WiFi stands for Wireless Fidelity, while LiFi stands for Light Fidelity. LiFi and WiFi are both primarily utilized for internet-based applications. LiFi employs light as a medium for data transmission, whereas WiFi uses electromagnetic waves at various radio frequencies. Light experiences less interference than radio waves and can therefore be employed in settings with greater density. LiFi is an optical communication technique, whereas WiFi is a radio communication method.
What is WiFi?
WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) is a wireless networking technology that connects computers (laptops and desktops), mobile devices (smartphones and wearables), and other equipment (printers and video cameras) to the Internet. It enables these devices, as well as many others, to communicate with one another, forming a network.
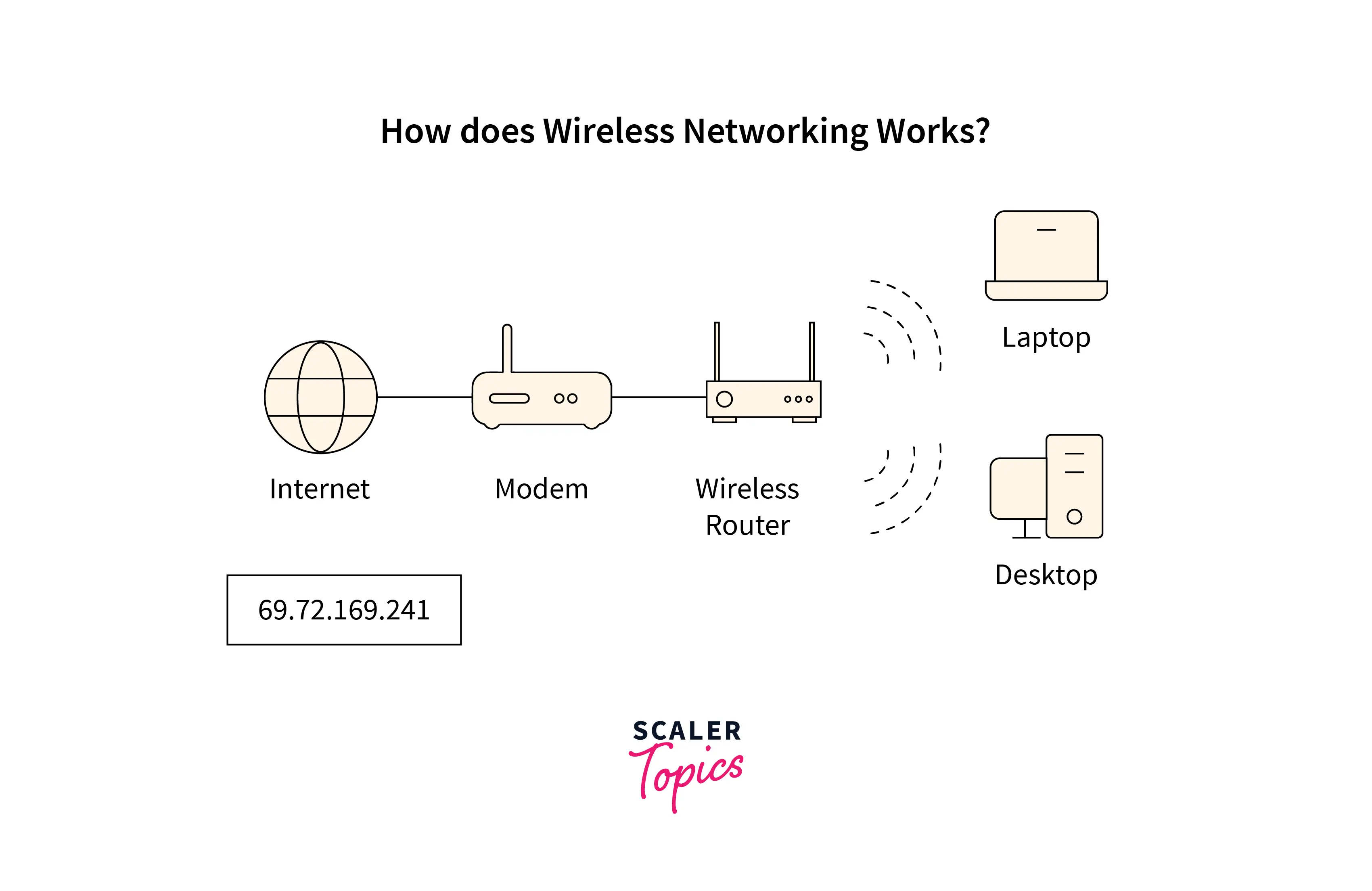
WiFi is widely used because it enables users to connect to networks without a physical cable between the device and the transmitter. When a radio frequency (RF) current is applied to an antenna, an electromagnetic field is formed that can travel through any space. WiFi provides an access point for users to connect and obtain access. These access sites can be reached from a distance of 20 to 50 meters. To connect to an access point, however, the user must have a wireless network adapter installed on the accessing device.
WiFi communicates between devices using radio frequencies or waves measured in gigahertz (GHz). WiFi signals use 2.4GHz or 5GHz, frequency bands. Dual-band devices allow you to select which frequency you want to use for your WiFi network. Each frequency band’s range and bandwidth distinguish them from one another. With slower speeds, the 2.4 GHz band extends WiFi coverage more widely. The 5GHz, in contrast, has a smaller service area and sends data much faster. Each WiFi frequency band contains multiple channels that allow our devices to send and receive data. These WiFi channels also reduce interference and overlap between your WiFi device and other devices. To understand the working of WiFi more briefly, refer to this article.
Radio Spectrum
The radio spectrum is part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies ranging from 0 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, known as radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particularly telecommunication. National regulations strictly regulate the generation and transmission of radio waves to prevent user interference, coordinated by an international agency, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Challenges with Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Capacity
- Availability
- Efficiency
- Security
- Less Nature Friendliness
Advantages of WiFi
- In order to access the internet from a distance, such as the far end of an office, it would be necessary to use exceedingly long cables, which can be expensive. Additional cables, which are likewise costly, will be needed for additional connections. WiFi made access to local networks and the internet possible without requiring direct physical connections to servers.
- Users can enjoy WiFi connections up to
50meters away from the source because radio waves can pass through walls. - WiFi internet connectivity is simple to set up. All you need is a WiFi router, which acts as the access point, and an internet service provider (ISP), which provides the internet connection. The key factor in the widespread use of WiFi internet connection is its simplicity of setup.
Disadvantages of WiFi
- WiFi networks are notoriously insecure. Its lack of security is caused by its extensive signal range, which allows network access within a
20to the50-meterradius. This permits others to connect to the network as long as they are in range. - Even if the connection is password-protected, others may attempt to hack into the network, exposing all private data.
- Another downside of WiFi connections is the unreliability of signals. This is because radio frequencies are still susceptible to numerous external interferences. These interferences can create many connection issues, including weak signals, poor reception, and even connection loss.
- WiFi connections are slower than conventional wired connections. Wireless connections often have speeds ranging from
1 to 54 Mbps, although wired connections typically have speeds of100 Mbpsor more significant.
What is LiFi?
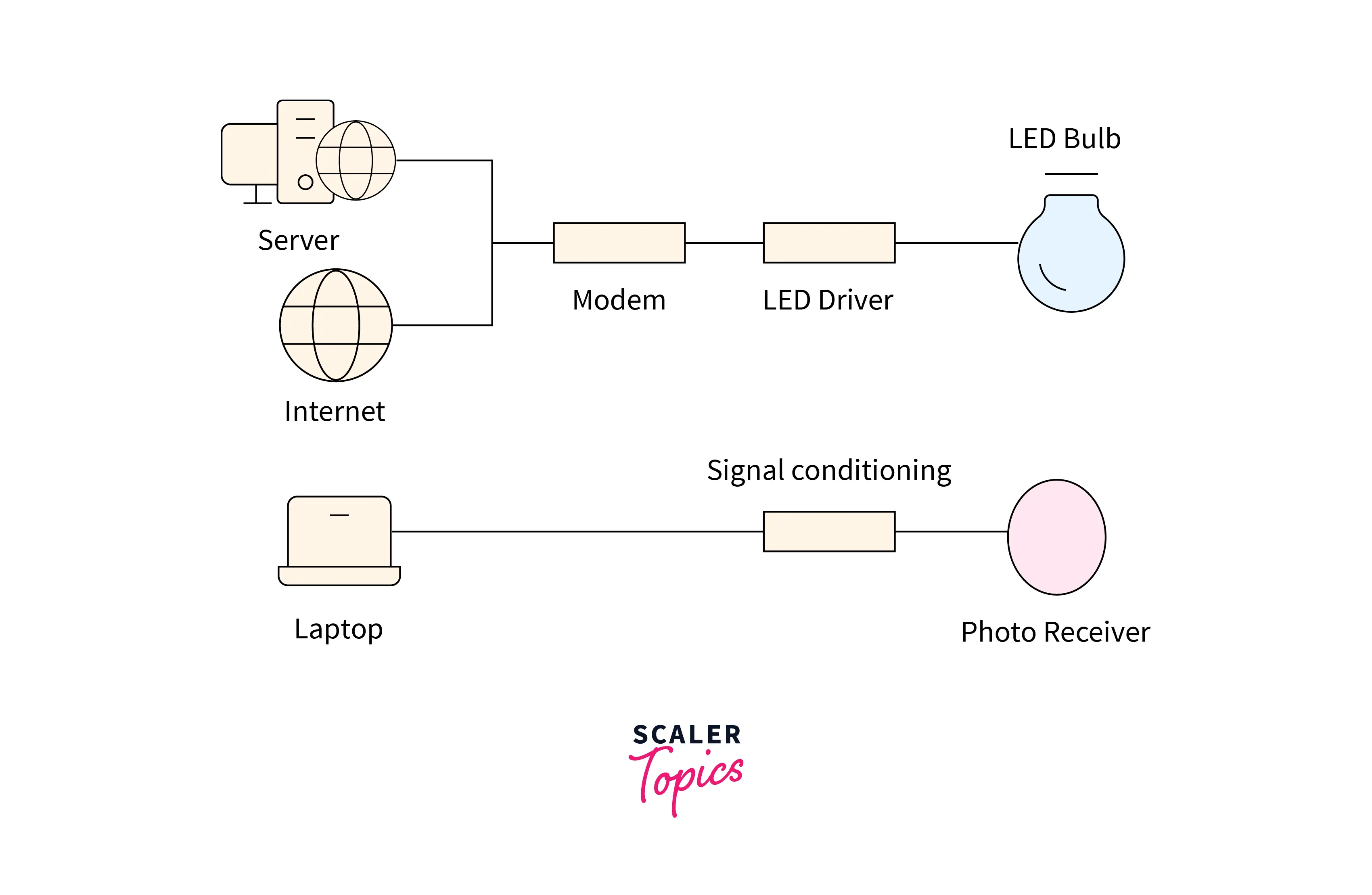
LiFi is light-based bi-directional, fully networked, wireless communication technology where the light source is used to transmit the data wirelessly. This is achieved by turning the LED ON and OFF very rapidly(Million times per second) so that the flicker is not observable by the human eye, and in this way, the data is transferred between the two devices wirelessly.
Working of LiFi
- It has two elements, i.e., a transmitting element (LED) and a Receiving element (silicon photodiode).
- The LED can be switched ON and OFF very quickly, which gives an excellent opportunity for data transfer in the form of Binary code.
- Switching ON an LED is logical
1, and switching off an LED is logical0. - We encode the data into the LEDs using a controller; we have to vary at which LEDs flicker depending on the data we want to encode to give strings of 0s and 1s.
Visible Light Spectrum
LiFi makes use of visible light as opposed to radio frequencies. Since the visible light spectrum is 10,000 times broader than the entire radio spectrum, LiFi can now utilize a more comprehensive range of available frequencies. The visible light spectrum spans wavelengths from the near ultraviolet to the near-infrared and frequencies from 430,000 to 770,000 GHz.
Why do We Use Visible Light Spectrum?
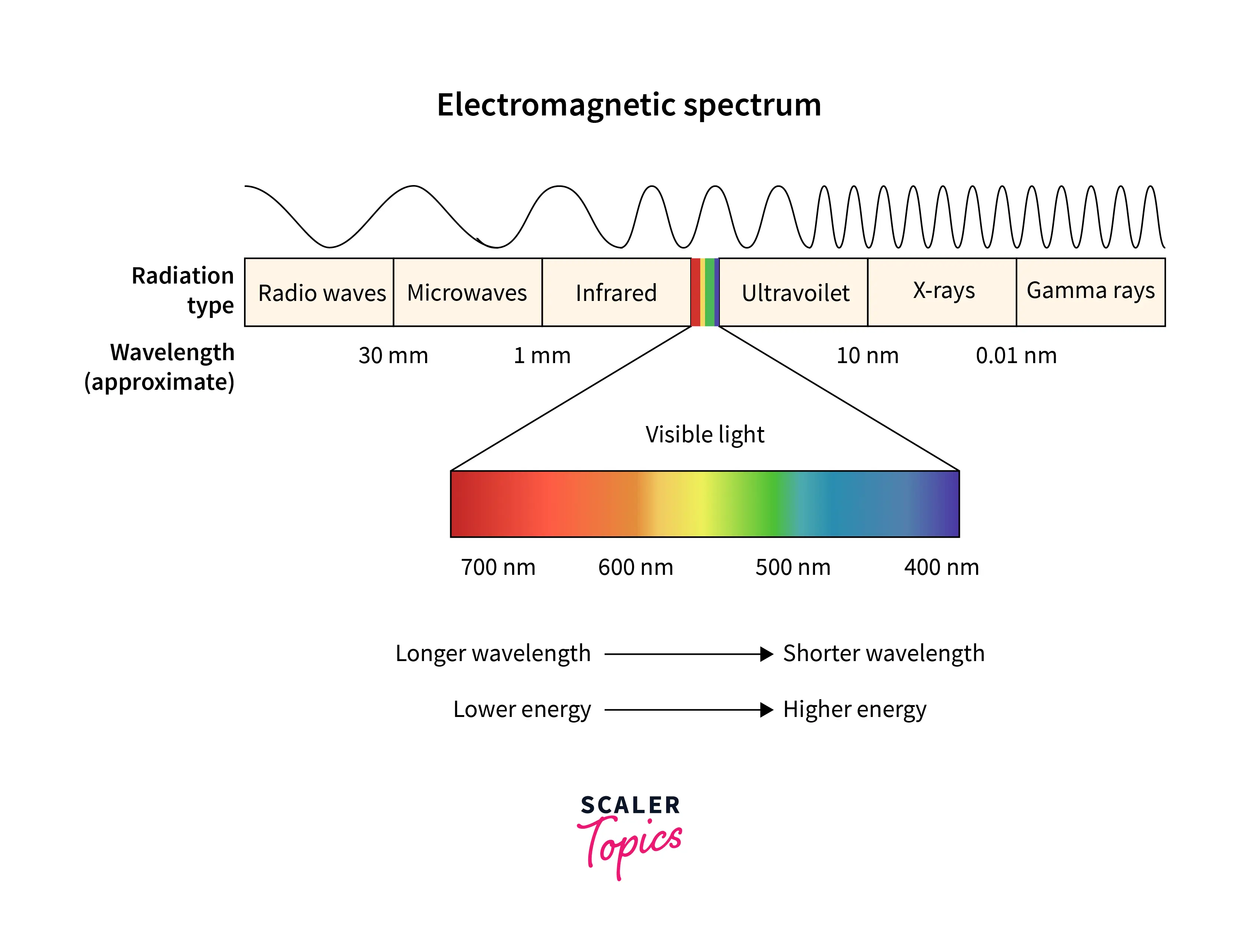
- Gamma rays are hazardous and thus can‘t be used for our purpose of communication.
- X-rays are good in hospitals and can‘t be used either.
- Ultra-violet rays are sometimes good for our skin, but for a long duration, it is dangerous.
- Infra-red rays are harmful to our eyes and therefore used at low power levels.
- We have already seen the shortcomings of radio waves.
- So, we are left with only the Visible light spectrum.
Advantages of LiFi
- Speed:- LiFi can provide speeds up to
100 Gbps. - Security:- Light can not cross the walls, so data cannot be hacked by outsiders, providing one more layer of security.
- Safety:- Unlike radio waves, light exposure is safer for humans.
- Congestion-free:- The bandwidth of the light spectrum is
1000times more than the radio spectrum; hence, it is congestion-free and free of electromagnetic interference. - Efficiency:- It uses LED for transmission, which minimizes the overall energy consumption.
Disadvantages of LiFi
- Light can’t pass through objects.
- A significant challenge facing LiFi is how the receiving device will transmit back to the transmitter.
- The high installation cost of the
VLCsystems. - Interferences from external light sources such as sun, light, standard bulbs, and opaque materials.
Comparison Table: LiFi vs WiFi
The table below briefly compares LiFi vs WiFi.
| Basis of comparison | LiFi | WiFi |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Light Fidelity | Wireless Fidelity |
| Working Environment | LiFi works in a highly dense environment because VSL(Visible Light Spectrum) is less susceptible to external interference. | Due to interference-related problems, WiFi only operates in less dense environments. |
| Invented by | LiFi was invented by Prof. Harald Hass in 2011. | WiFi was invented by NCR corporation in 1991. |
| Transmission Speed | Data transmission is very fast as compared to WiFi. | Data transmission is slow as compared to LiFi. |
| Security | Since light cannot get through the walls, LiFi significantly more secure data transfer will be possible. | Radio frequency signals can pass through walls; hence achieving secure data transfer is difficult. |
| Components | LiFi uses light signals and LED bulbs for wireless data transmission. | For wireless data communication, WiFi uses modems and radio frequency signals. |
| Frequency Bands | LiFi operates between 380 nm and 780 nm in the wavelength range. | WiFi operates at two frequency bands, i.e., 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. |
| Passage Through Sea Water or Salty Water | LiFi signals can operate in dense areas and travel through salty sea water due to less interference. | WiFi cannot operate in less dense areas and cannot pass sea water due to considerable interference. |
| Operation | It uses VSL(Visible Light Spectrum) for data transmission. | It uses Radio Waves for data transmission. |
| Coverage | LiFi covers an area of around 10 meters. | WiFi may reach an area up to 32 meters away. |
| Bandwidth | Unlimited bandwidth is available. | Limited bandwidth is available. |
| Cost | Installation cost is a bit high but overall Lower than WiFi. | Comparitively Higher than LiFi. |
| Standard | IEEE 802.15.7 | IEEE 802.11 |
| Application | LiFi is used in Healthcare, Underwater Communication, High-speed Internet through street lights, Smart power plants, and Airlines | WiFi is used to browse the internet via a WiFi hotspot. |
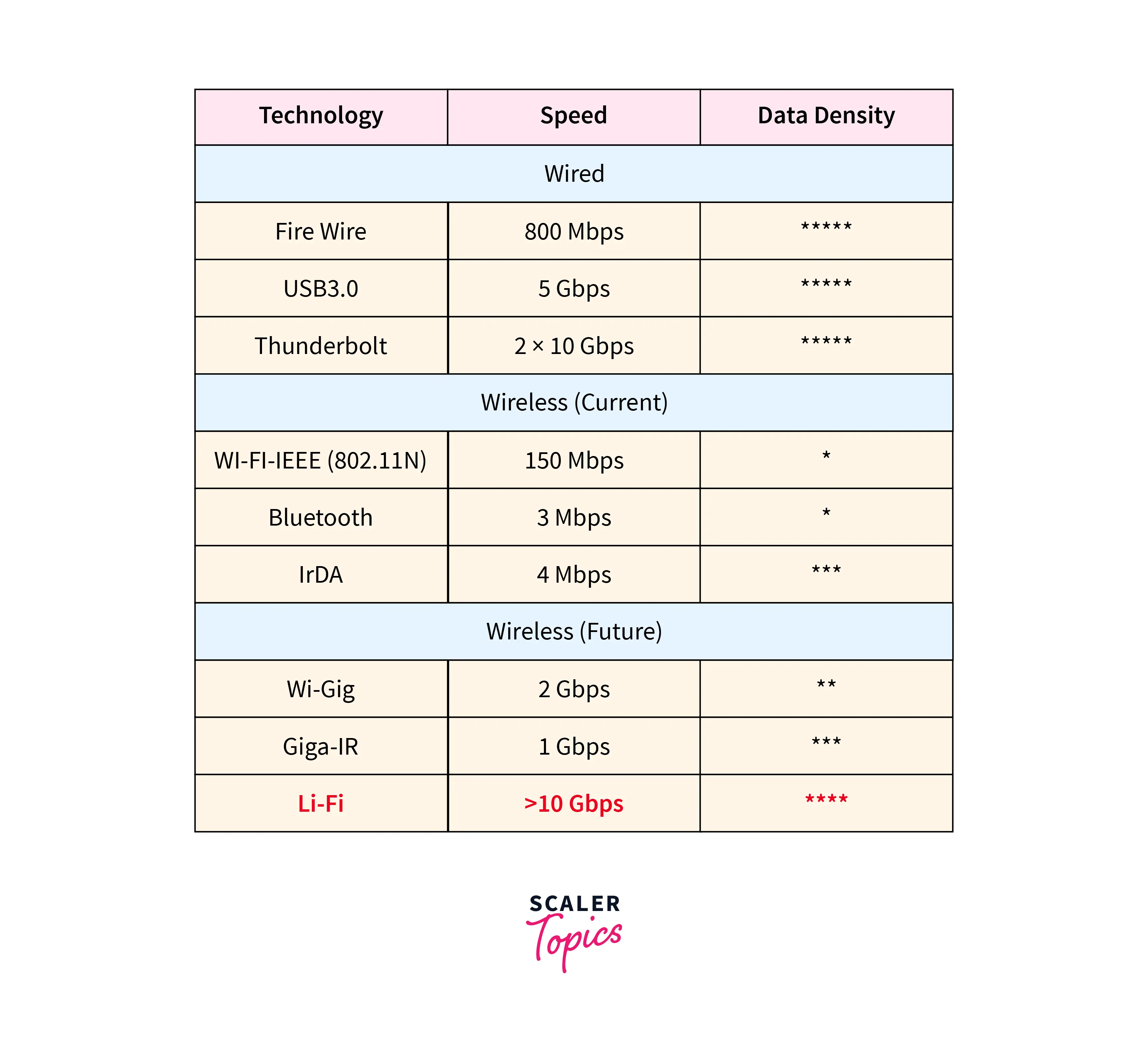
Speed Comparison between Various Technologies
The table below discusses the speed and data density comparison of LiFi vs WiFi vs other technologies.
Conclusion
- WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) is a wireless networking technology that connects computers (laptops and desktops), mobile devices (smartphones and wearables), and other equipment (printers and video cameras) to the Internet.
- WiFi signals use
2.4GHz or 5GHz, frequency bands. Dual-band devices allow you to select which frequency you want to use for your WiFi network. - The radio spectrum is part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies ranging from
0Hz to3,000GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, known as radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particularly telecommunication. - LiFi is light-based bi-directional, fully networked, wireless communication technology where the light source is used to transmit the data wirelessly.
- LiFi makes use of visible light as opposed to radio frequencies. Since the visible light spectrum is
10,000times broader than the entire radio spectrum, LiFi can now utilize a more comprehensive range of available frequencies. - Due to the shortage and less nature friendliness of radio waves we need to look for the communication alternative and Li-Fi is one of the biggest competitor. If this technology can be put into practical use, every bulb can be used something like a Wi-Fi hotspot to transmit wireless data and we will proceed toward the cleaner, greener, safer and brighter future.
- If we compare LiFi vs WiFi, we conclude WiFi is currently the most popular means of wireless communication between networking devices. But LiFi is the future of wireless communication.
