ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode and ATM is a switching technique that uses time division multiplexing for the communication of the data. And it is a connection-oriented technology. Data is converted in the fixed and small-size cells in the ATM.
Introduction to Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
The full form of the ATM is Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a switching technique and time division multiplexing(TDM) is used by ATMs for data communication.
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method in which multiple data streams are put onto a single signal by separation of the signal into different segments and a short duration is assigned to each.
- ATM is considered the connection-oriented network for cell relay by which voice, data, and video communication are supported.
- Data is encoded in the form of small cells of a fixed size so that they become acceptable to TDM and can be transferred on a physical network.
- 53 bytes is the size of an ATM cell which consists of a
48-bytepayload and 5 bytes for the header. - Asynchronous Transfer Mode is also established for the networks that can carry conventional data traffic that has high throughput and real-time and low-latency data such as video, and voice.
Refer to the below image for the ATM’s functional reference model.
How Does Asynchronous Transfer Mode Work?
ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode and this “asynchronous” means that ATM does not use a timer or any fixed speed for transmission of the information, but based on the hardware and flow reliability of the information ATM does the negotiation at the speed of the transmission. And in its name “transfer mode” means that the cells of fixed size are used by the ATM for information packaging.
The origin of the ATM technology is the B-ISDN(Broadband ISDN technology) and primarily it works on the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model layer 2.Virtual paths (VPS) and Virtual channels (VCs) are used by the Asynchronous Transfer Mode for the connection of the devices over the WAN.
The virtual channel(VC) is the series connection of one or more than one physical ATM links for the data transmission among remote stations. VC exists only at the time of data transmission and to ensure the reliability of the data transmission same VC is followed by all the cells of the given ATM.
And the collection of VCs is called the virtual path(VP). And all the VCs of the virtual path have a similar source and destination point.
Wireless ATM
Wireless ATM (WATM) is a wireless network with an ATM core. High-speed mobile communication is provided by this ATM. This is the technology that came into the world after the wired ATM’s success in responding to the increasing demands of wireless services in every field. Data, video, and voice are supported by WATM with the guaranteed QoS(Quality of Service).
Like other available wireless technologies, Broadcasting is done by the ATM cells from the base station and transferred to the mobile terminals, and the mobility function is performed by the ATM switch here.
VoATM
VoATM stands for Voice over Asynchronous Transfer Mode and it is the protocol that allows the transmission of video, voice, and data packets via an ATM network. This technology is similar to VoIP(Voice over Internet Protocol) which is a technology that allows that enables making voice calls using a broadband Internet connection in place of a regular phone line) but the only difference is that the IP protocol is not used by this and it is somewhat costly in terms of implementation. But for the network, a high-speed transport facility is provided by it. And this technology is considered beneficial for companies that have in place ATM networks.
ATM vs DATA Networks (Internet)
ATM is based on the “virtual circuit”: For the transmission, the path is reserved in the ATM, but IP(Internet Protocol) is the connectionless protocol and we cannot end-to-end resource reservations in the IP protocol data transmission.
ATM cells: ATM has fixed size cells of small size and there is a tradeoff between data and voice. While packets used in IP protocol are of variable size.
Addressing: Global NSAP addresses of 20 bytes are used by the ATM for the signaling and locally assigned labels of 32-bits in cells. And on the other hand, if we talk about IP the global address of 32-bits is by the IP is all the packets.
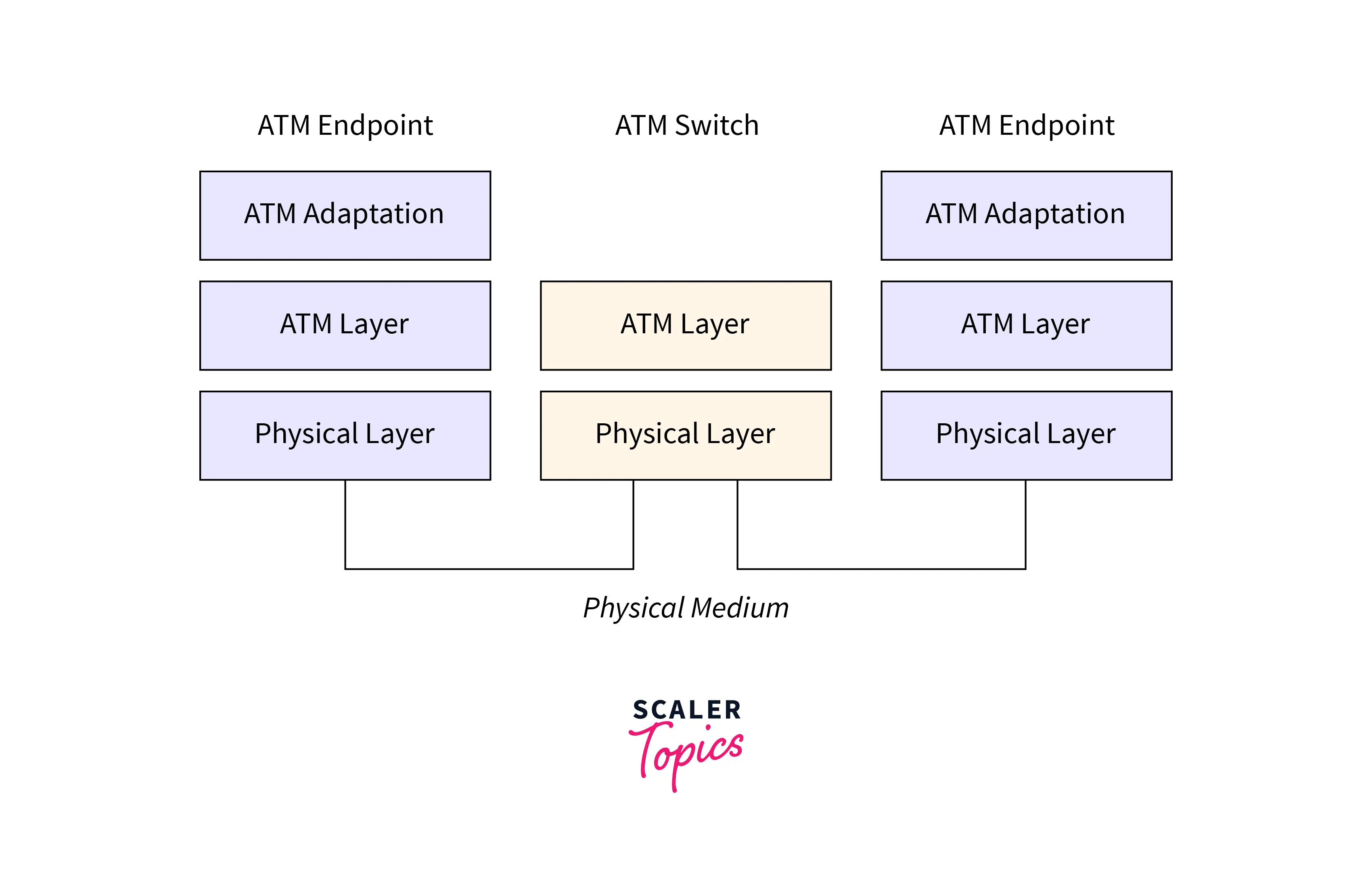
ATM Layers
Refer to the below image for the ATM Layers.

ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL)
It is a layer for isolation of Higher layer protocols and ATM processes details and user data prepared by it for converting it into cells and for converting segments into cell payload of 48 bytes. Transmission coming upper layer services are accepted by the AAL protocol and help in application mapping, e.g. voice, and data to the ATM cells.
Physical Layer
Medium-dependent transmission is managed by it. The transmission convergence sublayer and physical medium-dependent sublayer are two divisions of this layer. The main functions of this layer are given below:
- Cells are converted into a bit stream by it
- In the physical medium transmission and receipt of bits are controlled by it.
- ATM cell boundaries can also be tracked by it.
- It looks for cell packaging into proper frame types.
ATM Layer
Transmission, congestion, sequential delivery, switching, control, cell header processing, etc., is handled by it. And it is also responsible for simultaneously cell multiplexing and cell relay. Cell multiplexing is the sharing of the virtual circuit on the physical link. And the transmission of cells over an Asynchronous Transfer Mode network is known as cell relay and VPI and VCI information present in the cell Header is used.
The Application of Asynchronous Transfer Mode
- ATM WAN:- For transmitting cells over long distances it can be used as the WAN and the router that serves as an endpoint between the other networks and ATM networks having 2 stacks of the protocol.
- Multimedia virtual private networks and managed services:– LAN, voice, ATM, and video services can be managed by it and it enables full-service virtual private networking, and multimedia integrated access is involved in it
- Frame relay backbone:- Networking infrastructure is provided by the frame relay services for the range of data services and enables frame-relay ATM service to the internet working services.
- Residential broadband networks:- For finding highly scalable solutions, the networking infrastructure is provided by the ATM for the creation of residential broadband services.
- Telephone and private line networks carrier infrastructure:- Telephonic and private line traffic can be carried out by establishing ATM infrastructure which makes the SONET/SDH fiber infrastructure utilization effective.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Advantages
- ATM is beneficial as it provides the service of dynamic bandwidth that is especially suited for burst traffic.
- Data transmission can be done simply, predictably, and uniformly as all the data are encoded into identical cells.
- Mixed traffic is efficiently handled by the uniform packet size.
- Packet overload is decreased by small-sized headers and provides effective usage of bandwidth.
- ATM networks are speed and size-scalable.
Disadvantages
- There is an overhead of the cell header (5 bytes/cell)
- Achieving QoS has a complex mechanism.
- There may be a condition of cell loss due to congestion.
- Compared to LAN hardware, ATM switches are very expensive.
Conclusion
- ATM stands for
Asynchronous Transfer Mode. - Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a switching technique and time division multiplexing is used by ATMs for data communication.
Wireless ATM (WATM)is a wireless network with an ATM core.- VoATM stands for
Voice over Asynchronous Transfer Modeand it is the protocol that allows the transmission of video, voice, and data packets via an ATM network. - IP protocol is connectionless while ATM network is a connection-oriented technology.
- ATM Adaptation Layer, Physical Layer, and ATM layer are the layers of the ATM.
- Frame relay backbone, ATM WAN, etc. are some applications of the ATM network.
- Speed and size scalability are some advantages of the ATM network.