The data structures are nothing but a meaningful way of arranging, and storing the data in the computer for efficient utilization and processing depending upon the situation. A primitive data structure can store the value of only one data type. The size of a primitive data structure is known as it can store can only one data type. Examples of the primitive data type are integer, character, boolean, float, double, long, etc. Unlike the primitive data structure, a non-primitive data structure can store the value of more than one data type.
Scope of the Article
The article contains topics such as
- What are data structures (
data types), and their types namely-primitive data structureandnon-primitive data structure. - Overview of various primitive data structures along with their ranges and size.
- Overview of various non-primitive data structures along with their examples.
Each of the topics is explained clearly with diagrams and examples wherever necessary.
Takeaways
Data types:
- primitive data structures
- non-primitive data structures.
Cheatsheet for Classification of Data Structure
Before learning about the classification of data structure, let us first learn about data structures and data types.
Data types are nothing but the classification or categorization of the data items. Data types represent the kind of value and also tell what operations can be performed on a particular data. Various programming languages and various data types. On the other hand, the data structures are nothing but a meaningful way of arranging, and storing the data in the computer for efficient utilization and processing depending upon the situation.
Note: The data structures and data types are often used interchangeably.
Let us now learn about the classification of data structure. The data structure can be classified into two categories namely – primitive data structure and non-primitive data structure.
Refer to the diagram below to see the visual representation of the various data types along with their sizes.
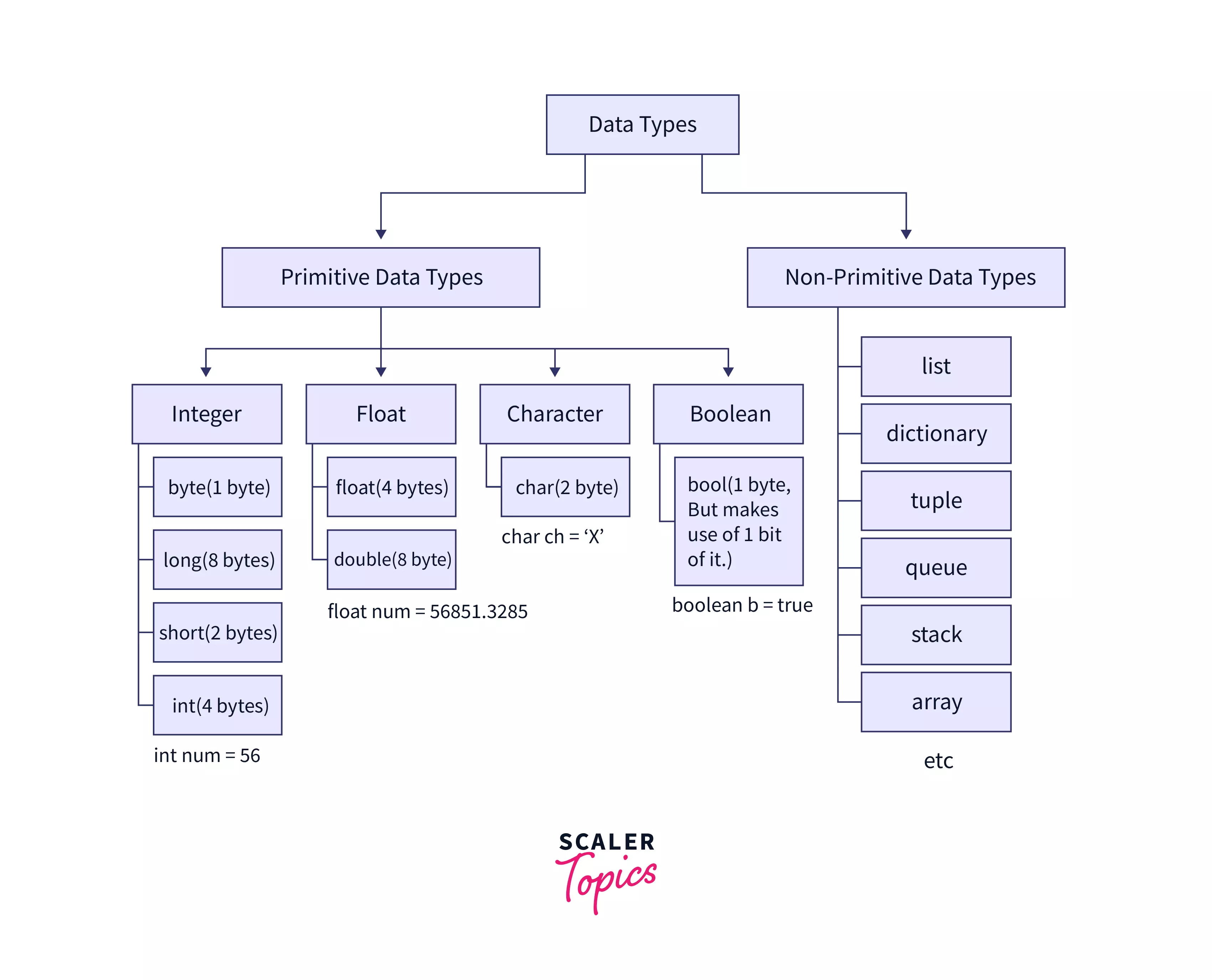
Let us briefly discuss the primitive data structures and non-primitive data structures.
Primitive Data Structure
A primitive data structure can store the value of only one data type. For example, a char data structure (a primitive data structure) can store only characters.
Key features of a primitive data structure:
- The size of a primitive data structure is known as it can store can only one data type.
- The primitive data structure will always store some data. It cannot contain the
NULLvalue. - Examples of the primitive data type are
integer, character, boolean, float, double, long, etc.
Now let us learn about the most commonly used non-primitive data structures along with their examples.
Bool
Bool or boolean is a primitive data structure that can be used to store only two values i.e. True or False. The size of a boolean data type is 1 byte but it only uses 1 bit of the 8 bits(1 byte = 8 bits) to store the value. A bool data type is used when we want to track whether a condition is true or false.
Example:
Python
a = True
C++
bool a = false;
Java
bool a = false;
Byte
A byte is a primitive data structure that is used to store 1-byte variables. The size of a byte data type is 1 byte.
Example: Java
byte a = 127;
Note: The byte data type is an 8-bit signed two’s complement integer.
Char
Character or char is a primitive data type that can be used to store the value of a single character (it can store lower case letters as well as upper case letters). The size of a character data type is 2 bytes.
Example: C++
char letter = 'a';
Java
char letter = 'z';
Int
Integer or int is also a primitive data type that can be used to store the numbers in the range: -$2^{31}$ to $2^{31-1}$ or (2147483648 to 2147483647). The size of a character data type is 4 bytes.
Example: C and C++
int number = 10;
Java
int number = 20;
Python
number = 30
Float
A floating-point number or float is a primitive data type that can be used to store fractional numbers. It’s range is: 3.4e−038 to 3.4e+038. The size of a character data type is 4 bytes.
Example: C and C++
float number = 10.56;
Java
float number = 20.25;
Python
number = 30.69
Note: There are two types of floating numbers. The float32 is a 32-bit number and the float64 is a 64-bit number.
Double
Double is also a primitive data type that can be used to store fractional numbers. Its range is 1.7e−308 to 1.7e+308. The size of a character data type is 8 bytes. We need to add d at the end of the number to denote it as a double number in java.
Example: C and C++
double number = 25.25;
Java
double number = 25.25d;
Note: Python does not have an inbuilt double data type.
Long
Long is a primitive data type that can be used to store the numbers in the range: $-2^{63}$ to $2^{63-1}$. The size of a long data type is 8 bytes. When we have a number larger than the range of integer then we use the long data type.
Example: C and C++
long number = 2555555;
Java
long number = 2555555;Short
Short is a primitive data type that can be used to store the numbers in the range: $-2^{15}$ to $2^{15-1}$. The size of a short data type is 2 bytes. When we have e smaller number than the range of integer then we can use a short data type as it takes only 2 bytes.
Example: C and C++
short int number = 255;
Java
short number = 12345;
Note: In C++, short is equivalent to short int.
Pointer
Pointer can also be referred to as a primitive data type that can be used to store the address of another variable. Pointers can store the address of other primitive and non-primitive data types as well. Pointer is supported by languages like C and C++.
Languages like Java and Python have references as a counterpart of pointers.
Example: C and C++
int number = 55;
int *a = &number;
Note: Pointer takes 8 bytes of memory.
Refer to the table below to find the range and size of the primitive data structure according to a 64-bit compiler.
| Data Type | Size in 64-bit compilers | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Bool | 1 byte | true or false |
| Byte | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| Char | 2 bytes | 0 to 2^16-1 |
| Int | 4 bytes | -2^31 to 2^31-1 |
| Float | 4 bytes | -3.4E+38 to +3.4E+38 |
| Double | 8 bytes | -1.7E+308 to +1.7E+308 |
| Long | 8 bytes | -2^63 to 2^63-1 |
| Short | 2 bytes | -2^15 to 2^15-1 |
Non-Primitive Data Structure
Unlike the primitive data structure, a non-primitive data structure can store the value of more than one data type. For example, a list in python can store various data types inside it.
values = [10, False, "String"] # values is a list
Key features of a primitive data structure:
- The size of a primitive data structure depends upon the type of data it stores.
- The primitive data structure will be just initialized without storing any data or value. It can contain the NULL value.
- Examples of the non-primitive data types are linked lists, stacks, queues, dictionaries, etc.
Now let us learn about the most commonly used non-primitive data structures along with their examples.
Array
An array is a linear collection of values stored at contiguous memory locations. Array stores homogeneous values(similar data type values).
To learn more about the arrays, refer to the article – Arrays in Data Structure.
Lists
A list is used to store one or more objects or data elements. Lists are used in python and java mostly. We can say that lists are similar to arrays.
File
A file is used to access a file from the system. A file is a collection of records.
Linked lists
As the name suggests, a linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links. The data element of a linked list is known as a node which contains two parts namely- the data part and the pointer. The data part contains the actual data and the pointer part contains a pointer that points to the next element of the linked list.
To learn more about the linked lists, refer to the article – Linked Lists in Data Structure.
Stack
Stack in a linear data structure that stores data sequentially based on the Last In First Out (LIFO) manner. So, the data which is inserted first will be removed last. Since the last element inserted is served and removed first, the queue data structure is also known as the Last Come First Served data structure.
To learn more about the stacks, refer to the article – Stacks in Data Structure.
Queue
Queue in a linear data structure that stores data sequentially based on the First In First Out (FIFO) manner. So, the data which is inserted first will be removed from the queue first. Since the first element inserted is served and removed first, the queue data structure is also known as the First Come First Served data structure.
To learn more about the queues, refer to the article – Queues in Data Structure.
Conclusion
- The data structures are nothing but a meaningful way of arranging, and storing the data in the computer for efficient utilization and processing depending upon the situation.
- The size of a primitive data structure is known as it can store can only one data type. Examples of the primitive data type are
integer, character, boolean, float, double, long, etc. Integeris a primitive data type that can be used to store the numbers in the range: $-2^{31}$ to $2^{31-1}$. A float is also a primitive data type that can be used to store fractional numbers.Charactercan be used to store the value of a single character (it can store lower case letters as well as upper case letters).Pointercan also be referred to as a primitive data type that can be used to store the address of another variable. Pointers can store the address of other primitive and non-primitive data types as well.- An
arrayis a linear collection of values stored at contiguous memory locations. A list is used to store one or more objects or data elements. - A
linked listis a sequential collection of data elements connected via links. The data element of a linked list is known as a node which contains two parts namely- the data part and the pointer. - Stack in a linear data structure that stores data sequentially based on the Last In First Out (LIFO) manner. Queue in a linear data structure that stores data sequentially based on the First In First Out (FIFO) manner.
Unlock the Power of Efficient Coding! Join Our Data Structures Courses Today and Transform Your Problem-Solving Abilities.