The IPv4 address or the Internet Protocol Address is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit addresses that are unique to every host or device on the internet. The IP address allows the host to be connected to other devices on the internet to communicate with them. There are two versions of Internet Protocol- IPv4 and IPv6.
What is the IPv4 Address?
Consider the example of the telephone. If we want to make a call to someone using a telephone, it is only possible when we know the phone number of the other person. Without knowing the phone number, it is not possible to make a call. In the same way, if we want to send data to any host on the internet, we need the address of the recipient. This allows us to uniquely identify the host on the internet so that the data is transferred and communication is established between that particular host.
IP addresses are of two types – IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. IPv4 is a 32-bit address and IPv6 are 128-bit address. The ‘v’ in IPv4 and IPv6 stands for version. The IPv4 address or the Internet Protocol Address is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol. It is a unique address.
The IPv4 address is divided into two parts – the network part and the host part(also referred to as netid and hostid). We will discuss these in-depth in the upcoming sections.
IPv4 addresses are 32 bit-addresses and are divided into 4 octets(1 octet = 8 bits). They are usually represented in dotted decimals, but binary representation is another way to represent them.
Example : 192.168.1.152192.168.1.152 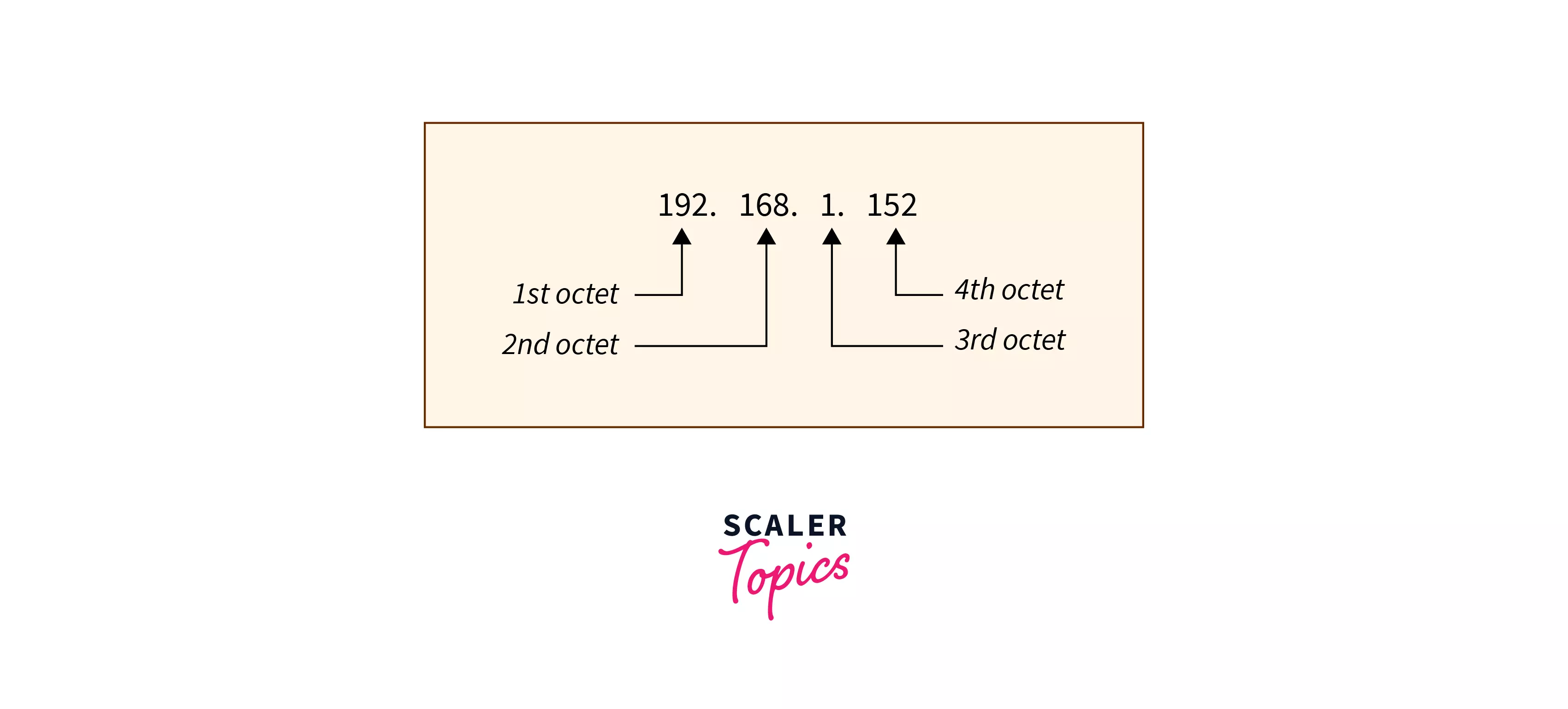
Let us see the different notations of an IPv4 address: 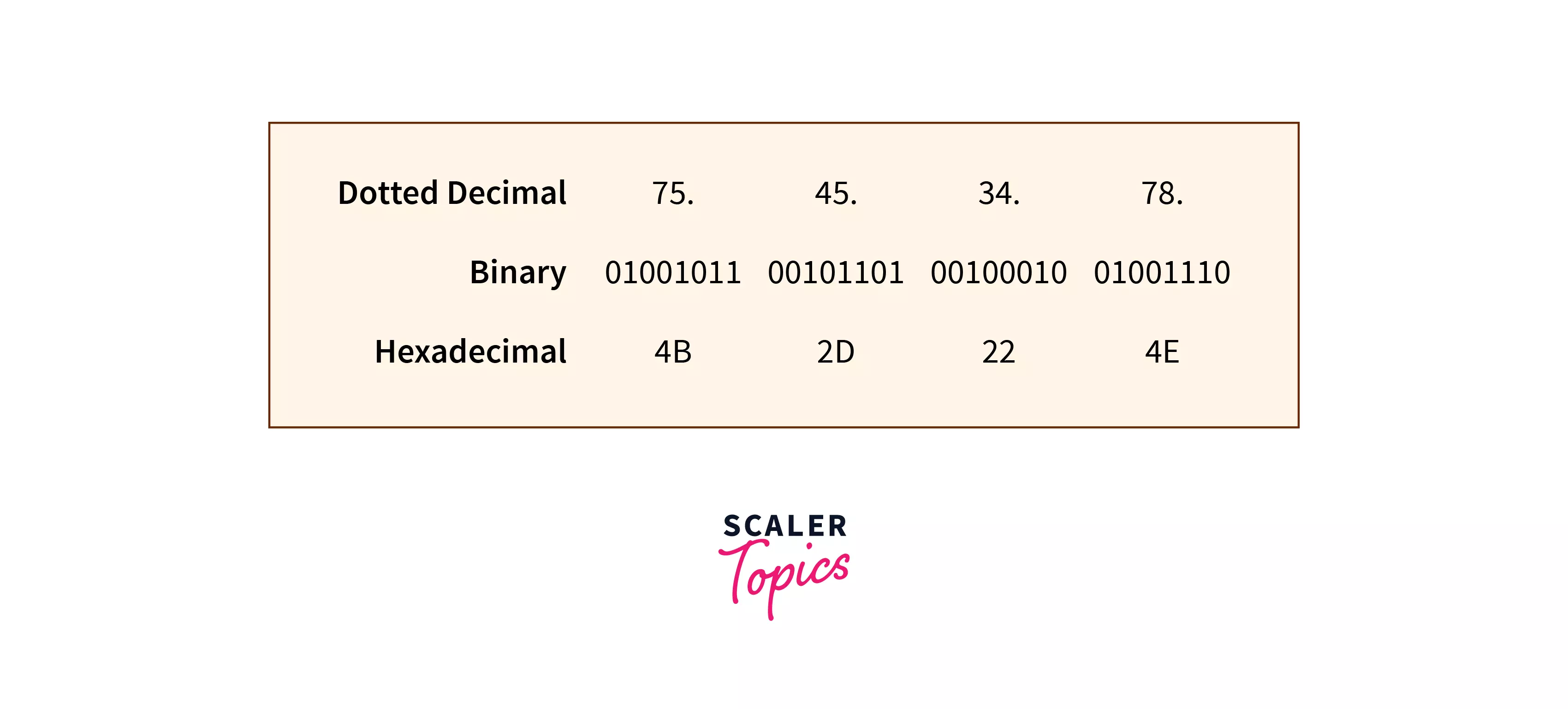
Why Do We Use IPv4 Addressing?
As discussed above, we need a unique address to identify the sender and the receiver so that the data can be transmitted after establishing the connection between the sender and the recipient. If our device wants to access other services on the internet, it needs a unique address i.e., the IP address.
The IPv4 address works on the network layer which is responsible for the transmission of data in the form of packets. It is a connectionless protocol. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address space which provides 4,294,967,2964,294,967,296 (232232) unique addresses, but large blocks are reserved for particular networking purposes.
Different Types of Addressing Modes
Addressing mode refers to the mechanism of hosting an address on a given network. There are three different types of addressing modes supported by IPv4.
- Unicast addressing mode
- Broadcast addressing mode
- Multicast addressing mode
Let us discuss in-depth each addressing mode.
Unicast addressing mode:
As the name suggests, the data is sent to only a single host(uni=one). There is one source and one receiver. The relationship between the source and the destination network is one-to-one. The destination address field consists of a 32-bit IP address that belongs to the destination host. It is the most common mode of addressing.
Broadcast addressing mode :
In broadcast addressing mode, the data is sent to all the devices in the network, i.e., multiple hosts. The destination address field of the packet consists of the IP address called the Special Broadcast address which is represented by 255.255.255.255255.255.255.255. The client then sends the packet which is received by all other servers on the network.
Multicast addressing mode :
In multicasting addressing mode, there is one source and a group of destinations. The data, i.e., the packets are neither sent to one host nor multiple hosts but are instead sent to a group of hosts. The relationship between the source and the destination is one too many. The destination address consists of a special address starting with 224.x.x.x224.x.x.x.
Parts of IPv4
As discussed at the start of the article, there are 2 parts of the IPv4 address- the network part and the host part. The network part is also known as the net id whereas the host part is also known as the host id.
Before we discuss them in-depth, let us first discuss the classes of IPv4 addresses. There are 5 types of classful addressing namely- Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E. They are classified based on address space which is divided into a fixed number of blocks and has a fixed number of hosts.

Here, each class has a fixed number of hostid and netid. Now let us comprehend what the network part and host part means.
Network part :
The network part is also known as net id which is used to classify the network to which the host is connected.
Host part :
The host part is also known as the host id which is the part of the IP address which is used to uniquely identify the host on a network.
Characteristics of IPv4 Address
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit long.
- They are either represented in binary, dotted-decimal, or hexadecimal notation. The most common form to represent IPv4 addresses is the dotted decimal notation.
- IPv4 addresses are classified into classful addressing where the address space is divided into five classes- Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E.
- IPv4 addresses are unique, so two devices on a network can never have the same IP address.
- IPv4 address consists of two parts – the network part and the host part.
- The IPv4 packet header consists of 20 bytes of data and the number of the header field is 12.
- IPv4 is a connectionless protocol.
- IPv4 has 3 modes of addressing- unicast, broadcast, and multicast.
- IPv4 can be assigned manually or by a protocol known as DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
- IPv4 can be unreliable while transmitting packets.
Advantages of IPv4 Addressing
- IPv4 is a connectionless protocol.
- The IPv4 routing can be handled easily by all the systems.
- Across a large network, IPv4 can connect various devices and along with connection, the verification can also be done. This is done without the use of NAT(Network Address Translation).
- The process of routing is carried out smoothly because the addresses are combined more effectively.
- Privacy and security are maintained in IPv4 as the data is encrypted in the packets.
- The encoding in IPv4 is flawless.
Disadvantages of IPv4 Addressing
- IPv4 can be assigned manually or by a protocol known as DHCP and if it is done through DHCP, it needs a lot of management for its infrastructure.
- Since IPv4 was established way back, its implementation did not provide security against threats introduced today. Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) enables network security to IPv4 by specifying the use of the internet. However the problem arises when IPSec is not built-in and its implementation is optional.
- Most of the IP addresses are reserved in the United States.
- To overcome the drawbacks of IPv4, IPv6 was introduced.
Conclusion
- The IPv4 address or the Internet Protocol Address is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol.
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit addresses that are unique to every host or device on the internet.
- An IP address allows the host to be connected to other devices on the internet to communicate with them.
- The IPv4 address is divided into two parts- the network part and the host part(also referred to as netid and hostid).
- There are three different types of addressing modes supported by IPv4 – Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast addressing mode.
- The IPv4 address works on the Network Layer which is responsible for the transmission of data in the form of packets. It is a connectionless protocol.
- IPv4 can be assigned manually or by a protocol known as DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
- To overcome the drawbacks of IPv4, IPv6 was introduced.