A transmission media in data communication is a physical path between the sender and the receiver and it is the channel through which data can be sent from one location to another. Data can be represented through signals by computers and other sorts of telecommunication devices. These are transmitted from one device to another in the form of electromagnetic signals. These Electromagnetic signals can move from one sender to another receiver through a vacuum, air, or other transmission media. Electromagnetic energy mainly includes radio waves, visible light, UV light, and gamma rays.
What is Transmission Media?
Transmission Media is a means of establishing a communication medium to send and receive information in the form of electromagnetic signal waves. It operates with various physical elements, therefore, it is placed beneath the physical layer while being worked on by physical elements from the physical layer. The Local Area Network (LAN), which contains both the transmitter and the receiver, is the network that operates via the transmission medium. The electrical or optical signals are transmitted through either copper or fiber-based transmission media.
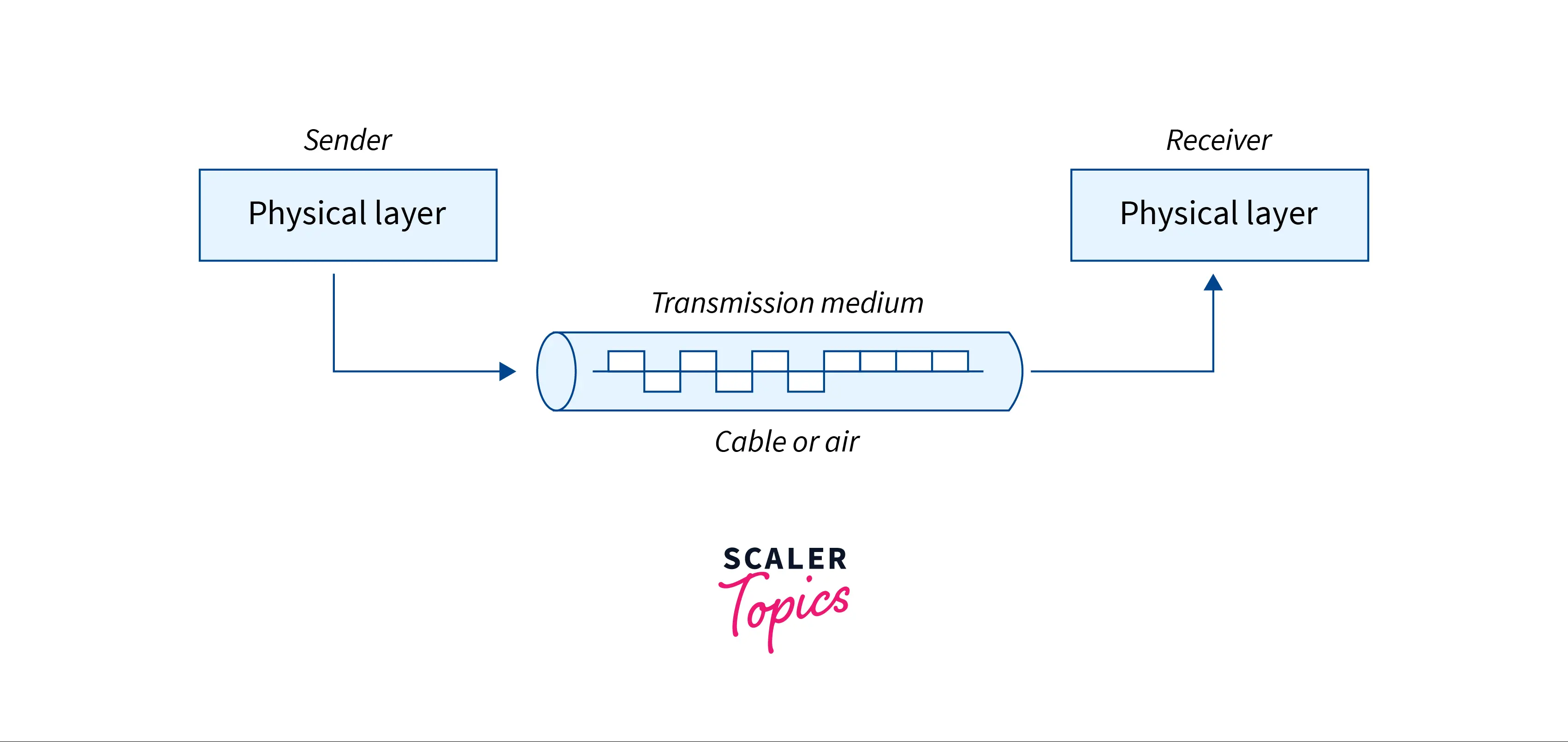
Transmission media functions as a physical path between the sender and the receiver in data communication. For example, in a copper cable network, bits are available in the form of electrical signals, whereas in a fiber network, bits are available in the form of light pulses. The parameters of the medium and signal can be used to determine the quality and characteristics of data transmission. Delay, bandwidth, maintenance, cost, and ease of installation are all characteristics of various transmission media.
Types of Transmission Media
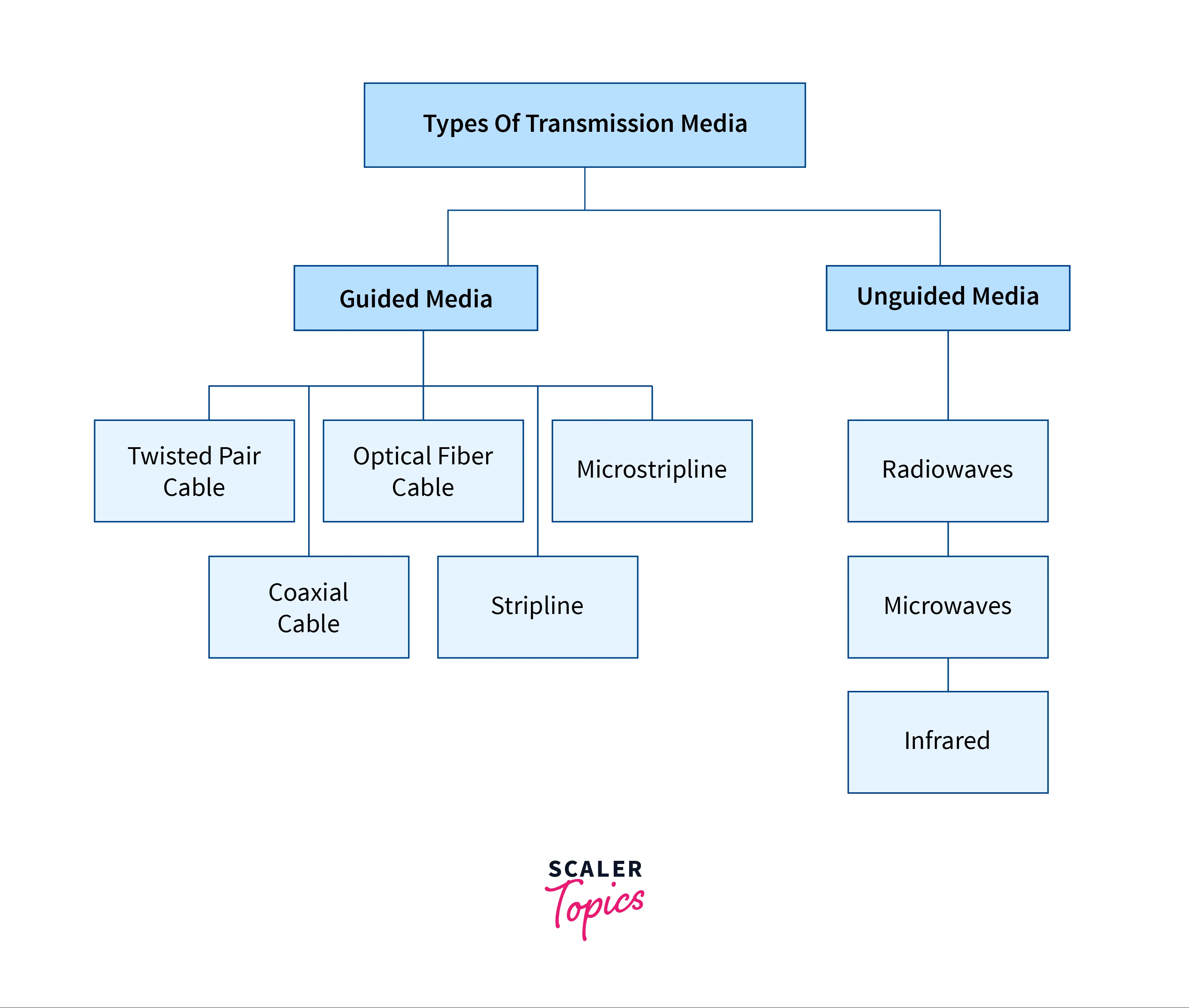
Types of Transmission Media are:
- Guided Media.
- Unguided Media.
Guided Media
Guided media is also referred to as wired media. Sometimes it is also referred to as bounded media because it is bounded to a specific limit in the communication network. In guided media, the transmission signal properties are controlled and focused in a fixed constricted channel, which can be implemented with the help of physiologically connected contacts. One of the most prominent aspects of Guided Media is its fast transmission velocity. Other reasons why users choose directed media over unguided media include transmission security and the ability to regulate the network within a limited geographical area.
Advantages of Guided Media
- The cost of guided media is very low (inexpensive) and easily available.
- This is very Flexible and Lightweight.
- Very easy to set up and install.
- Provides high transmission speed.
Disadvantages of Guided Media
- Bandwidth is very low in guided media.
- Susceptible to interference and noise- (Noise is an electrical disturbance that can degrade communication).
- High maintenance and installation costs.
Various types of guided media are based on the type of connecting material used for creating the network:
- Twisted Pair Cable:- Twisted Pair Cables are created by twisting two different protected cables around each other to make a single cable. Shields are often built of insulated materials that allow both cables to transmit independently. This twisted wire is then enclosed inside a protective coating to make it easier to use. Twisted pair cables are generally of two types:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP):- UTP is made up of two insulated copper wires twisted around one another. This cable can block interference and does not require a physical shield for this purpose. It is employed in telephonic applications.
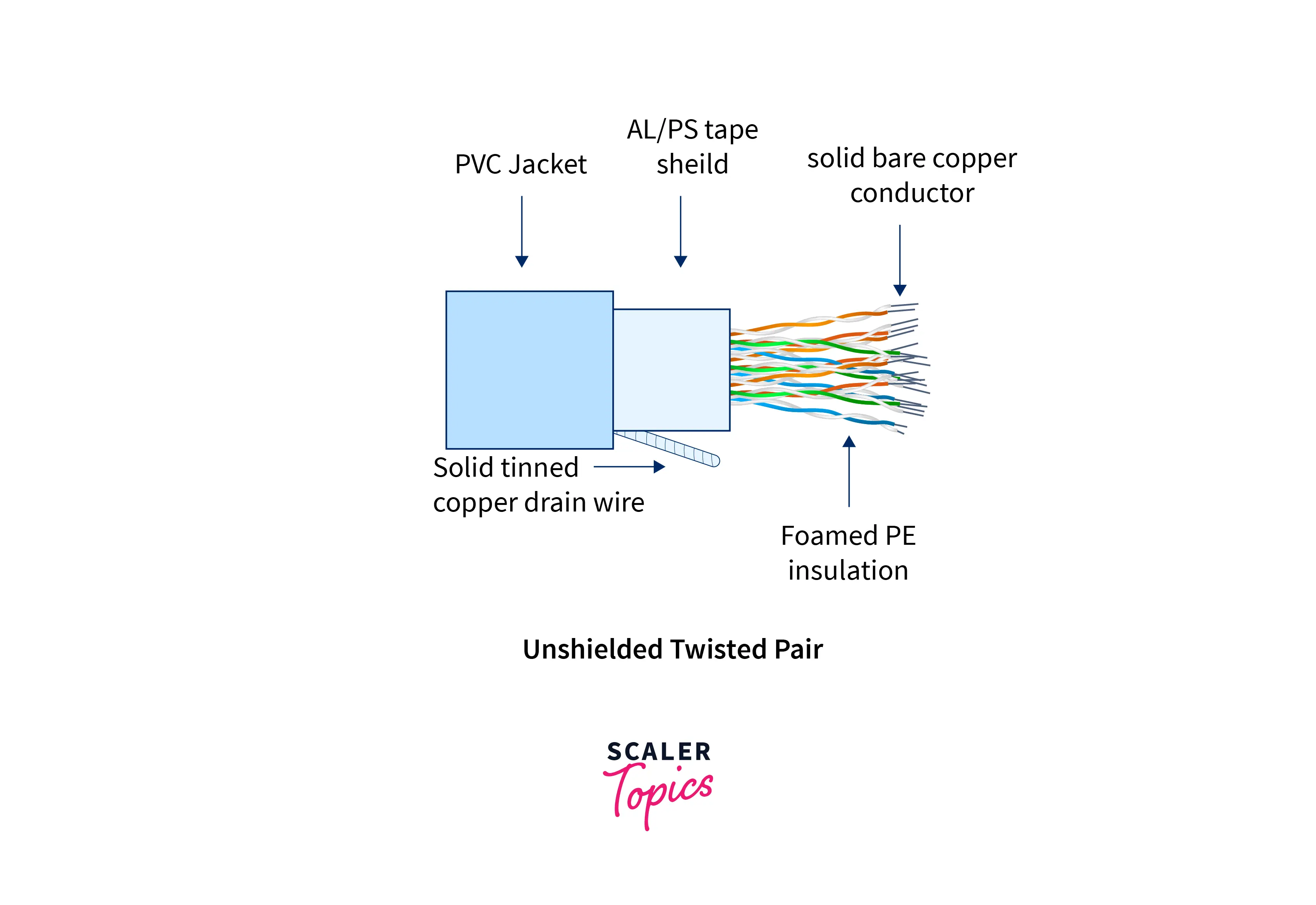 Advantages of UTP
Advantages of UTP- Low cost.
- Provides High Speed.
- Easy to install.
- It is susceptible to external interference.
- Due to attenuation, it is limited to short-distance transmission.
- Low performance as compared to STP.
- Shielded Twisted Pair(STP):- This cable has a specific jacket (a copper braid coating or a foil shield) to prevent external interference. It is utilized in high-data-rate Ethernet and telephone voice and data channels.
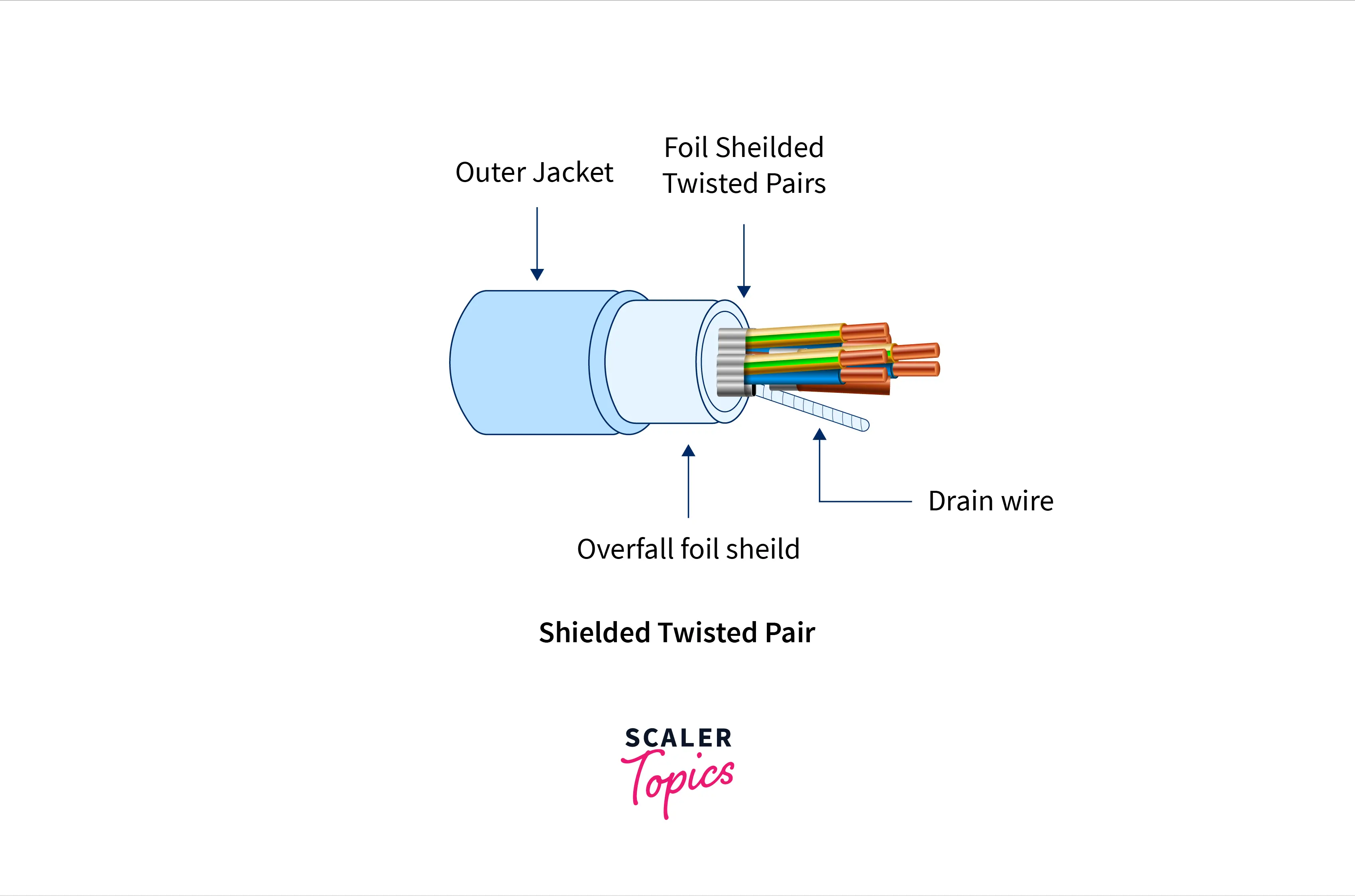 Advantages of STP
Advantages of STP- High speed than UTP.
- Better performance.
- No crosstalk(or interference).
- Difficult to install and manufacture.
- Expensive.
- Coaxial Cable:- It has an outer plastic coating with an insulation layer of PVC or Teflon and two parallel conductors with their insulated protection cover. This type of cable is well-known for its role in supplying a television network in homes.
 Advantages of Coaxial Cable
Advantages of Coaxial Cable- Easy to install and expand the range.
- High Bandwidth.
- Less expensive.
- Less noise
- Single cable failure can disturb the entire network.
- Bulky
- Very expensive over long distances
- They do not support high-speed transmission, this is another disadvantage of coaxial cable
- Optical Fiber Cable:- Optical Fibre Cables are glass-based cables that transmit light signals. The reflection concepts are employed for light signal transmission over cables. It is recognized for allowing bulkier data to be delivered with more bandwidth and reduced electromagnetic interference during transmission. Because the material is non-corrosive and weightless, these cables are preferable to twisted cables in most instances.
 Advantages of Optical Fiber Cable
Advantages of Optical Fiber Cable- High bandwidth.
- Lightweight
- Negligible attenuation.
- Fastest data transmission.
- Very costly.
- Hard to install and maintain.
- Fragile.
- They are unidirectional, which means they will need another fiber for bidirectional communication.
- Stripline:- It is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium designed in the 1950s by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre. A stripline is the first type of planar transmission line. It is also known as a waveguide because strip lines transmit high-frequency waves using a conducting substance. This substance is placed between two ground plane layers, often shorted to offer EMI immunity.Advantages of Striplines
- Smaller than the co-axial line.
- Lower radiation loss.
- Greater frequency bandwidth.
- Good electromagnetic shielding.
- Troubleshooting is complex.
- Expensive.
- Microstripline:- A microstrip is a transmission line consisting of a conductor manufactured on a dielectric substrate with a grounded plane. It is easily downsized and incorporated with microwave equipment, making it a popular transmission line choice.
Unguided Media
Unguided media is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. It can be described as a wireless transmission medium without a physical link to the network’s nodes or servers. In comparison to guided media, electromagnetic signal waves are less secure because they are transmitted in the air over a wider geographic area.
Why do we need Unguided Media?
- Wireless data transfer is essential in regions like hilly terrain where installing cables and wires is extremely difficult or impossible.
- It is used for short-range communication such as data transfer between two cell phones, TV remote operation, and data transfer between a computer and cell phone residing in the same closed area.
Advantages of Unguided Media
- Used for large-distance transmission.
- Highly convenient for users.
- Maintenance and installation cost is less compared to guided media.
Disadvantages of Unguided Media
- Less secure.
- Unavailability of bandwidth.
Unguided media can be classified into three types based on the signals used for the transmission.
- Radio Waves:- These waves are relatively simple to create and can easily pass through structures. The transmitting and receiving antennas of this do not need to be aligned. These waves have a frequency range of 3 kHz to 1GHz. In AM and FM radios, these wavelengths are employed for transmission.
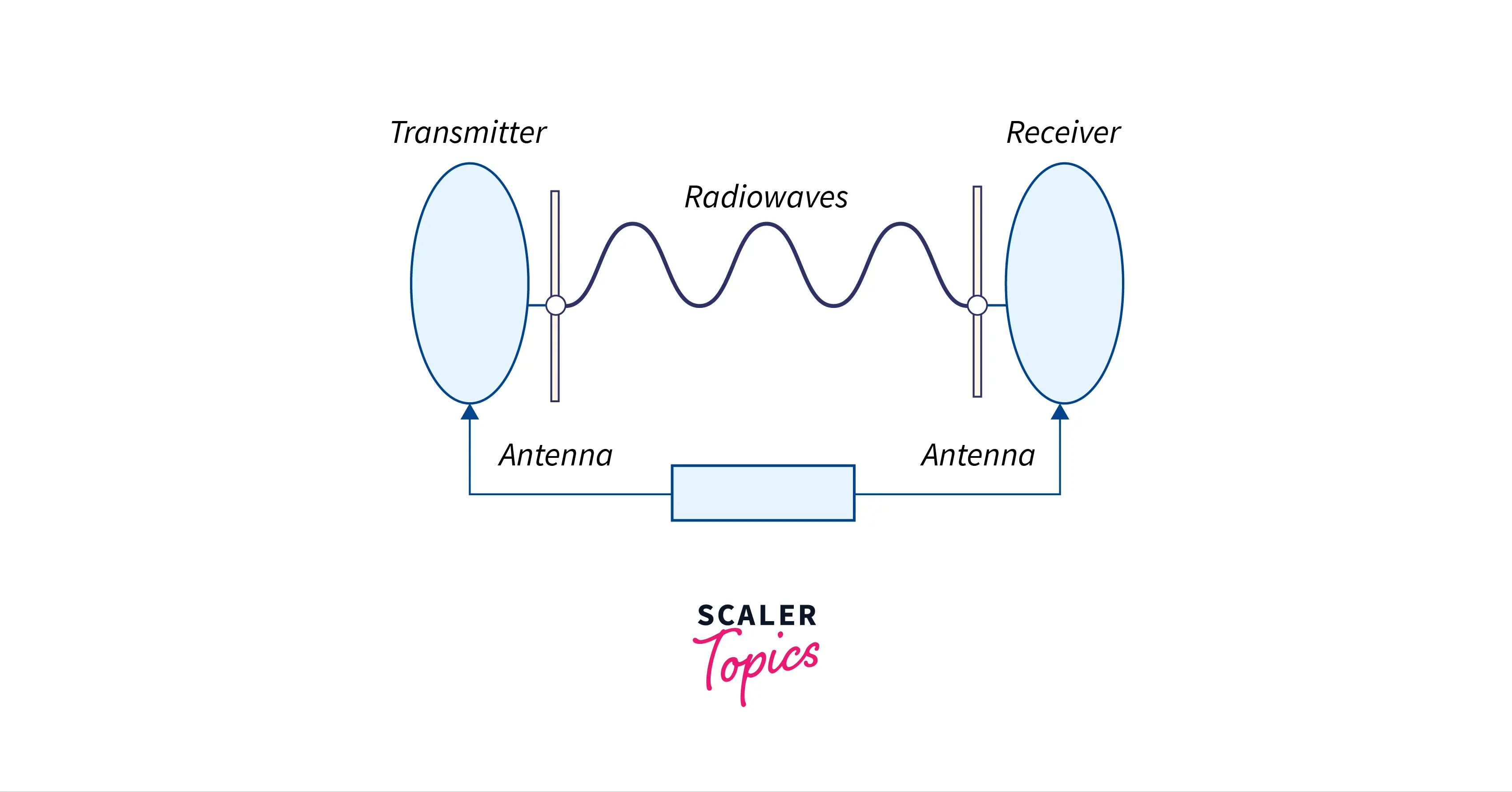
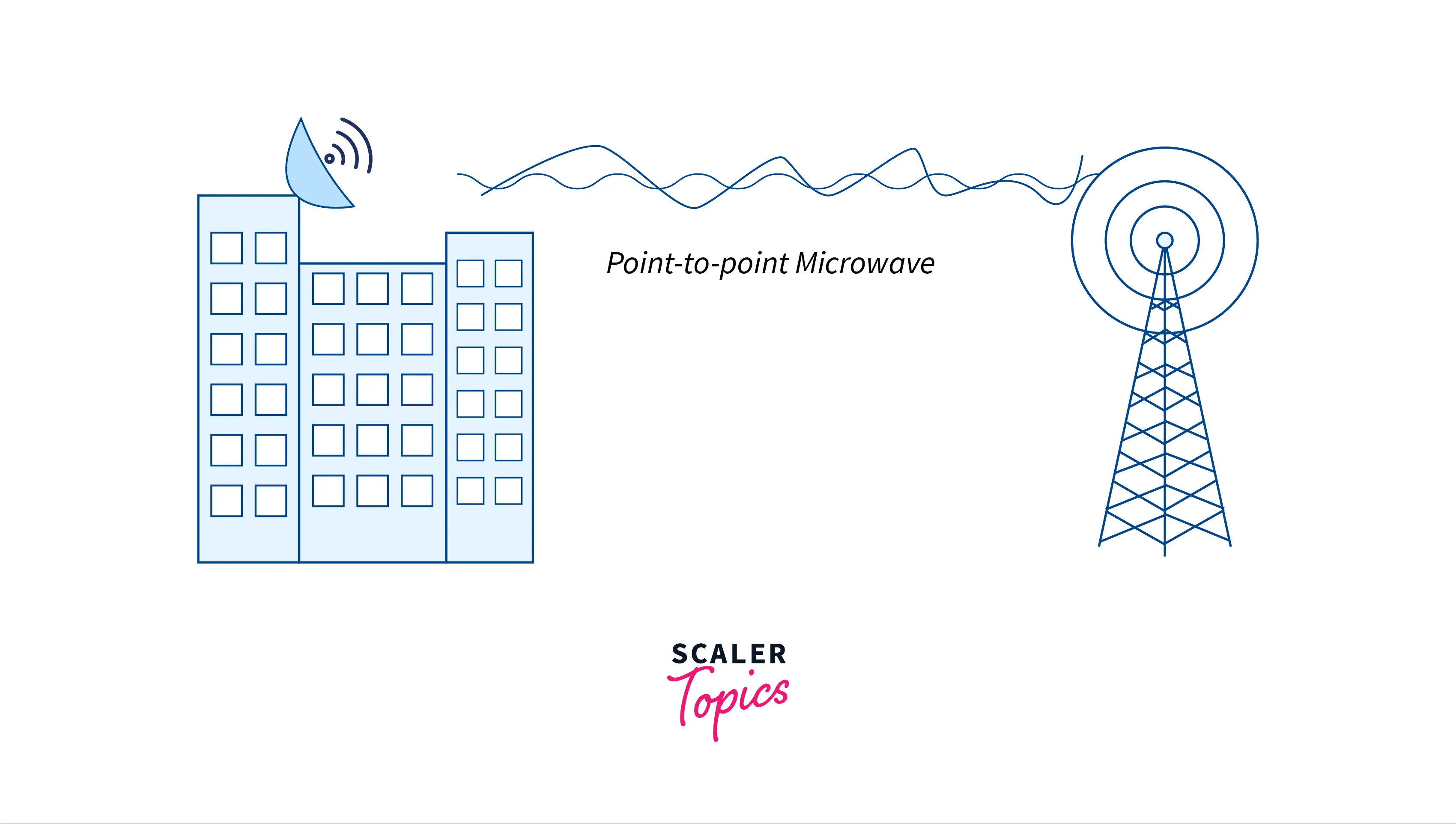
- Micro Waves:- Since it is a sightline transmission, the sending and receiving antennas must be perfectly aligned. The signal’s range can be directly proportional to the height of the antenna. Microwaves have a frequency range between 1GHz and 300GHz. These are widely utilized in mobile phone communication and TV delivery.
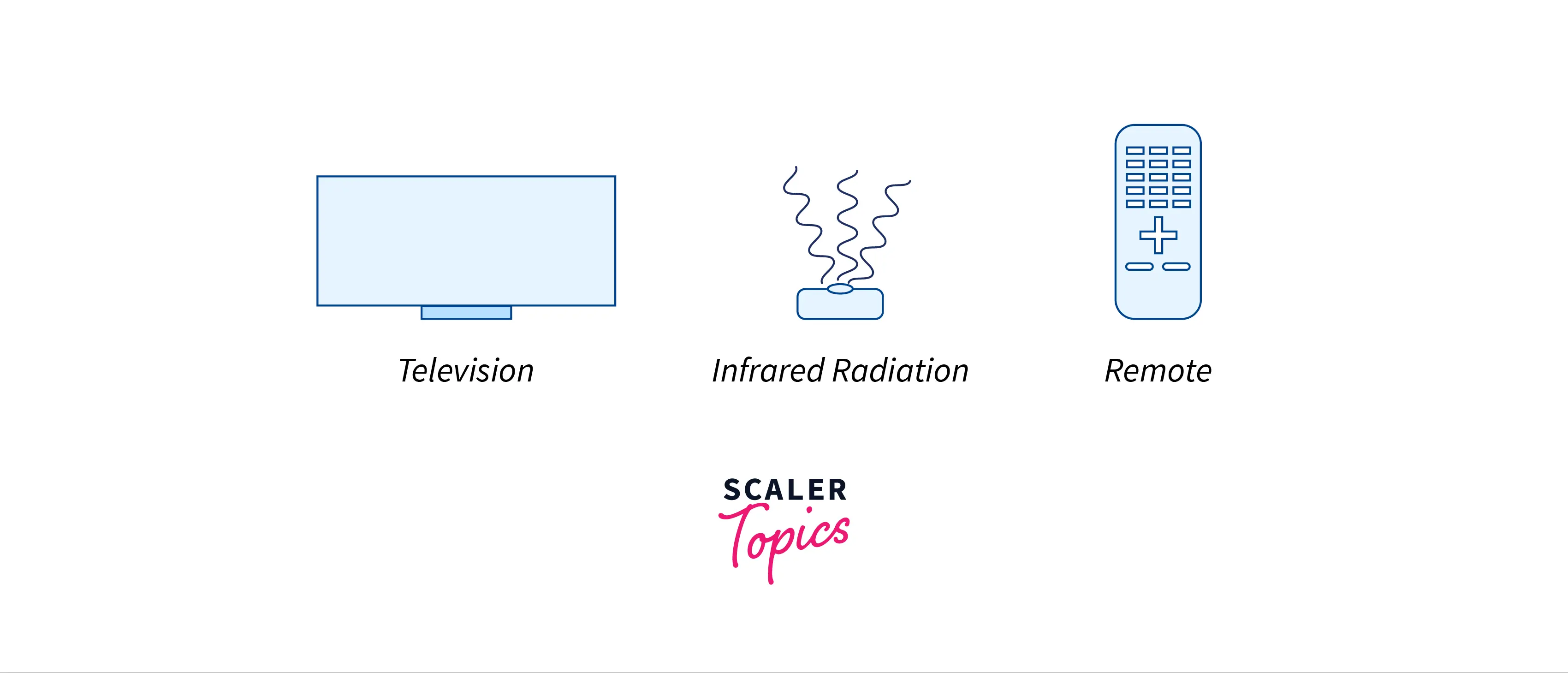
- Infrared:- Due to their inability to pass past obstacles, infrared (IR) radiation is used in extremely short-distance communication. So it prevents system intrusion. These waves have a frequency range of 300GHz to 400THz. The wireless mouse, printer, wireless keyboard, and television remotes all employ these waves.
Some Factors Regarding Designing of the Transmission Media
We should keep some factors in mind before designing a transmission media, and these factors are:
- Bandwidth:- The term “bandwidth” primarily refers to a medium’s or channel’s capacity for data transmission. If all other parameters are constant, the greater the bandwidth of a media, the higher the data transmission rate of a signal.
- Radiation:- The term “radiation” describes the signal leakage from a medium due to undesirable electrical properties.
- Absorption of Noise:- The term “noise absorption” describes how susceptible media are to outside electrical noise. Data signal distortion could result from this noise. It should be less.
- Attenuation:- Attenuation is the energy loss that occurs when a signal is broadcast externally. The amount of energy lost is primarily determined by frequency. Attenuation is caused by radiation as well as physical media properties.
Transmission Impairment Causes
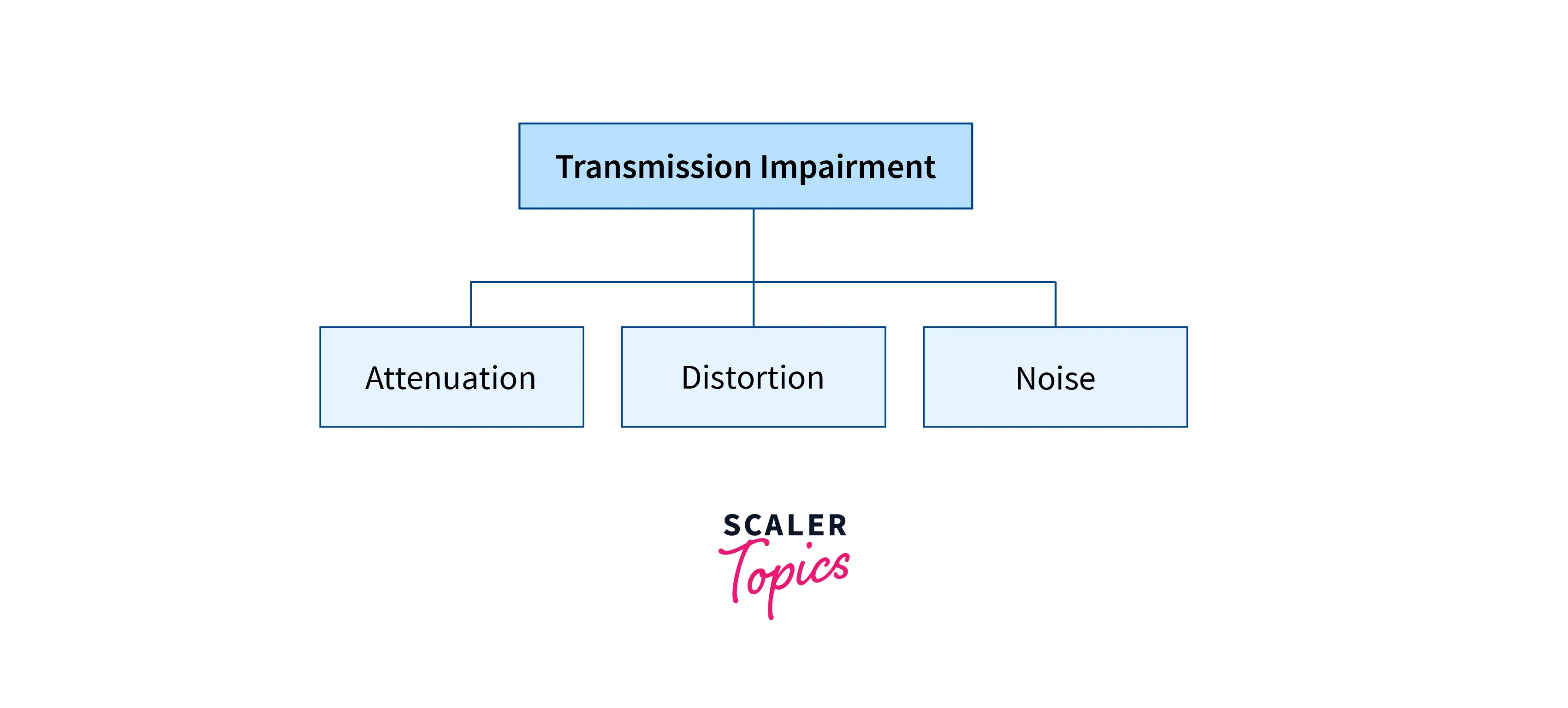
- Attenuation:- Attenuation is the loss of energy, which occurs as the strength of the signal decreases with increasing distance.
- Distortion:- When the form of the signal changes, distortion happens. Different signals with various frequencies are used to analyze this form of distortion. Due to the differing propagation speeds of each frequency component, the delay distortion is caused when they arrive at the same location at different times.
- Noise:- When data is transmitted via a transmission medium, an undesired signal is added to it, resulting in noise.
Conclusion
- Transmission media functions as a physical path between the sender and the receiver in data communication.
- The signals are transmitted between the sender and receiver in the form of electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnetic signals can move from one sender to another receiver through a vacuum, air, or other transmission media.
- Delay, bandwidth, maintenance, cost, and ease of installation are all characteristics of various transmission media.
- There are two Types of Transmission Media i.e., guided media and unguided media.
- In guided media, the transmission signal properties are controlled and focused in a fixed constricted channel, which can be implemented with the help of physiologically connected contacts.
- Unguided Media is described as a wireless transmission medium without a physical link to the network’s nodes or servers.
