Problem Statement
Given a 2D matrix having $n$ rows and $m$ number of columns. Print a transpose of the given matrix.
The transpose of a matrix is a new matrix that is obtained by exchanging the rows and columns.
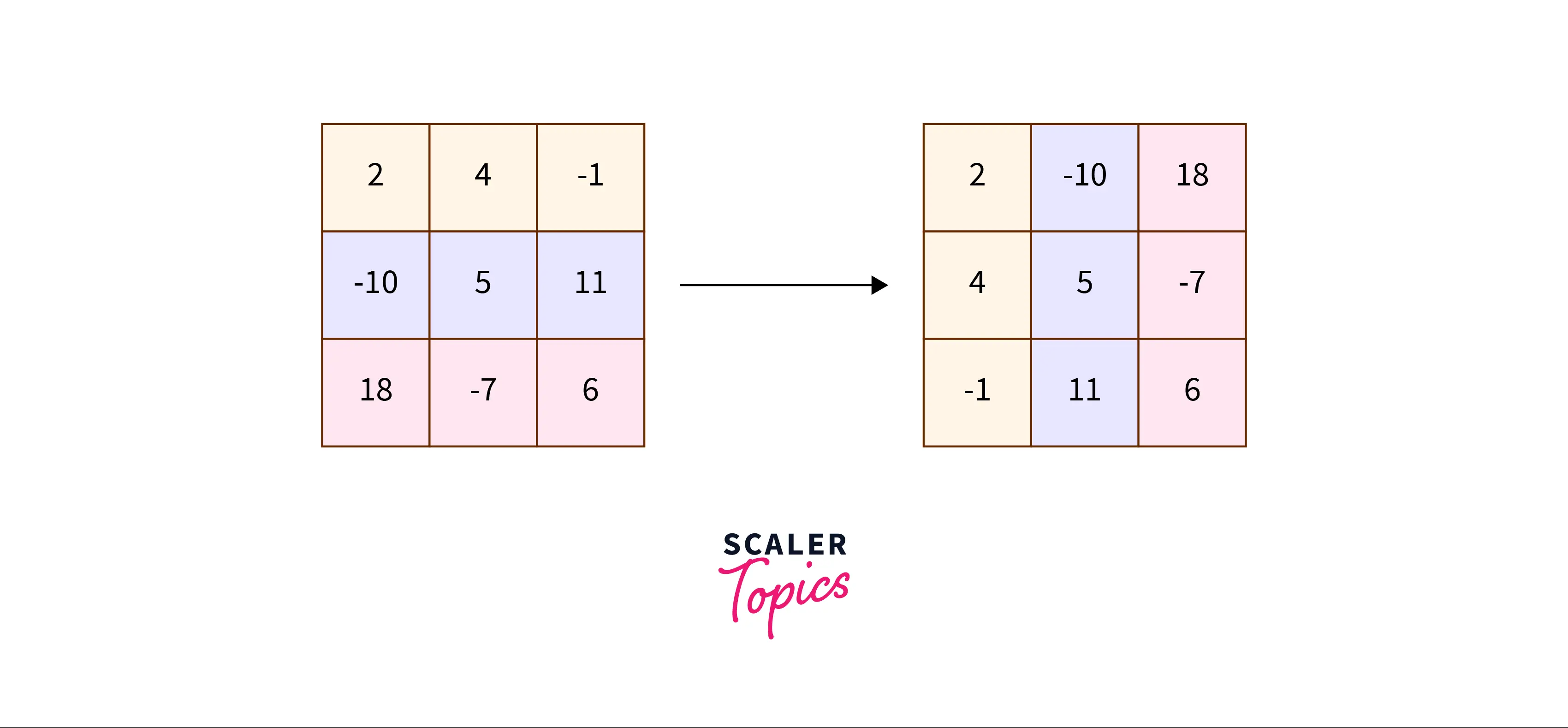
Example
Let us have a look at some examples on how to transpose a matrix.
Example1
Input:
2
3
2 4 6 -5 7 0Output:
Entered matrix:
2 4 6
-5 7 0
Transpose of the matrix:
2 -5
4 7
6 0Example2
Input:
3
3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Output:
Entered matrix:
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Transpose of the matrix:
1 4 7
2 5 8
3 6 9Example Explanation
Let us have a look at some examples to understand how to transpose a matrix.
Example 1:
In this example, first the user enters the value of $n=2$ and $m=3$, followed by $n \times m = 2 \times 3 = 6$ numbers as input, i.e. $2\ 4\ 6\ -5\ 7\ 0$.
Hence the matrix formed is
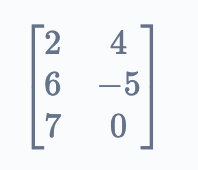
Once the code transposes this matrix, i.e. it interchanges the columns as rows and vice versa, the output becomes
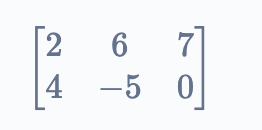
This is the transpose of the given matrix.
Example 2:
In this example, first the user enters the value of $n=3$ and $m=3$, followed by $n \times m = 3 \times 3 = 9$ numbers as input, i.e. $1\ 2\ 3\ 4\ 5\ 6\ 7\ 8\ 9$.
Hence the matrix formed is
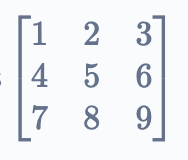
Once the code transposes this matrix, i.e. it interchanges the columns as rows and vice versa, the output becomes
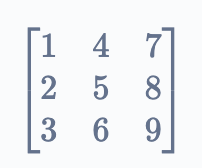
This is the transpose of the given matrix.
Constraints
The following are the constraints assumed while we perform transpose of a matrix.
$n ==$ number of rows
$m ==$ number of columns
$1 <= m, n <= 1000$
$1 <= m * n <= 10^5$
$-10^9 <= matrix[i][j] <= 10^9$
Approach 1 – Using Functions – For Loop
Algorithm
- Take input of $n$ and $m$
- take input in matrix array of size $n \times m$.
- create another transpose_matrix array of size $m \times n$ transpose of the input matrix.
- Loop through the matrix array and convert its rows into columns of transpose_matrix array using
transpose_matrix[ i ][ j ] = matrix[ j ][ i ]; - print matrix array and transpose_matrix array which contains transpose of the matrix.
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
C++ implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// function to transpose a given 2D matrix
vector<vector<int>> transpose(vector<vector<int>>& matrix){
vector<vector<int>> transpose_matrix;
vector<int> temp;
int n= matrix.size();
int m= matrix[0].size();
for(int i=0; i< m; i++){
for(int j=0; j< n; j++){
temp.push_back(matrix[j][i]);
}
transpose_matrix.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
}
return transpose_matrix;
}
int main() {
// take input of n and m
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
// take input of n x m matrix
vector<vector<int> > matrix;
int val;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
vector<int> temp;
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin>>val;
temp.push_back(val);
}
matrix.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
}
// print the n x m matrix
cout<<"Entered matrix: \n";
for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++){
for (int j=0; j<matrix[i].size(); j++){
cout<<matrix[i][j]<< " ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
// call the function to transpose the matrix
matrix=transpose(matrix);
// print the transpose of n x m matrix
cout<<"\nTranspose of the matrix: \n";
for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++){
for (int j=0; j<matrix[i].size(); j++){
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main{
// function to transpose a given 2D matrix
public int[][] transpose(int[][] matrix){
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] transpose_matrix = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
transpose_matrix[j][i] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
return transpose_matrix;
}
public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// take input of n and m
int n = input.nextInt();
int m = input.nextInt();
String newline = System.lineSeparator();
// take input of n x m matrix
int[][] matrix = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
matrix[i][j] = input.nextInt();
}
}
// print the n x m matrix
System.out.print("Entered matrix:\n");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
// call the function to transpose the matrix
Main obj = new Main();
int[][] transpose_matrix = obj.transpose(matrix);
// print the transpose of n x m matrix
System.out.print("\nTranspose of the matrix:\n");
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
System.out.print(transpose_matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Python implementation
# function to transpose a given 2D matrix
def transpose(matrix, transpose_matrix, n, m):
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
transpose_matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]
# driver code
# take input of n and m
n = int(input())
m = int(input())
# take input of n x m matrix
matrix=[[int(input()) for x in range (m)] for y in range(n)]
# print the n x m matrix
print("Entered matrix:")
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
print(matrix[i][j], " ", end='')
print()
print()
# To store result
transpose_matrix = [[0 for x in range(n)] for y in range(m)]
# call the function to transpose the matrix
transpose(matrix, transpose_matrix,n,m)
# print the transpose of n x m matrix
print("Transpose of the matrix:")
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
print(transpose_matrix[i][j], " ", end='')
print()
Output
Input
2
3
2 4 6 -5 7 0
Output:
Entered matrix:
2 4 6
-5 7 0
Transpose of the matrix:
2 -5
4 7
6 0
Time Complexity
The time complexity for transposing the matrix here will be O(n2) since we are using nested for loops to process the matrix array.
Space Complexity
The space complexity for transposing the matrix in this case will be O(n2) since we are using an extra matrix to store the result of the transpose operation.
Algorithm
- Take input of $n$ and $m$
- take input in matrix array of size $n \times m$.
- print the matrix array.
- loop for $n$ times
a. In the $i$th loop, loop from $i+1$ element to $n$ times and swap the matrix[i][j] element with matrix[j][i] element - print matrix array that is now transposed.
Note: This algorithm will only work for square matrices having $n \times n$ dimension, i.e. $m==n$
Code Implementation(in C++, java , python)
C++ Code Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// take input of n and m
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
// take input of n x m matrix
vector<vector<int> > matrix;
int val;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
vector<int> temp;
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin>>val;
temp.push_back(val);
}
matrix.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
}
// print the matrix array
cout<<"Entered matrix: \n";
for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++){
for (int j=0; j<matrix[i].size(); j++){
cout<<matrix[i][j]<< " ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
// transpose the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++){
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
// print the transposed matrix array
cout<<"\nTranspose of the matrix: \n";
for (int i=0; i<matrix.size(); i++){
for (int j=0; j<matrix[i].size(); j++){
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main{
public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception{
// take input of n and m
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
int m = input.nextInt();
String newline = System.lineSeparator();
// take input of n x m matrix
int[][] matrix = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
matrix[i][j] = input.nextInt();
// print the matrix array
System.out.print("Entered matrix:\n");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
// transpose the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = i+1; j < m; j++){
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j]= matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i]= temp;
}
}
// print the transposed matrix array
System.out.print("\nTranspose of the matrix:\n");
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Python implementation
# take input of n and m
n = int(input())
m = int(input())
# take input of n x m matrix
matrix=[[int(input()) for x in range (m)] for y in range(n)]
# print the matrix array
print("Entered matrix:")
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
print(matrix[i][j], " ", end='')
print()
print()
# transpose the matrix
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i+1, n):
matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i] = matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]
# print the transposed matrix array
print("Transpose of the matrix:")
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
print(matrix[i][j], " ", end='')
print()
Output
Input:
3
3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Output:
Entered matrix:
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Transpose of the matrix:
1 4 7
2 5 8
3 6 9
Time Complexity
The time complexity for the tranpose of the matrix here will be $O(n^2)$ since we are using nested for loops to process the matrix array.
Space Complexity
The space complexity for the transpose of the matrix in this case will be $O(1)$ since no extra space has been taken.
Conclusion
- The transpose of a matrix is a new matrix that is obtained by exchanging the rows and columns.
- If we take extra space and transform the matix then it takes $O(n^2)$ time complexity and $O(n^2)$ space complexity.
- If we do not take extra space and transform the matix then it takes $O(n^2)$ time complexity and $O(1)$ space complexity.