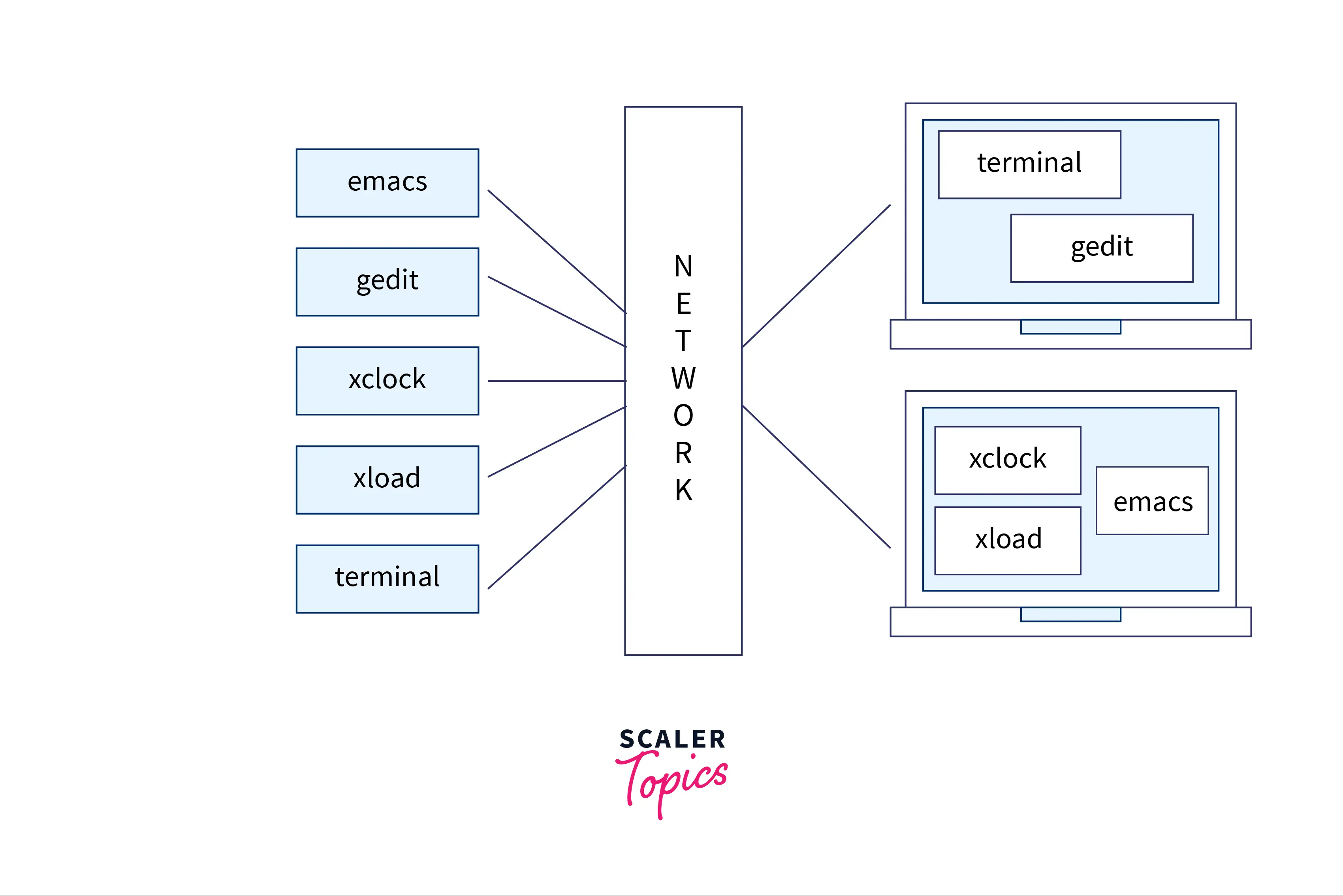
Here the system does not directly interact with the machines. Rather, it uses a network protocol. It gives us the added advantage of applications not having to run on the same machine where they are displayed.
Here are some common characteristics to look at:
- The port number for the X Window System starts from 6000. There is an incremental addition of one for every new server added.
- It is open-source and cross-platform.
- It is also known as X or X11.
8. SMTP
The SMTP protocol is necessary for the completion of email-related jobs.
Email services have been used extensively since their emergence in the late 1960s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology when a message was sent from one device to another using ARPANET.
Hence, it becomes crucial to understand SMTP. It stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol and assists in sending mail over the Internet.
The SMTP protocol uses two basic models to work efficiently:
- End-to-end Method:
It helps in communicating with email servers between different organizations. - Store-and-forward Method:
It helps in communicating with email servers within the same organization.
Let us now look at some characteristics of this protocol:
- The port number is number 25.
- It uses email addresses as a basis to function and send messages to devices.
- Like email, the SMTP program is also of a client-server architecture.
Master the complexities of computer networking with our Free Computer Networking course. Join now & learn to navigate the world of data transmission & protocols.
Conclusion
- Protocols in the application layer help in building models for users to interact with software applications over the World Wide Web.
- DNS service helps to convert domain names of websites into IP addresses.
- TELNET is used for communication through the command line interface between any two hosts.
- FTP is used to share and make changes to files.
- TFTP is a more basic version of FTP and works similarly but provides fewer services.
- Using NFS, we can share files remotely over the internet.
- LPD helps in printing jobs between UNIX systems and remote servers.
- X Window defines a protocol for writing GUI applications.
- The SMTP protocol builds a communication network between two email servers.