Digital Subscriber Line is abbreviated as DSL and provides the service of internet transmission with the help of a copper wire telecommunication line. And it maintains the speed of transferred data. Asymmetric DSL (ADSL), Consumer DSL (CDSL), DSL Lite, High-bit-rate DSL (HDSL), etc. are the types of DSL.
What is DSL?
A communication medium that provides the service of transferring internet using the copper wire telecommunication line is known as a digital subscriber line (DSL, but originally known as a digital subscriber loop). DSL’s main function is to maintain the high speed of data that is needed to be transmitted.
- DSL provides the service to carry internet access and information into businesses and homes.
- DSL technology generally provides high bandwidth digital communication on standard telephone lines that are made from copper wires.
History
When the telephone companies are getting benefited due to the industry’s monopolization, this increment in the profit of the emerging cable companies gave the hint to the telephone companies for researching new methods for video transmission on the existing copper lines.
One day, the process of digital signal transmission by copper wires and at high frequency was discovered by the engineers and they found that the data transmission rates can be delayed by the interference caused by the upload speeds and symmetrical download.
Joseph W. Lechleide was the father of the DSL. in 1955, he joined Bell Labs. And before the 1980s he had come up with the idea of uneven bandwidth allocation between the speed of the downloading and the uploading. Now it is called the Asymmetrical DSL. Electrical interference in the lines of the copper is eliminated significantly by this technology. But this invention failed in competing with the cables. For proving the utility of the Asymmetrical DSL, he has to wait till the initialization of the Internet.
In the starting, the speed of the dial-up is considered as the internet browsing function which is early more than the satisfaction. But the speed of the dial-up is not enough when the complexity of the websites starts increasing and more data-rich content is started.
That is the moment when the invention of Joseph W. Lechleider came into the role. At the same time, telecom companies do not need to invest in changing the infrastructures of the copper line into expensive (albeit faster) alternatives.
Features
- DSL is considered as the technology under the xDSL general name and here x can stand for ADSL, HDSL, or RADSL.
- DSL originally is a component of ISDN and ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network and it is also known as IDSL of DSL`.
- DSL is also used in a telephone’s network local loop, which means the telephone network that establishes the connection between the end office of the telephone company and the customer premises.
- Bandwidth is provided by more than the bandwidth telephone line by some of the DSL services that services are known as broadband services.
- On the customer premises, DSL fitters are used with non-DSL connections.
- Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) is used by the telephone company at its end office so multiple DSL users are allowed to connect to the high-speed backbone network.
- For the data transmission, sinusoidal wave transmission is used by the DSL. At the customer premises, DSL modems are used for the modulation and demodulation of the waves.
Variations of DSL
- Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
- Consumer DSL (CDSL)
- DSL Lite
- High bit-rate DSL (HDSL)
- ISDN DSL (IDSL)
- Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
- Very high data rate DSL (VDSL)
Operations
Local hoops are used for the connection of the telephone to the telephone exchange. Local hoop is mainly intended for speech transmission. As the long-distance trunks are converted to digital operation from analog operation slowly. And at this point, the idea of data transmission through the local hoop holds, which ultimately leads to the DSL. Local hoops establish the connection between the telephone exchange with mostly all subscribers having the power of transmitting at the frequency above 3400 Hz. The upper limit is equal to the tens of MHz based on the loop quality and length. And this local hoop’s unused bandwidth is utilized by the DSL by establishing the channels 431.5 HZ wide. For downstream and upstream the usable channels pool is divided into bands based on the frequency. Interference is reduced by this segregation. When the groups of the channel have been created then the bonding of the individual channels is done into a virtual circuit pair, 1 in each direction. The quality of every channel is continuously monitored by the DSL transceivers similar to analog modem monitoring. And after monitoring it will remove or add the channel based on the situation and whether it is usable or not. Subscribers can connect to the service like ISP or other network services after the establishment of downstream and upstream circuits. Transporting technology of the DSL facilities utilizes high-frequency carrier wave modulation. The bits pattern is modulated into high-frequency impulses for sending it to the opposite modem as every DSL circuit terminates with the modem at each end. Signals that are received from the far-end modem are demodulated so that they can be converted into the bits pattern and the modem can pass it to the interfaced equipment like a computer, switch, etc. in the digital form. Signals received from the far-end modem are demodulated to yield a corresponding bit pattern that the modem passes on, in digital form, to its interfaced equipment, such as a computer, router, switch, etc.
Naked DSL
The method in which only DSL services are provided over a local loop is known as Naked DSL. When a user does not want to use traditional voice service as voice is received on the top of the DSL or with the help of another network, then this method of DSL is very useful. In the USA, it is known as an unbundled network element (UNE), in Belgium, it is termed as raw copper, in Australia it is defined as the unconditioned local loop(ULL) and known as Single Order GEA (SoGEA) in the UK.
Types of DSL
Symmetric DSL
In this type of DSL, data can be transferred in both directions but at the same speed. And also have the bandwidth for downloading and uploading the data.
Asymmetric DSL
A service that allows data to travel in different directions at different speeds. Data downloading is faster than uploading data.
Downstream
Traffic travels from the network operating center to the customer.
Upstream
Traffic travels from the customer to the network operating center.
ADSL
In an asymmetric digital subscriber line(ASDL), traffic travels at different speeds depending on its direction. ADSL supports a wide range of data services. There are three information channels provided by ADSL. These are an ordinary telephone (POTS) channel, an upstream channel, and a higher-capacity downstream channel. In all these channels, voice communication is possible even with data traffic. Using frequency-division multiplexing, these channels can be separated. Its range is 2–3.4 miles, downstream speed is 1.5–7 Mbps and upstream speed is 16–640 kbps.
ADSL Lite
The slower version of ADSL is ADSL lite. It is created so that it can be worked for digital loop carrier systems and also for distances above 3 miles. Its downstream speed is 384 kbps − 1.5 Mbps and its upstream speed are 384–512 kbps.
HDSL
In High-bit-rate digital subscriber lines, the facility of Tl is provided in both directions to all those applications that need communication symmetry for example- corporate internet, audio, high-volume email, and many more.
IDSL
In this service, ISDN-ready local loops are used. It is an international communication standard designed for transmitting data, audio, and video on digital telephone lines.
SDSL
For operating Single-pair symmetric high-bit-rate digital subscriber lines, a single copper twisted pair is required.
RDSL
The facility of adjustable downstream and upstream speed is provided by read-adaptive digital subscriber lines. Bit rates are set according to the line condition or a customer requirement. Suppose the line is busy then it decreases the bit rate which makes it more robust as compared to others. Its downstream speed is 40 kbps − 7 Mbps, its upstream speed is up–768 kbps and its range are 2–3.4 miles.
VDSL
Very high-bit-rate asymmetric digital subscriber lines are used whenever there is a requirement for high bandwidth. As it provides very high bandwidth but along with high bandwidth it is limited to short distances only and also needed fiber optic cables. It is created to provide the service of video-on-demand over copper phone lines. Its downstream speed is 13–52 Mbps and its range is 1,000 ft.
Typical Setup
The DSL modem is associated with the phone line on the customer side. The other end of the line is connected to the DSLAM by the telephone company, and a large number of individual DSL links are concentrated in a single box by the DSLAM. Because of the attenuation between the user’s DSL modem and DSLAM we can not put DSLAM too far from the customer. One DSLAM is common for some residential blocks.
Refer to the below image for the typical setup of the DSL 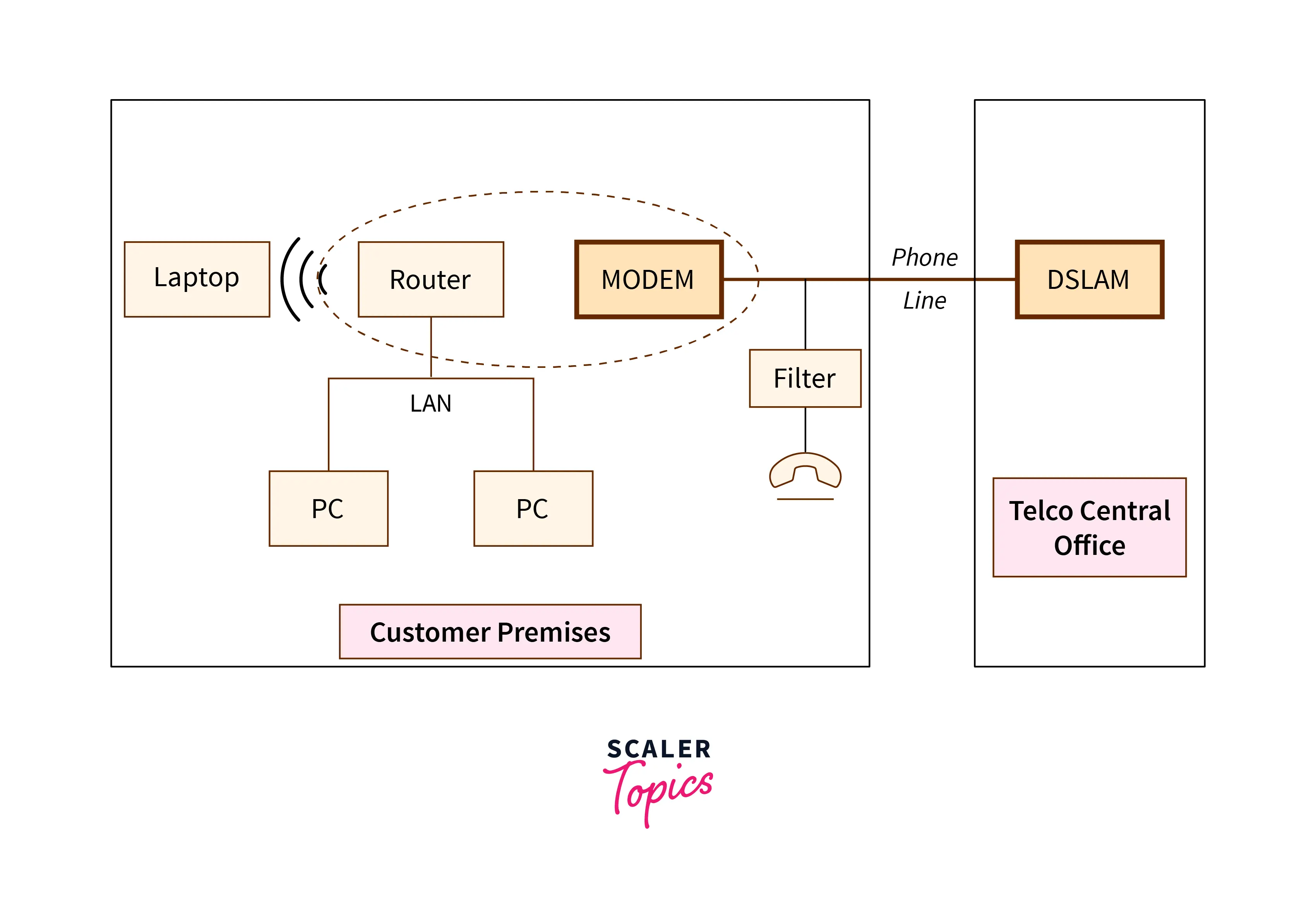
The above-given figure describes the whole system of simple DSL connections (in blue). On the right side, there is DSLAM which resides in the telephone company’s telephone exchange. The left side represents customer-premise equipment along with your optical fiber. Local area networks are managed by the routers and these local area networks are used for the connection between PCs and other wireless. Modern can also be used by the users as modems have both wireless access and router. This method generally makes the connection simple.
Exchange Equipment
Digital subscriber line access multiplexer abbreviated as DSLAM creates the termination of the DSL circuits. All connections are terminated by the DSLAM and also original digital data is recovered by this.
Customer Equipment
Refer to the below image for the customer equipment of the typical setup of the DSL 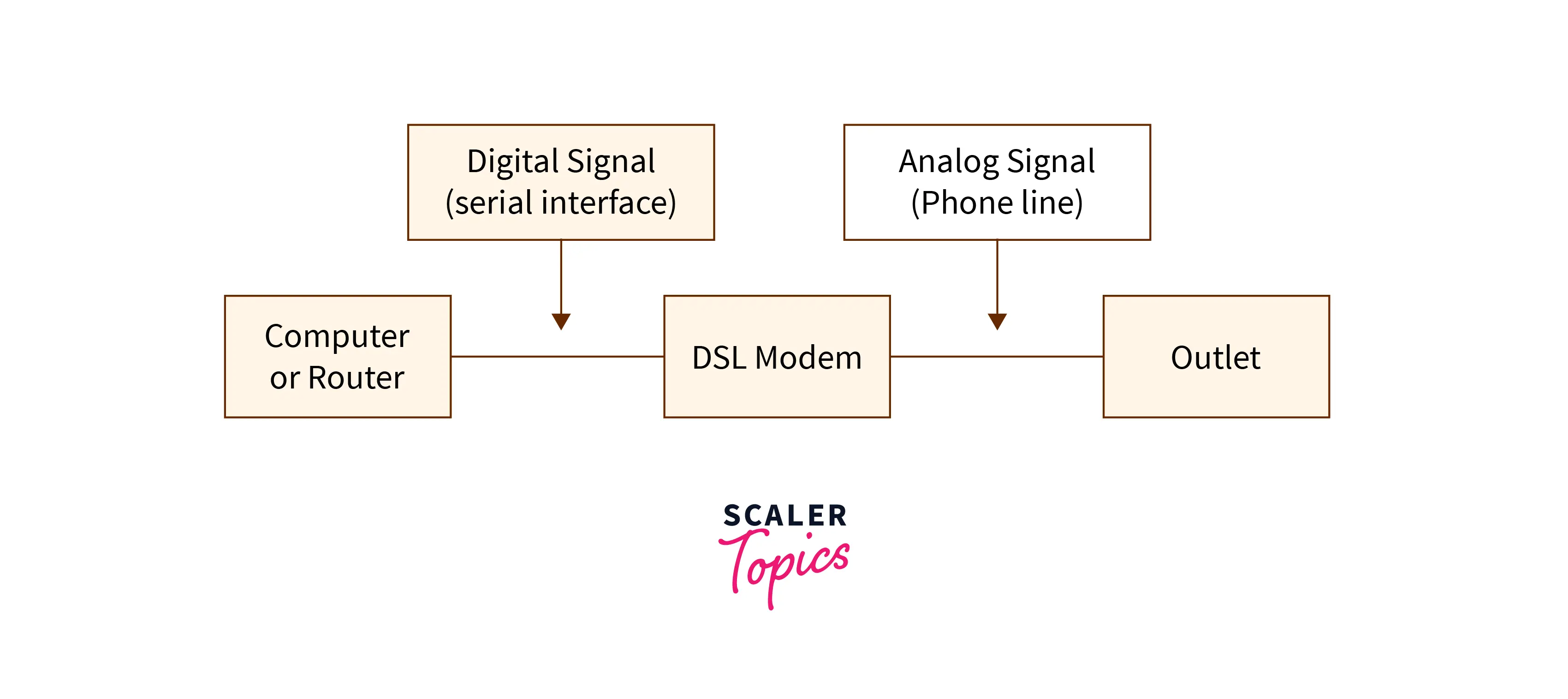
There is a DSL modem on the connection’s customer end. And this converted computer used digital signals and suitable frequency range voltage signals into the data so that it can be used with the phone line. There are some DSL variations such as HDSL in which the modem will directly connect to the computer through a serial interface and the use of protocols like ethernet or V.35. But there are some other cases also in which customer equipment needs to be combined with the functionality of higher-level. This functionality includes routing, firewall system or much other applications-specific hardware or software required. The equipment in this type of case is known as a gateway. There is a demand for proper DSL filter installation by most DSL technologies for separating DSL signals from low-frequency voice signals. This separation can be done at the demarcation point or can be done with the filters that are installed at the telephone outlets which are present inside the customer premises. Most modern DSL Gateways combined routing and other functionality. After this, the system boots up and the DSL connection is synchronized. And then, the internet IP services are created and connections are established between the service provider and the local area network with the help of protocols such as PPPoE, and DHCP.
How Does It Work?
A DSL internet connection only needs telephone line wires for receiving the signal and for transmitting the signal it needs a modem and internet access. For installing DSL, there is no requirement for an active landline or we can say that telephone is also not required for its installation. DSL internet functionality can only work in a limited physical distance and is also not able to work in areas where DSL technology is not supported by the local telephone infrastructure. We cannot use the service everywhere. DSL connection receives the data faster as compared to sending the data on the internet.
Benefits of DSL
- DSL needs no additional wiring for its connection. DSL connection works with your existing system of telephone wiring. So, there is no need to put extra effort to implement DSL on your phone system.
- DSL technology is not so expensive. It is very cost-effective and also provides the best connectivity.
- Service providers provide the availability of DSL modems.
- DSL allows users to use both telephone lines and the internet at the same time. And it is possible because there are different frequencies in which the voice and the digital signals are travelling.
- Users have the choice to select among different connection speeds and pricing from different providers.
The Difference between DSL and Cable Internet
Digital Subscriber Line abbreviated as DSL is considered one of the oldest technologies on the internet. And it is considered the precursor to dial-up. It allows data transmission and allows us to create connections with the internet solely by the local phone line. Two main types of DSL are symmetric DSL and asymmetric DSL. Lower uploading and Higher downloading speed are provided by the asymmetric DSL while on the other hand same downloading and uploading speed is provided by symmetric DSL. Continuous and dedicated links are provided by DSL to our company. A dedicated and continuous link means that there is no sharing of the link with any potential neighbors. And if we talk about the configuration then the appropriate equipment is decided by our internet provider based on our subscription. The following scenarios are used in the majority of cases:
- A DSL modem is considered as the charge of the connection established between a PC and telephone line that consists of DSL services.
- Line splitter with two connections one connection is for the DSL and another one is for the phone line and that allows data transmission from our modem and provides this data to our device. Cable internet is different from DSL as the existing coaxial cable in place of telephone lines is used by the DSL for carrying the cable to our office. The modem creates a connection with the office coaxial cable and converts the data sent and received by our device into a signal. One of the major differences between DSL and cable internet is that cable internet results in poor performance and lags in time and at the time of high internet traffic, it lags time. The reason behind this is that cable networks work on the network that is shared.
Conclusion
- DSL(Digital Subscriber Line) is a communication medium that provides the service of transferring internet using the copper wire telecommunication line.
- ADSL, HDSL, Downstream, IDSL, RDSL, etc. are some of the types of DSL.
- Exchange equipment and Customer Equipment are two components of the DSL setup.
- DSL Internet Connection requires only a telephone line for receiving the signal and it uses a modem and internet access to send the signal.
- No additional wiring, Less expensive, etc. are some of the advantages of the DSL.
- Cable network works on the shared network which results in poor performance.