Hotspot 2.0 (HS2), also known as Passpoint” or “Next Generation Hotspot, represents a significant evolution in public Wi-Fi access. This innovative standard, driven by the Wi-Fi Alliance and endorsed by the Wireless Broadband Alliance, simplifies and secures the process of connecting to public wireless hotspots. It’s built on the IEEE 802.11u standard, enhancing how devices discover and securely connect to network hotspots.
In today’s world, hotspots are ubiquitous in airports, libraries, hotels, coffee shops, and more. Traditionally, users connect to these hotspots manually by selecting a network and entering a simple password. However, Hotspot 2.0 revolutionizes this procedure by facilitating seamless roaming across Wi-Fi networks and even between Wi-Fi and cellular networks, without the need for additional user sign-on and authentication each time.
The backbone of HS2 lies in its advanced protocols that enable features like cellular-like roaming, increased bandwidth, and on-demand services for wireless-equipped devices. It incorporates the 802.11i based WPA2 Enterprise security specification, providing a secure method of authentication and encryption.
The development of Hotspot 2.0 is ongoing, with each release introducing new functionalities. The initial focus was on network discovery and selection, along with enhanced security mechanisms. Future updates, including Release 2.0 and 3.0, aim to further streamline user experience with features like online sign-up and more comprehensive network selection policies.
This seamless integration and enhanced security framework position Hotspot 2.0 at the forefront of public Wi-Fi access, promising a more connected and secure experience for users worldwide.
Hotspot 2.0 Releases
The Hotspot 2.0 customary has gone through updates, like any leading standard:
- HS 2.0 Unleash 1:
Hotspot 2.0, Release 1 established the common notions following Hotspot 2.0. HS 2.0 established proficiency for spontaneous Wi-Fi connection disclosed, picking, and 802.1X authentication all founded on the Access Network Query Protocol (ANQP). - HS 2.0 Unleash 2:
Release 2 was launched in Oct 2014 and involved many diverse enhancements to authorize the far superior operation of the general Hotspot 2.0 notion. Unleash 2 launches features for standardizing the control of the credentials. Features include how the above-mentioned credentials are furnished and kept on the system, and how they are utilized in connection selection.
Hotspot 2.0 Benefits
There are several advantages to the use and implementation of Hotspot 2.0 – Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint. These advantages relate to users and operators alike:
- Much easier Wi-Fi access:
One of the key benefits for users is that Hotspot 2.0 provides much easier access to Wi-Fi networks. One log-in is needed to line the system up and then the system will do the rest: looking for accessible networks and then gaining entry. - Enables new value streams:
The utility of HS 2.0 permits operators to explore new services and revenue opportunities through inter-carrier Wi-Fi roaming, reaching new devices and new venues for the present subscriber base. - Reduces churn:
The improved client satisfaction through the convenience of the use of Wi-Fi can lead to increased client satisfaction and successively can scale back the extent of churn - Offers a high level of security:
The standards utilized in Hotpot 2.0 – Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint give a high level of security, higher than that unremarkably offered by several non-Hotspot 2.0 Wi-Fi access points.
Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint is seen by several as one of the foundations for the Wi-Fi roaming standards presently taken from across the globe. Not only can it give higher in-country access but it will conjointly global roaming. Multi-operator trials on Passpoint-certified instrumentality are underneath the method as part of the Future Generation Hotspot program.
Working of Hotspot 2.0 Networks
Hotspot 2.0 connections aim to supply cellular-style “roaming” for Wi-Fi connections. As you progress all over the world, your device can link you to access public hotspots mechanically.
There are numerous advantages to this:
Public Hotspots Set Off Easier and Much Secure
After you visit an airport or coffee shop, your device can mechanically understand that it is the real public airport Wi-Fi network and connect mechanically. You don’t need to guess whether or not “FREE_AIRPORT_WIFI” is the real network, connect manually, and click on it through a sign-in screen.
Network Suppliers will Band Together
Hotspot 2.0 networks are designed to perform superior once service suppliers partner with alternative suppliers. Let’s Assume, you have Comcast Xfinity internet at home, which has access to Xfinity Wi-Fi hotspots around the universe. The Aim is for Comcast to partner with alternative hotspot suppliers, therefore Comcast customers might get online on alternative hotspot supplier networks and alternative companies’ customers might get online at Comcast hotspots.
Encryption is Compulsory
Several current public Wi-Fi hotspots are open Wi-Fi networks, which suggests individuals will listen to your browsing. Hotspot 2.0 networks need operation-grade WPA2 encryption. 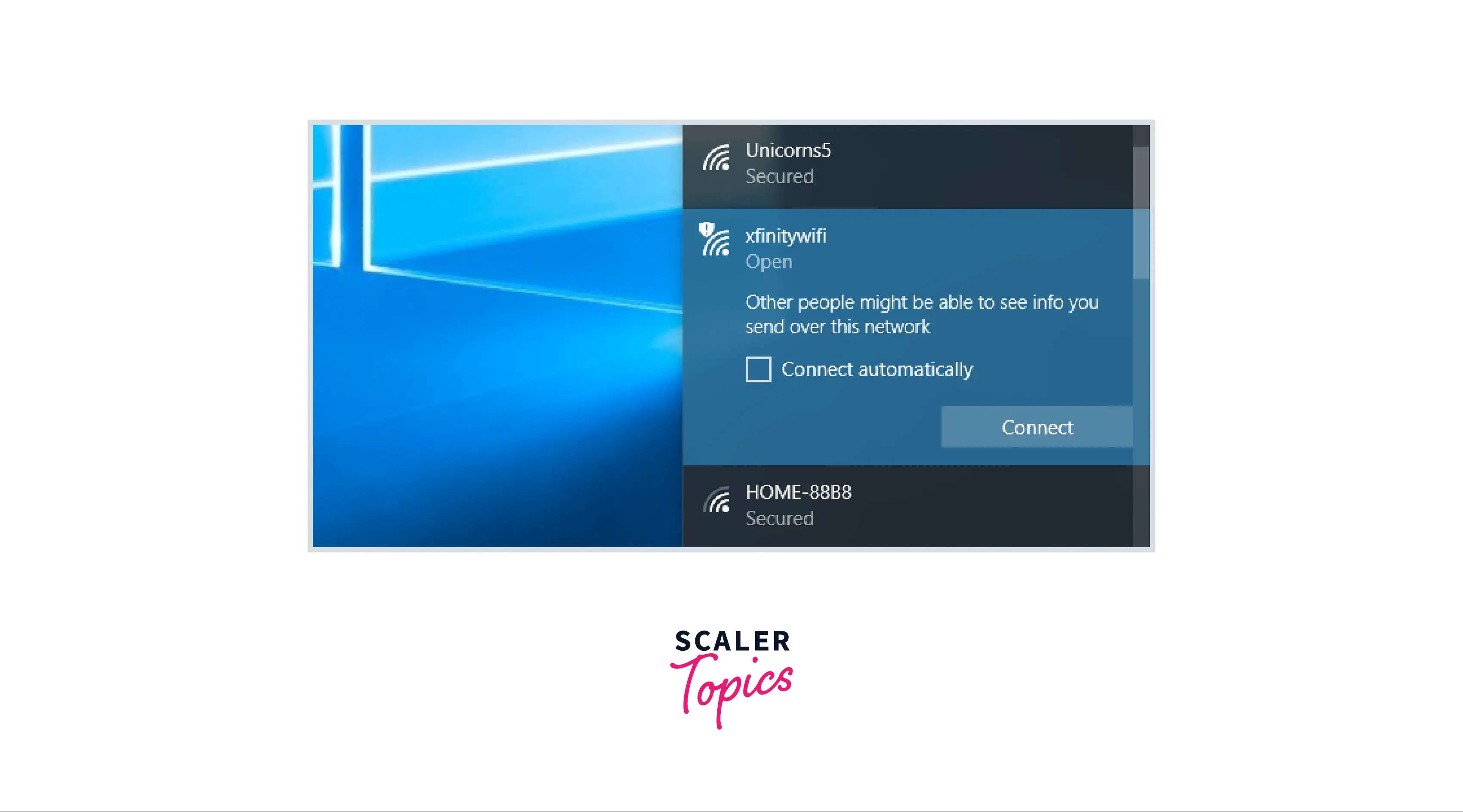
Thus few firms named these attributes As “Passpoint” or “Next Generation Hotspots”. It supports the 802.11u Wi-Fi standard.
How to Use Hotspot 2.0 Networks?
Hotspot 2.0 connections are created to be easy to use. As an example, Time Warner has extended Hotspot 2.0 support to its network of Wi-Fi hotspots. To attach to at least one, you simply click the “TWCWiFi-Passpoint” hotspot in the list of nearest Wi-Fi connections and inform your device to seize. You’ll then see a login screen wherever you have to give your Time Warner Cable login credentials. And once you sign in, your device can mechanically connect with related Passpoint connections in the future.
Suppliers may also give you profiles before time. As per the example, Boingo provides a Hotspot 2.0 profile that can connect you to related hotspots in a diversity of airports. Install this profile utilizing your browser and your device can mechanically connect with those hotspots once you visit those airports.
Whether you simply connect with a Hotspot 2.0 connection or install profiles before time, it’s created to “just work”. Windows 10 offers an “Online Sign-Up” facility that will give you a listing of network suppliers Once you try and be part of a Hotspot 2.0 connection for the primary time. Once you set it up, your device will mechanically connect with alternative Hotspot 2.0 connections in the future.
How to Connect to Hotspot 2.0 Wi-Fi Networks on Windows 10?
Hotspot 2.0 connections use WPA2-Enterprise for confirmation and encoding linking customers and approach points. Additionally, we don’t need to scrutinize multiple networks attempting to search out which of them you will be able to hook up with along with your credentials. Windows 10 mechanically comes across and links to the right Hotspot 2.0 connection on your behalf.
1. How to Tell if Your PC Supports Hotspot 2.0?
Hotspot 2.0 is comparatively up to date, and it’s accessible on Windows 10 appliances with unanimous hardware.
We can fast examine to visualize if your gadget bears Hotspot 2.0, utilizing the subsequent steps:
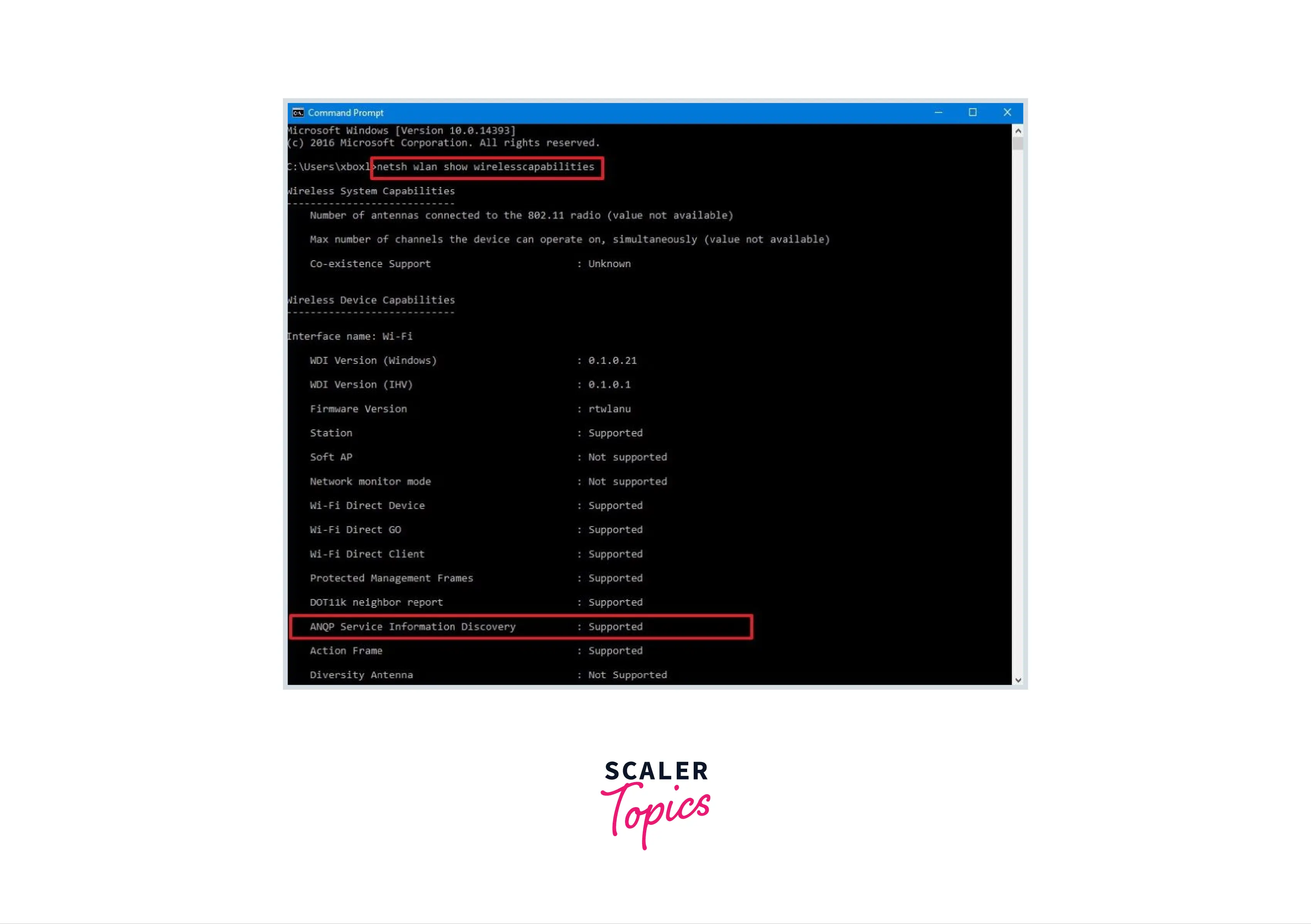
- Step 1 : Open Start->.
- Search for Command Prompt and press on the result.
- Then Type the subsequent command and press Enter : netsh wlan show wireless capabilities if the given command output manifests that your PC assists ANQP Service Information Discovery, you can connect to Hotspot 2.0 networks.
2. How to Enable Hotspot 2.0 Networks?
When you recognize your device works with the new commonplace, you will use the subsequent steps to show the characteristics so that it lists the suppliers Once we are attempting to attach once choose a Hotspot 2.0 network.
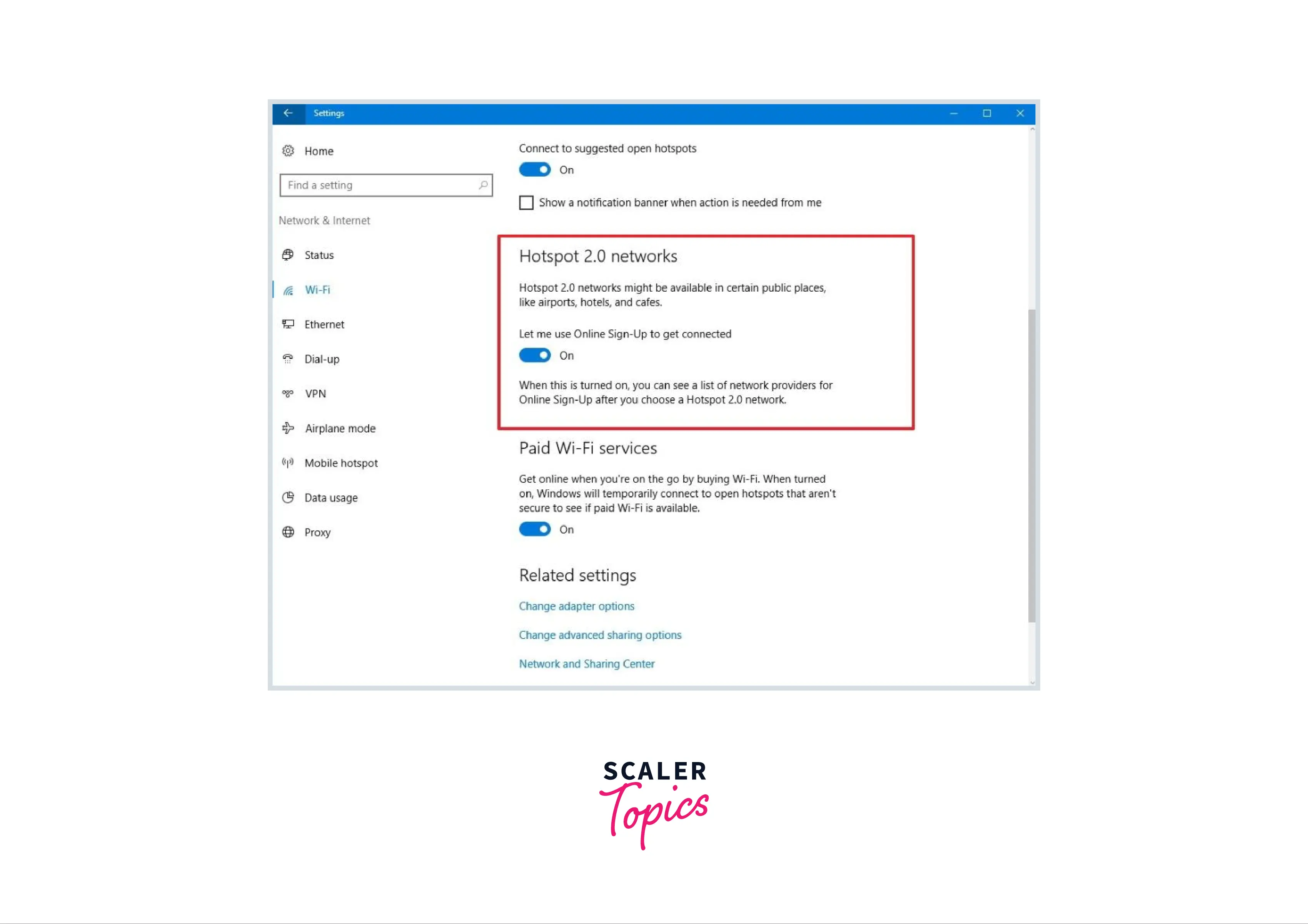
- Step 1 : Open Settings.
- Press on Network & Internet option.
- Then press on Wi-Fi.
- Under the “Hotspot 2.0 networks”, activate the Let me use the Online Sign-Up option to get a joined toggle switch.
After the choice is authorized, Hotspot 2.0 connections seem in your list of Wi-Fi networks Once they’re available.
3. How to Connect to Hotspot 2.0 Networks?
The affiliation method is incredibly straightforward. You simply pop the network connection from the list and press the link button. You may then get a sign-in prompt to attach to your supplier. This is often a single-time sign-in method, and once you get your credentials, your system can connect online mechanically when a Hotspot 2.0 network is obtained.
It’s also potential for suppliers to supply profiles to form the method even easier to attach to Hotspot 2.0 connections. As an example, Boingo could be a mobile wireless supplier that permits you to copy or transfer and install a profile operating on your browser to attach mechanically to a variety of airport hotspots by making use of available networks.
Tip :
- When you transfer a profile, you want to disconnect from your present Wi-Fi network and rejoin for some new profile to figure out.
- Perhaps the foremost attention-grabbing side of Hotspot 2.0 connection is that suppliers will partner to permit customers to quickly and firmly connect online through totally different suppliers.
Hotspot 2.0 Settings
Hotspot 2.0, additionally called Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint, could be customary for public-access Wi-Fi that permits absolute roaming among Wi-Fi connections and cellular connections. It is supported by the IEEE 802.11u custom for interworking with external networks. With the appearance of Androids and tablets, the information draining and strain on cellular connections have enhanced considerably. Hotspot 2.0 permits cellular network-like roaming that needs very little or no guide interference permitting users to mechanically switch to a Wi-Fi network, whenever it is accessible, and let go of the cellular connection.
Passpoint-certified mobile machines will flawlessly be linked to an AP(Access Point) if the Wi-Fi profile appealed on the Acess Point has Hotspot 2.0 authorized and the communicating settings organized. Once a Wi-Fi profile with Hotspot 2.0 settings is claimed to the Access Point that is located at the operator location, the Access Point will advertise accessible network favors licensing Passpoint-certified mobile gadgets to accordingly locate and choose a Wi-Fi network.
A mobile gadget will appeal to a Hotspot 2.0 Access Point for data associated with the abilities and favors supplied by the Access Point aside from the corporation with the Access Point. Based on the information collected from the Access Point, it will decide whether or not it needs to be attached to the Access Point or not. This transmission linking the AP and therefore the mobile devices grasps place utilizing the (ANQP) Access Network Query Protocol.
1. Network Discovery and Selection
One of the foremost functions self-addressed within the IEEE 802.11u standard is automatic network finding and choice. This characteristic uses a GAS which stands for generic advertisement service as a platform to permit transmission among non-Access Point devices and an outer network without connecting with an Access Point.
To broadcast hold up for Hotspot 2.0, the Interoperation bit in the Extended abilities information components has to be set within the Beacon and Probe Response frames. The non-Acess Point systems involve the Interoperation component in Probe Request frames(PRF).
Granting data to non-AP(Access Point) devices within the pre-alliances stage has these benefits :
- Non-AP systems can create conversant selections concerning attaching a BSS supported by the services published.
- Multiple wireless connections are often enquired in parallel which minimizes the time needed to relate to a network that matches the necessities of non-AP systems.
2. Fields Added in Beacon & Probe Response
For arranging data relating to the service supplied, these further fields have been added to the beacon frame:
- Interworking
- Advertisement Protocol
- Roaming Consortium
- Emergency Alert Identifier
In tallying to those fields, a non-AP gadget will appeal for further information by utilizing ANQP(Access Network Query Protocol) which uses Public action frames to divide information at Layer-2(L-2) except needing the non-AP systems associated with the BSS. Once the non-AP device/system has collected all the knowledge, it will pile up with a hotspot wherever it will be victoriously authentic and support the profile that is organized on the system.
3. ANQP Elements
The ANQP components are explained to supply extra pieces of information which are listed below.
Venue Name Information:
The descriptions of the venue wherever the AP is deployed. This specifies the cluster and kind of venue, like a hospital, college, or factory, and therefore the name of the venue wherever the AP is installed.
Emergency Call Number Information:
List of emergency/crisis contact numbers to an emergency acknowledgment, as managed by a (PSAP)public safety answering point, which is utilized in a particular geographical region.
Network Authentication Type Information :
List of document types and corresponding extra information.
Roaming Consortium List:
A list of organization attributes, which are distinctive hexadecimal strings, picks out the service suppliers assisted by the network and therefore the roaming consortia that the network could be a member of.
IP Address Type Availability Information:
Information regarding the supply of IP address version and the kind that would be allocated to the system once the association is.
NAI Realm List:
List of NAI realms like services corresponding to service providers or different entities whose connections or services are reachable between the AP. alternatively, for every NAI(Network Access Identifier) realm, a listing of 1 or above EAP(Extensible Authentication Protocol) Methodology subfields that the NAI realm uses for authentication can be enclosed.
3GPP Cellular Network Information :
Cellular data, like network advertisement data(such as network codes and country codes), helps a 3GPP non-AP system in selecting an AP to obtain 3GPP networks.
4. Authentication
Hotspot 2.0 will be used solely with WPA2-Enterprise safety background and it keeps up these EAP methodologies :
- Credentials EAP Method
- Certification EAP-TLS
- USIM/SIM EAP-SIM, EAP-AKA
- Username / Password (with server-side certification) EAP-TTLS with MSCHAPv2
Conclusion
- Hotspot 2.0 reaches this the whole time with a very thorough overhaul of the WiFi connection procedure. It’s built on IEEE 802.11u instructions which supply query operations to have a “communication” between systems and therefore the access point regarding the abilities of the connection before the alliance. The customer then makes an automatic call regarding whether or not to attach to this Wi-Fi network or not, or probably to a different one that is conjointly in range.
- It also absorbs the IEEE 802.11i-based mostly WPA2 Enterprise security specification that allows a replacement secure methodology of authentication (EAP) and cryptography.
- The starting work done on Hotspot 2.0 (release 1) is concentrated on network uncovering and choice, and recently developed security mechanisms. Release 2.0, presently in the last stages of evolution, includes online sign-up features as well as an operator policy for network choice. The online sign-up characteristics can considerably make end-user system configuration provisioning easier, which is the sole of the barriers hostile to the release 1 assumption.
- WiFi Association is additionally functioning on release 3.0 which can cover a lot of advanced characteristics.
- In the user aspect, the advantages will be basically: transparent network finding and choosing, an easy and intuitive online sign-up and authentication provision (with release 2), and safer conversation.