Multicasting is a method of communication that allows data to be sent to more than one destination simultaneously. It is commonly used for applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and live streaming. Multicast networking relies on the simple idea that a single packet can be delivered by a server and received by a large number of receivers.
What is Multicasting in Computer Network?
Multicastingin computer networks is a type of group communication in which data is sent simultaneously from a sender to multiple recipients or network nodes. This type of communication supports both one-to-many and many-to-many interactions, allowing senders to transmit data packets to multiple receivers across LANs or WANs. Multicasting helps optimize network resources and reduce data traffic by sending data to numerous nodes simultaneously.
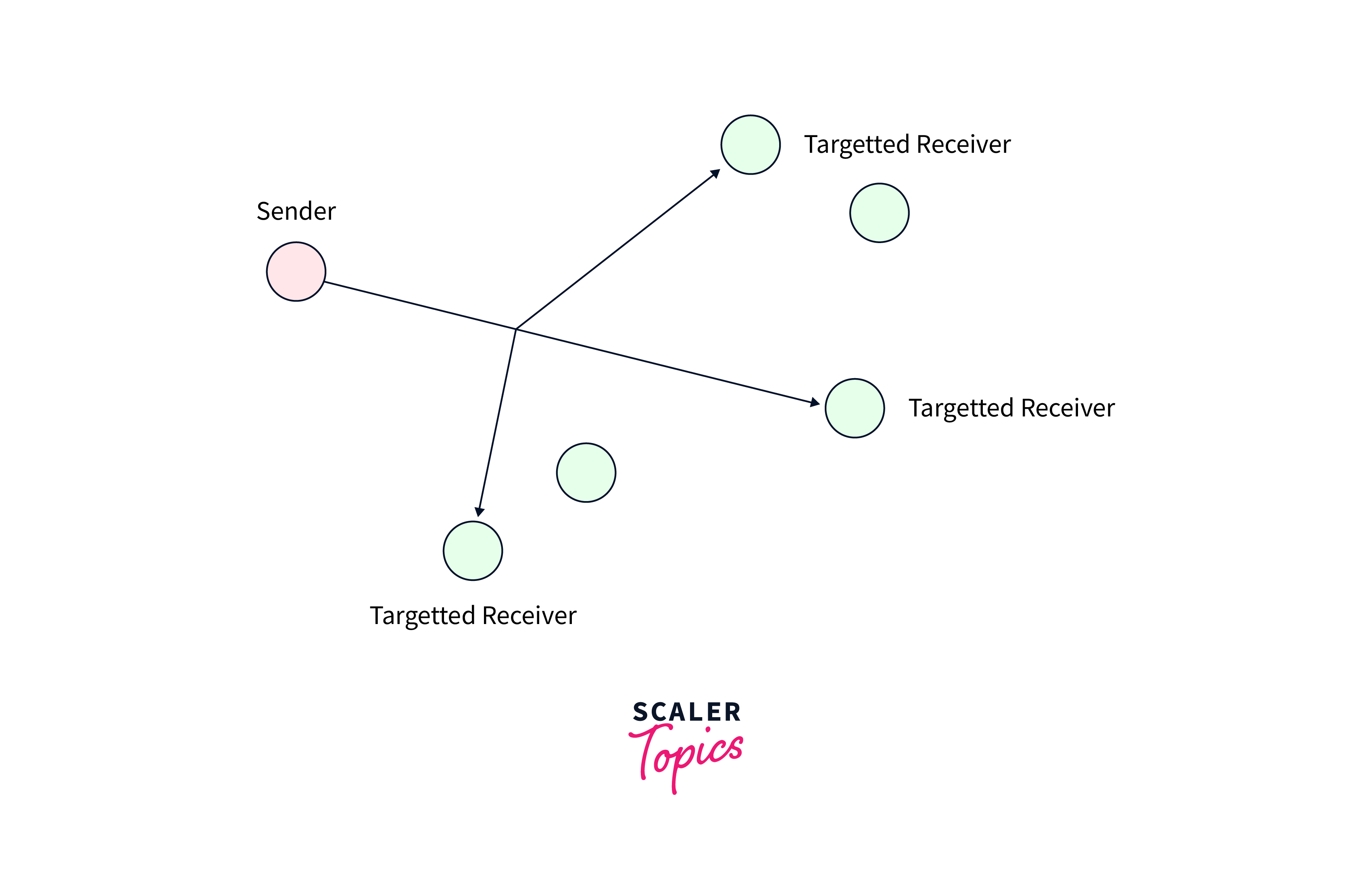
Multicastingand broadcast differ in their level of selectivity. All devices receive broadcast packets in a particular network segment or broadcast domain, whereas multicasting packets are only received by devices expressing interest in receiving them. This selective nature of multicasting allows for targeted delivery to specific recipients instead of sending the data to all devices on the network segment. In order to accomplish this task, one approach would be to send individual copies of the data to each user or node in the network. However, this method could be more efficient and can result in increased network latency. Multicasting comes into play to address these issues. Multicasting allows for a single data transmission that can be divided among multiple users, effectively reducing the bandwidth required for communication. This approach ensures more efficient and optimized data delivery in the network.
Applications of Multicasting
Let’s see various applications of Multicasting:
- Video Streaming: Multicasting distributes live video streams or multimedia to multiple viewers, such as online webinars or live sports events.
- IP Multicasting: It refers to multicasting that occurs over the Internet. To transfer data, these multicast use the internet protocol (IP).
- IoT (Internet of Things): When multiple devices in IoT applications require data from a central source, multicasting can be beneficial in terms of conserving bandwidth and enhancing communication efficiency.
- Video conferencing: Multicasting in video conferencing distributes audio and video streams to all participants, reduces network load, and enables smoother communication.
- Software Updates distribution: Multicasting efficiently distributes software updates, patches, or large files to many devices in a network while conserving bandwidth and reducing network congestion compared to unicast or broadcast methods.
- Distance Learning: Delivering educational content to many remote participants simultaneously, such as online lectures, webinars, and training sessions, can be achieved through multicasting.
IP Multicasting
Multicastingis a technique used to transmit data to a group of recipients simultaneously. When this technique takes place over the Internet, it is called IP Multicasting. IP Multicasting uses the Internet Protocol (IP) to transmit data.
Multicast trees are used in IP multicasting to transmit data to multiple receivers efficiently. A multicast tree is a data stream that flows from a single source and is distributed to multiple receivers. The branches of these trees are formed at the routers. These branches are responsible for deciding which path to forward the data by optimizing the path of transmission.
In IP multicasting, the data flows from the source toward the receivers by following the tree branches created by the routers. The multicasting technique enables many devices in a network to receive the same data simultaneously without needing the bandwidth to send separate data to each device.
The IP Multicasting uses two primary protocols for its execution:
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) enables recipients to access multicast data or information. To receive a multicast message, a host must join the multicast group using IGMP.
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)is a routing protocol utilized by network routers to create multicast trees and efficiently transmit data to multiple recipients.
Ethernet Multicasting
Ethernet Multicastingrefers to the process of multicast communication at the data link layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model) in Ethernet networks. In Ethernet multicast, multicast frames are distinguished by setting a 1 bit in the least significant bit (LSB) of the first byte in the destination address. This mechanism efficiently transmits data to multiple recipients within an Ethernet network.
Primary Uses for Multicast Networking
IPv6networks utilize multicast instead of broadcast. Multicast is employed for various important network infrastructure tasks such as router discovery, address allocation, and neighbor discovery, replacing the need for ARP. It offers several advantages due to its fundamental characteristics. Since packets are replicated and distributed by the network, a server only needs to send each packet once, making it suitable for scenarios where multiple receivers must receive the same data. However, multicast is one-way, necessitating separate protocols for responses. Additionally, dropped packets must either be insignificant or have recovery mechanisms built separately. These characteristics prove particularly beneficial in these places.
- Distributing AV data streams: IP multicasting provides audio/visual data to multiple users simultaneously, such as in IP-based cable TV. Users subscribe to data streams, allowing seamless channel switches with slight interruptions due to occasional dropped packets.
- Real-time stock-market data: For fairness, real-time stock market data uses multicasting to ensure that all participants receive data simultaneously. However, due to the value of data, backup systems that use TCP unicast assist in recovering lost packets.
- Military and Defense: Multicasting plays a crucial role in military and defense contexts by enabling effective and secure communication among units, ships, and command centers. So, multicasting must ensure reliable and synchronized distribution of essential data without data loss.
- Emergency Alerts and Notifications: Multicasting is an effective means of disseminating emergency alerts and notifications to a wide audience, including weather warnings, public safety messages, and disaster recovery information. It is imperative that packet loss is minimized in these scenarios.
Conclusion
Multicastingis a method of communication that allows data to be sent to more than one destination simultaneously.Multicastingoffers significant advantages when there is a requirement for one-to-many or many-to-many communication patterns without the drawbacks of broadcasting or individual unicast transmissions.- IP Multicasting uses the IP to transmit data.
- Ethernet multicast refers to the process of multicast communication at the data link layer of the
OSImodel in Ethernet networks. - Video Streaming,
IoT (Internet of Things), Video conferencing and Software Updates distribution are some of the applications of the Multicasting.
