Problem Statement
k number of arrays are given, the task is to merge all the given integer arrays in such a manner that the resultant array is sorted in the runtime only.
Note: arrays are of equal size.
Example:
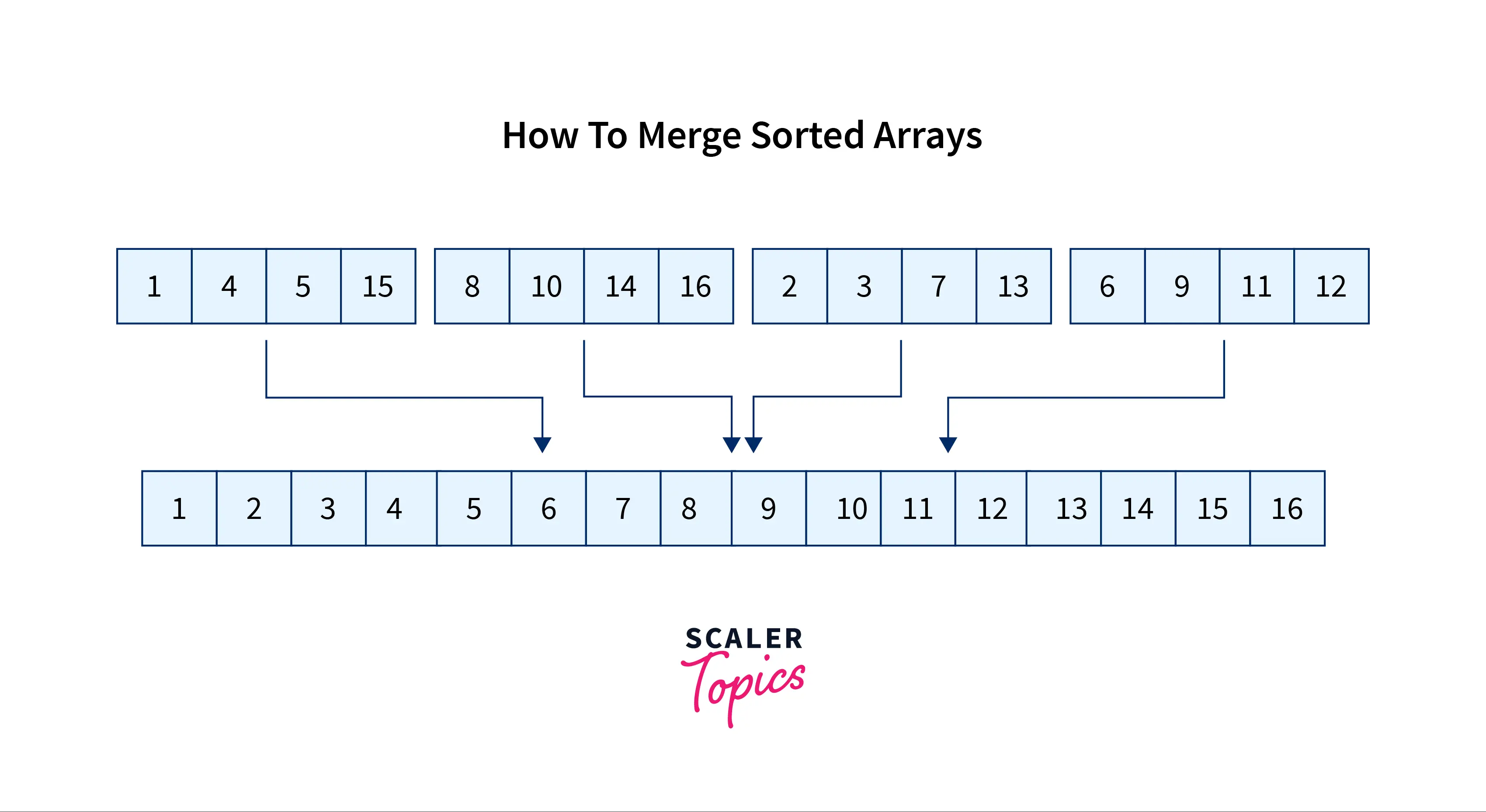
k = 4, n = 4
arr[][] = { {1, 4, 5, 15},
{8, 10, 14, 16},
{2, 3, 7, 13}} ,
{6,9,11,12};Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16Explanation
The array at the output is sorted by combining elements of all the three arrays of input.
Constraints
$1 <=n<=10^5$
The Sum of the size of all the arrays will be less than $10^5$
$1<=s[i]<=10^9$
Approach 1 (Naive Approach)
In the naive approach, create an array of size $(k*n)$ and copy elements of the array in another array which is an output array and sort the final output array.
The algorithm of the naive approach is:
- Create an array for output of size $(k*n)$
- Traverse the matrix given from start to end and copy or insert all the elements in an output array.
- Sort the output array and print it.
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
C++ program to merge k sorted arrays
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// method for printing the array
void ArrayPrint(vector<int>arr){
for (auto x: arr)
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// method which is used for merging the elements of k array
void ArrayMerge(vector<vector<int>>arr, vector<int>&outputArr){
for(auto v: arr)
for(auto x: v)
outputArr.push_back(x);
sort(outputArr.begin(),outputArr.end());
}
int main(){
// Changing the number of elements in an array
vector<vector<int>>arr = {vector<int>{2, 6, 12, 34},
vector<int>{1, 9, 20, 1000},
vector<int>{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
int n = arr.size();
int m = arr[0].size();
vector<int>outputArr;
ArrayMerge(arr, outputArr);
cout << "Merged array is " << endl;
ArrayPrint(outputArr);
return 0;
}Java program to merge k sorted arrays
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// class to merge arrays
class Main {
public static void ArrayMerge(int[][] arr, int a, int[] outputArrr){
int c = 0;
// traverse the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
outputArrr[c++] = arr[i][j];
}
Arrays.sort(outputArrr);
}
// method for printing the array
public static void printArray(int[] arr, int size){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
// main method
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] arr = { { 2, 6, 12, 34 },
{ 1, 9, 20, 1000 },
{ 23, 34, 90, 2000 } };
int k = 4;
int n = 3;
int[] outputArrr = new int[n * k];
// calling the function for merging the array
ArrayMerge(arr, n, outputArrr);
System.out.println("Merged array: ");
printArray(outputArrr, n * k);
}
}python program for merging the array
#function to merge arrays
def ArrayMerge(arr, a, outputArr):
c = 0;
# iterating through the array and merging the elements
for i in range(a):
for j in range(4):
outputArr[c] = arr[i][j];
c += 1;
outputArr.sort();
def ArrayPrint(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end = " ");
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [[ 2, 6, 12, 34],[ 1, 9, 20, 1000 ],[ 23, 34, 90, 2000 ]] ;
k = 4;
n = 3;
outputArr = [0 for i in range(n * k)]
# calling the function for merging the array
ArrayMerge(arr, n, outputArr);
print("Merged array is ");
ArrayPrint(outputArr, n * k);Output
Merged array is
1 2 6 9 12 20 23 34 34 90 1000 2000Time ComplexityO(k*n*log(k*n))
Because the resulting array is of N*k size.
Space ComplexityO(k*n), The output array is of size nk.
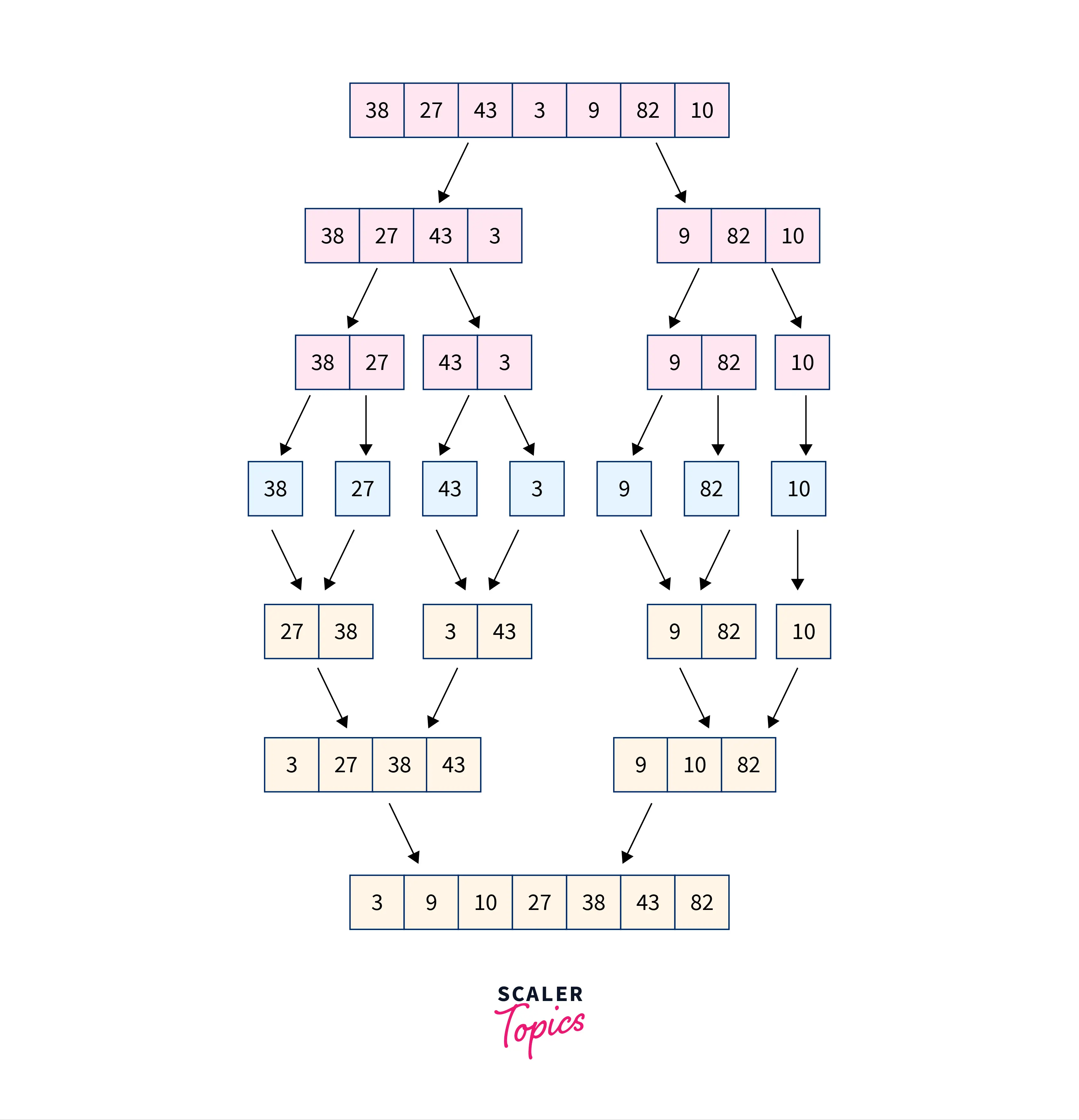
Approach 2 (Efficient Approach )
Algorithm
- Create a function that is recursive, takes the
karray, and returns the output array. - If the value of
kin the recursive function is1then return the array else if the value ofkis2then, merge the array in linear time. - If the value of
k > 2, then divide the group ofkelements in an array in two equal parts and call the function recursively. This means0tok/2in the first recursive function andk/2to k in the other recursive function. - Print the output array
Example:
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
C++ program to merge k sorted arrays of size n each
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define n 4
// method for merging the array
void ArrayMerge(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1,
int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i<n1 && j <n2)
{
// Check if current element of first
// array is smaller than current element
// of second array. If yes, store first
// array element and increment first array
// index. Otherwise do same with second array
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
// if i < n1 then putting the element of first array
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
// if j < n2 then putting the element of second array
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
// method for printing the array
void ArrayPrint(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i=0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// method for merging the array
void mergeKArrays(int arr[][n],int i,int j, int outputArr[])
{
// if i and j, both are equal then put the element in output array
if(i==j)
{
for(int p=0; p < n; p++)
outputArr[p]=arr[i][p];
return;
}
//merge the array
if(j-i==1)
{
ArrayMerge(arr[i],arr[j],n,n,outputArr);
return;
}
int out1[n*(((i+j)/2)-i+1)],out2[n*(j-((i+j)/2))];
//divide the array into halves
mergeKArrays(arr,i,(i+j)/2,out1);
mergeKArrays(arr,(i+j)/2+1,j,out2);
//merge the outputArr array
ArrayMerge(out1,out2,n*(((i+j)/2)-i+1),n*(j-((i+j)/2)),outputArr);
}
int main()
{
int arr[][n] = {{2, 6, 12, 34},
{1, 9, 20, 1000},
{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
int k = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int outputArr[n*k];
mergeKArrays(arr,0,2, outputArr);
cout << "Merged array is " << endl;
ArrayPrint(outputArr, n*k);
return 0;
}Java program to merge k sorted arrays of size n each.
import java.util.*;
class Main{
static final int n = 4;
static void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1,
int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i<n1 && j <n2)
{
// Check if current element of first
// array is smaller than current element
// of second array. If yes, store first
// array element and increment first array
// index. Otherwise do same with second array
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
static void ArrayMerge(int arr[][], int i, int j, int outputArr[])
{
if(i == j)
{
for(int p = 0; p < n; p++)
outputArr[p] = arr[i][p];
return;
}
if(j - i == 1)
{
mergeArrays(arr[i], arr[j], n, n, outputArr);
return;
}
int []outputn1 = new int[n*(((i + j) / 2) - i + 1)];
int []outputn2 = new int[n*(j - ((i + j) / 2))];
//dividing the array into two halves
ArrayMerge(arr, i, (i + j) / 2, outputn1);
ArrayMerge(arr, (i + j) / 2 + 1, j, outputn2);
// merging the outputArr array
mergeArrays(outputn1, outputn2, n * (((i + j) / 2) - i + 1), n * (j - ((i + j) / 2)), outputArr);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Change n at the top to change number of elements
// in an array
int arr[][] = {{2, 6, 12, 34},
{1, 9, 20, 1000},
{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
int k = arr.length;
int []outputArr = new int[n*k];
ArrayMerge(arr,0,2, outputArr);
System.out.print("Merged array is " +"\n");
printArray(outputArr, n*k);
}
}Python program to merge k sorted arraysof size n each.
n = 4
# function to merge both the arrays
def ArrayMerge(arrayay1, arrayay2, n1, n2, arrayay3):
i, j, k = 0, 0, 0
# Traversing both the arrayay
while (i < n1 and j < n2):
# Check if current element of first
# arrayay is smaller than current element
# of second arrayay. If yes, store first
# arrayay element and increment first arrayay
# index. Otherwise do same with second arrayay
if (arrayay1[i] < arrayay2[j]):
arrayay3[k] = arrayay1[i]
k += 1
i += 1
else:
arrayay3[k] = arrayay2[j]
k += 1
j += 1
# Store remaining elements of first arrayay
while (i < n1):
arrayay3[k] = arrayay1[i]
k += 1
i += 1
# Store remaining elements of second arrayay
while (j < n2):
arrayay3[k] = arrayay2[j]
k += 1
j += 1
# function to print arrayay elements
def ArrayPrint(array, size):
for i in range(size):
print(array[i],end = " ")
# This function takes an arrayay of arrayays
# as an argument and all arrays are assumed
# to be sorted. It merges them together
# and prints the final sorted output.
def mergeKArrays(array, i, j, output):
global n
if (i == j):
for p in range(n):
output[p] = array[i][p]
return
if (j - i == 1):
ArrayMerge(array[i], array[j],
n, n, output)
return
out1 = [0 for i in range(n * (((i + j) // 2) - i + 1))]
out2 = [0 for i in range(n * (j - ((i + j) // 2)))]
# Divide the arrayay into halves
mergeKArrays(array, i, (i + j) // 2, out1)
mergeKArrays(array, (i + j) // 2 + 1, j, out2)
# Merge the output arrayay
ArrayMerge(out1, out2,
n * (((i + j) / 2) - i + 1),
n * (j - ((i + j) / 2)), output)
array = [ [ 2, 6, 12, 34 ],
[ 1, 9, 20, 1000 ],
[ 23, 34, 90, 2000 ] ]
k = len(array)
output = [0 for i in range(n * k)]
mergeKArrays(array, 0, 2, output)
print("Merged arrayay is ")
ArrayPrint(output, n * k)Output
Merged array is
1 2 6 9 12 20 23 34 34 90 1000 2000Time Complexity
$O( n * k * log k)$
Because there are log(k) levels at each recursive level which are divided into two halves at each k level.
Space Complexity
$O( n * k * log k)$
Each level requires O(n * k) space for storing elements in an array.
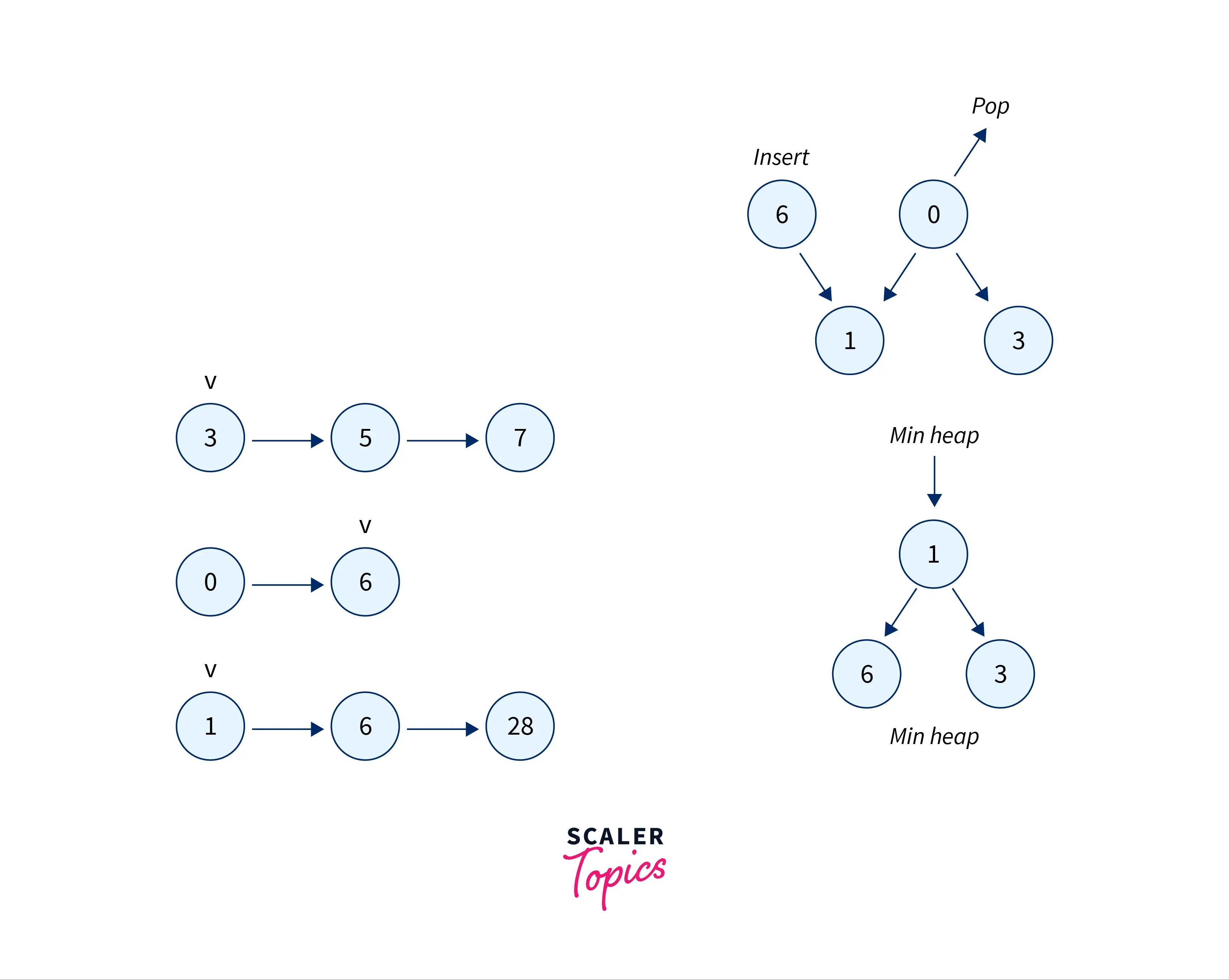
Approach 3 (Using min-heap)
Algorithm
- Create a min-heap and insert into it all the first elements of all the
knumber of arrays. - Iterate through the loop until the length becomes
0 - Remove the element from the top of the min-heap and add it to output array
- Insert the next element in the same array until there are no more elements left.
Example:
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
// C++ program to merge k sorted array
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define n 4
// A min-heap node
struct MinHeapNode
{
// The element to be stored
int element;
// index of the array from which the element is taken
int i;
// index of the next element to be picked from the array
int j;
};
// Prototype of a utility function to swap two min-heap nodes
void swap(MinHeapNode *x, MinHeapNode *y);
// A class for Min Heap
class MinHeap
{
// pointer to array of elements in heap
MinHeapNode *harr;
// size of min heap
int heap_size;
public:
// Constructor: creates a min heap of given size
MinHeap(MinHeapNode a[], int size);
// to heapify a subtree with root at given index
void MinHeapify(int );
// to get index of left child of node at index i
int left(int i) { return (2*i + 1); }
// to get index of right child of node at index i
int right(int i) { return (2*i + 2); }
// to get the root
MinHeapNode getMin() { return harr[0]; }
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
void replaceMin(MinHeapNode x) { harr[0] = x; MinHeapify(0); }
};
// This function takes an array of arrays as an argument and
// All arrays are assumed to be sorted. It merges them together
// and prints the final sorted output.
int *mergeKArrays(int arr[][n], int k)
{
// To store output array
int *output = new int[n*k];
// Create a min heap with k heap nodes.
// Every heap node has first element of an array
MinHeapNode *harr = new MinHeapNode[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
// Store the first element
harr[i].element = arr[i][0];
// index of array
harr[i].i = i;
// Index of next element to be stored from the array
harr[i].j = 1;
}
// Create the heap
MinHeap hp(harr, k);
// iterate through heap and get min element
for (int count = 0; count < n*k; count++)
{
// Get the minimum element and store it in output
MinHeapNode root = hp.getMin();
output[count] = root.element;
// Find the next element that will replace current
// root of heap.
if (root.j < n)
{
root.element = arr[root.i][root.j];
root.j += 1;
}
// If root was the last element of its array, INT_MAX is for infinite
else root.element = INT_MAX;
// Replace root with next element of array
hp.replaceMin(root);
}
return output;
}
MinHeap::MinHeap(MinHeapNode a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1)/2;
while (i >= 0)
{
MinHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// A recursive method to heapify a
// subtree with a root at the given index.
// This method assumes that the subtrees
// are already heapified
void MinHeap::MinHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l].element < harr[i].element)
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r].element < harr[smallest].element)
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i)
{
swap(&harr[i], &harr[smallest]);
MinHeapify(smallest);
}
}
// function to swap two elements
void swap(MinHeapNode *x, MinHeapNode *y)
{
MinHeapNode temp = *x; *x = *y; *y = temp;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i=0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[][n] = {{2, 6, 12, 34},
{1, 9, 20, 1000},
{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
int k = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int *output = mergeKArrays(arr, k);
cout << "Merged array is " << endl;
printArray(output, n*k);
return 0;
}Java program to merge k sorted array
// min heap node class
class MinHeapNode
{
int element; // element to be stored
int i; // index
// index of the next element
int j;
// min heap node method
public MinHeapNode(int element, int i, int j)
{
this.element = element;
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
};
class MinHeap{
MinHeapNode[] harr; // Array of elements in heap
int heap_size;
// this method builds heap from given array
public MinHeap(MinHeapNode a[], int size){
heap_size = size;
harr = a;
int i = (heap_size - 1)/2;
while (i >= 0)
{
MinHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree
// with the root at the given index This method
// assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
void MinHeapify(int i){
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l].element < harr[i].element)
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r].element < harr[smallest].element)
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i)
{
swap(harr, i, smallest);
MinHeapify(smallest);
}
}
// to get index of left child of node at index i
int left(int i) { return (2*i + 1); }
// to get index of right child of node at index i
int right(int i) { return (2*i + 2); }
// to get the root
MinHeapNode getMin(){
if(heap_size <= 0){
System.out.println("Heap underflow");
return null;
}
return harr[0];
}
// to replace root with new node
// "root" and heapify() new root
void replaceMin(MinHeapNode root) {
harr[0] = root;
MinHeapify(0);
}
// A utility function to swap two min heap nodes
void swap(MinHeapNode[] arr, int i, int j) {
MinHeapNode temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
};
class Main{
// A utility function to print array elements
static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for(int i : arr)
System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// This function takes an array of
// arrays as an argument and All
// arrays are assumed to be sorted.
// It merges them together and
// prints the final sorted output.
static void mergeKSortedArrays(int[][] arr, int k)
{
MinHeapNode[] hArr = new MinHeapNode[k];
int resultSize = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
MinHeapNode node = new MinHeapNode(arr[i][0],i,1);
hArr[i] = node;
resultSize += arr[i].length;
}
// Create a min heap with k heap nodes. Every heap node
// has first element of an array
MinHeap mh = new MinHeap(hArr, k);
int[] result = new int[resultSize]; // To store output array
// Now one by one get the minimum element from min
// heap and replace it with next element of its array
for(int i = 0; i < resultSize; i++)
{
// Get the minimum element and store it in result
MinHeapNode root = mh.getMin();
result[i] = root.element;
// Find the next element that will replace current
// root of heap. The next element belongs to same
// array as the current root.
if(root.j < arr[root.i].length)
root.element = arr[root.i][root.j++];
// If root was the last element of its array
else
root.element = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Replace root with next element of array
mh.replaceMin(root);
}
printArray(result);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int[][] arr= {{2, 6, 12, 34},
{1, 9, 20, 1000},
{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
System.out.println("Merged array :");
mergeKSortedArrays(arr,arr.length);
}
};Python program to merge k sorted array
#function to merge k sorted arrays
def merge(lists):
final_list = [] #output array
heap = [(mylst[0], i, 0) for i, mylst in enumerate(lists) if mylst]
heapq.heapify(heap)
# iterating through the heap and merging the elements
while heap:
val, list_ind, element_ind = heapq.heappop(heap)
final_list.append(val)
if element_ind + 1 < len(lists[list_ind]):
next_tuple = (lists[list_ind][element_ind + 1],
list_ind, element_ind + 1)
heapq.heappush(heap, next_tuple)
return final_listOutput
Merged array is
1 2 6 9 12 20 23 34 34 90 1000 2000Time Complexity
$O( n * k * log k)$ because insertion and deletion of element in min heap requires log k time.
Space Complexity
$O(k)$ space required by min-heap.
Merge k Sorted Arrays | Set 2 (Different Sized Arrays)
Approach
We would use a min-heap that would return the smallest element in constant time O(1) instead of searching through all k elements.
Example:
Input:
k = 3
arr[][] = { {1, 3},
{2, 4, 6},
{0, 9, 10, 11}};Output:
0 1 2 3 4 6 9 10 11 Algorithm
- Create an array for storing the output
- Create a min heap of
ksize and insert the first element of heap in all the array - Till the priority queue is not empty,, repeat the below steps:
- Remove min element from the heap and store it in the output array
- Insert the next element of array and do it until the array is empty
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
C++ program to merge k sorted arrays of n size
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, pair<int, int> > ppi;
vector<int> mergeKArrays(vector<vector<int> > arr)
{
vector<int> output;
// priority queue to store the vector pair
priority_queue<ppi, vector<ppi>, greater<ppi> > pq;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
pq.push({ arr[i][0], { i, 0 } });
while (pq.empty() == false) {
ppi curr = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// i ==> Array Number
// j ==> Index of array number
int i = curr.second.first;
int j = curr.second.second;
output.push_back(curr.first);
// checking if the next element belongs to same array as the current array.
if (j + 1 < arr[i].size())
pq.push({ arr[i][j + 1], { i, j + 1 } });
}
return output;
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > arr{ { 2, 6, 12 },
{ 1, 9 },
{ 23, 34, 90, 2000 } };
vector<int> output = mergeKArrays(arr);
cout << "Merged array is " << endl;
for (auto x : output)
cout << x << " ";
return 0;
}Java program to merge k sorted arrays of n size
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main {
private static class HeapNode
implements Comparable<HeapNode> {
int x;
int y;
int value;
// method of heap node
HeapNode(int x, int y, int value)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.value = value;
}
@Override public int compareTo(HeapNode hn)
{
if (this.value <= hn.value) {
return -1;
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
}
// merging of array function
public static ArrayList<Integer>
mergeKArrays(int[][] arr, int K)
{
ArrayList<Integer> result
= new ArrayList<Integer>();
PriorityQueue<HeapNode> heap
= new PriorityQueue<HeapNode>();
// iterating through the array and adding it to the heap
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
heap.add(new HeapNode(i, 0, arr[i][0]));
}
HeapNode curr = null;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
curr = heap.poll();
result.add(curr.value);
// Check if next element of curr min exists, if yes the add it to the heap
if (curr.y < (arr[curr.x].length - 1)) {
heap.add(
new HeapNode(curr.x, curr.y + 1,
arr[curr.x][curr.y + 1]));
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] arr = { { 2, 6, 12 },
{ 1, 9 },
{ 23, 34, 90, 2000 } };
System.out.println(Main.mergeKArrays(arr, arr.length).toString());
}
}Python program to merge k sorted arrays of n size
from heapq import merge
# function for meging k arrays
def mergeK(arr, k):
l = arr[0]
for i in range(k-1):
# when k = 0 it merge arr[1] with arr[0]
l = list(merge(l, arr[i + 1]))
return l
def printArray(arr):
print(*arr)
# main
arr =[[2, 6, 12 ],
[ 1, 9 ],
[23, 34, 90, 2000 ]]
k = 3
l = mergeK(arr, k)
printArray(l)Output
Merged array is
1 2 6 9 12 23 34 90 2000Time Complexity
O(N Log k) because it is heap-based.
Space Complexity
O(N) because of output array.
Conclusion
- Approach 1 (
Naive Approach)- create an array of size k*n and copy elements of the array in another array which is an output array and sort the output array.- Time Complexity :
O(k*n*log(k*n)) - Space Complexity:
O(k*n)
- Time Complexity :
- Approach 2 (
Efficient Approach)- Create a function that is recursive, takes the k array, and returns the output array.- Time Complexity-
O( n * k * log k) - Space Complexity-
O( n * k * log k)
- Time Complexity-
- Approach 3 (
Using min-heap)- Create a min-heap and insert into it all the first elements of all the k number of arrays. Iterate and remove the element from the top of the min-heap.- Time Complexity-
O( n * k * log k) - Space Complexity-
O(k)
- Time Complexity-
- Merge k sorted arrays | Set 2 (Different Sized Arrays)- The approach for this is to use heap data structure along with the priority queue.
- Time Complexity-
O(N Log k) - Space Complexity-
O(N)
- Time Complexity-